|
1
|
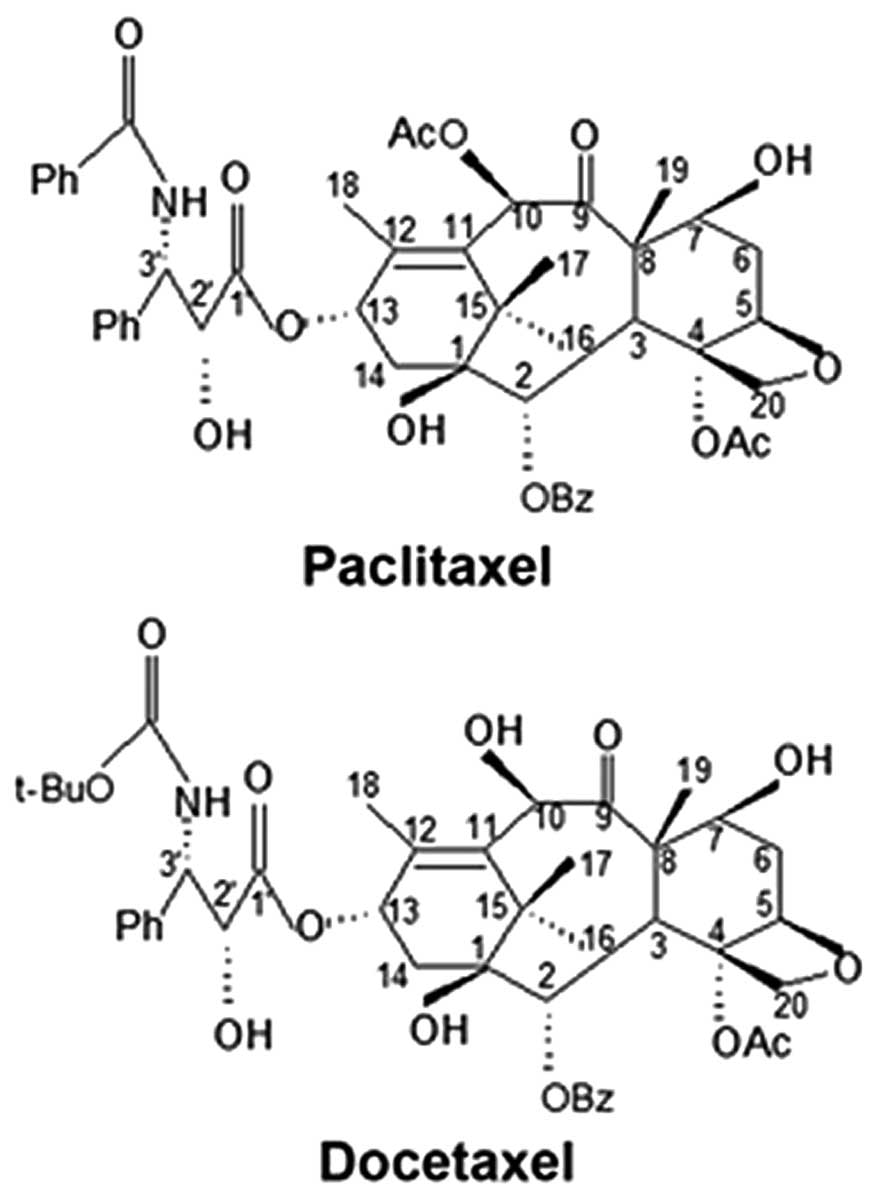
Gelmon K: The taxoids: paclitaxel and
docetaxel. Lancet. 344:1267–1272. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
King KM, Lupichuk S, Baig L, Webster M,
Basi S, Whyte D and Rix S: Optimal use of taxanes in metastatic
breast cancer. Curr Oncol. 16:8–20. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shepherd FA, Dancey J, Ramlau R, et al:
Prospective randomized trial of docetaxel versus best supportive
care in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated
with platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 18:2095–2103.
2000.
|
|
4
|
Galletti E, Magnani M, Renzulli ML and
Botta M: Paclitaxel and docetaxel resistance: molecular mechanisms
and development of new generation taxanes. ChemMedChem. 2:920–942.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maeda S and Tsukihara T: Structure of the
gap junction channel and its implications for its biological
functions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 68:1115–1129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vinken M, Vanhaecke T, Papeleu P, Snykers
S, Henkens T and Rogiers V: Connexins and their channels in cell
growth and cell death. Cell Signal. 18:592–600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holder JW, Elmore E and Barrett JC: Gap
junction function and cancer. Cancer Res. 53:3475–3485.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mesnil M, Crespin S, Avanzo JL and
Zaidan-Dagli ML: Defective gap junctional intercellular
communication in the carcinogenic process. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1719:125–145. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kandouz M and Batist G: Gap junctions and
connexins as therapeutic targets in cancer. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 14:681–692. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jensen R and Glazer PM:
Cell-interdependent cisplatin killing by Ku/DNA-dependent protein
kinase signaling transduced through gap junctions. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:6134–6139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Q, You T, Yuan D, et al: Cisplatin
and oxaliplatin inhibit gap junctional communication by direct
action and by reduction of connexin expression, thereby
counteracting cytotoxic efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
333:903–911. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Prise KM and O'Sullivan JM:
Radiation-induced bystander signalling in cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:351–360. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harada K, Nonaka T, Hamada N, et al:
Heavy-ion-induced bystander killing of human lung cancer cells:
role of gap junctional intercellular communication. Cancer Sci.
100:684–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang RP, Hossain MZ, Huang R, Gano J, Fan
Y and Boynton AL: Connexin 43 (cx43) enhances chemotherapy-induced
apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Int J Cancer. 92:130–138.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giessmann D, Theiss C, Breipohl W and
Meller K: Decreased gap junctional communication in neurobiotin
microinjected lens epithelial cells after taxol treatment. Anat
Embryol (Berl). 209:391–400. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piechocki MP, Lonardo F, Ensley JF, Nguyen
T, Kim H and Yoo GH: Anticancer activity of docetaxel in murine
salivary gland carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:870–877.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koreen IV, Elsayed WA, Liu YJ and Harris
AL: Tetracycline-regulated expression enables purification and
functional analysis of recombinant connexin channels from mammalian
cells. Biochem J. 383:111–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Goldberg GS, Bechberger JF and Naus CC: A
preloading method of evaluating gap junctional communication by
fluorescent dye transfer. Biotechniques. 18:490–497.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Davidson JS, Baumgarten IM and Harley EH:
Reversible inhibition of intercellular junctional communication by
glycyrrhetinic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 134:29–36. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Loewenstein WR and Kanno Y: Intercellular
communication and the control of tissue growth: lack of
communication between cancer cells. Nature. 209:1248–1249. 1966.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Naus CC and Laird DW: Implications and
challenges of connexin connections to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:435–441. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leithe E, Sirnes S, Omori Y and Rivedal E:
Downregulation of gap junctions in cancer cells. Crit Rev Oncog.
12:225–256. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanna EA, Umhauer S, Roshong SL, et al:
Gap junctional intercellular communication and connexin43
expression in human ovarian surface epithelial cells and ovarian
carcinomas in vivo and in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 20:1369–1373.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rüttinger C, Bergmann M, Fink L, et al:
Expression of connexin 43 in normal canine testes and canine
testicular tumors. Histochem Cell Biol. 130:537–548.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanczuga-Koda L, Sulkowska M, Koda M,
Rutkowski R and Sulkowski S: Increased expression of gap junction
protein - connexin 32 in lymph node metastases of human ductal
breast cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 45(Suppl 1): S175–S180.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang W, DeMattia JA, Song H and Couldwell
WT: Communication between malignant glioma cells and vascular
endothelial cells through gap junctions. J Neurosurg. 98:846–853.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saito-Katsuragi M, Asada H, Niizeki H, et
al: Role for connexin 26 in metastasis of human malignant melanoma:
communication between melanoma and endothelial cells via connexin
26. Cancer. 110:1162–1172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lavelle F, Bissery MC, Combeau C, Riou JF,
Vrignaud P and André S: Preclinical evaluation of docetaxel
(Taxotere). Semin Oncol. 22:3–16. 1995.
|
|
29
|
Harris AL: Emerging issues of connexin
channels: biophysics fills the gap. Q Rev Biophys. 34:325–472.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Beyer EC, Paul DL and Goodenough DA:
Connexin family of gap junction proteins. J Membr Biol.
116:187–194. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Srinivas M, Hopperstad MG and Spray DC:
Quinine blocks specific gap junction channel subtypes. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10942–10947. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tao L and Harris AL: 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl
borate directly inhibits channels composed of connexin26 and/or
connexin32. Mol Pharmacol. 71:570–579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Suga M, et al:
Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 3.5 A
resolution. Nature. 458:597–602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bouvier D, Spagnol G, Chenavas S, et al:
Characterization of the structure and intermolecular interactions
between the connexin40 and connexin43 carboxyl-terminal and
cytoplasmic loop domains. J Biol Chem. 284:34257–34271. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|