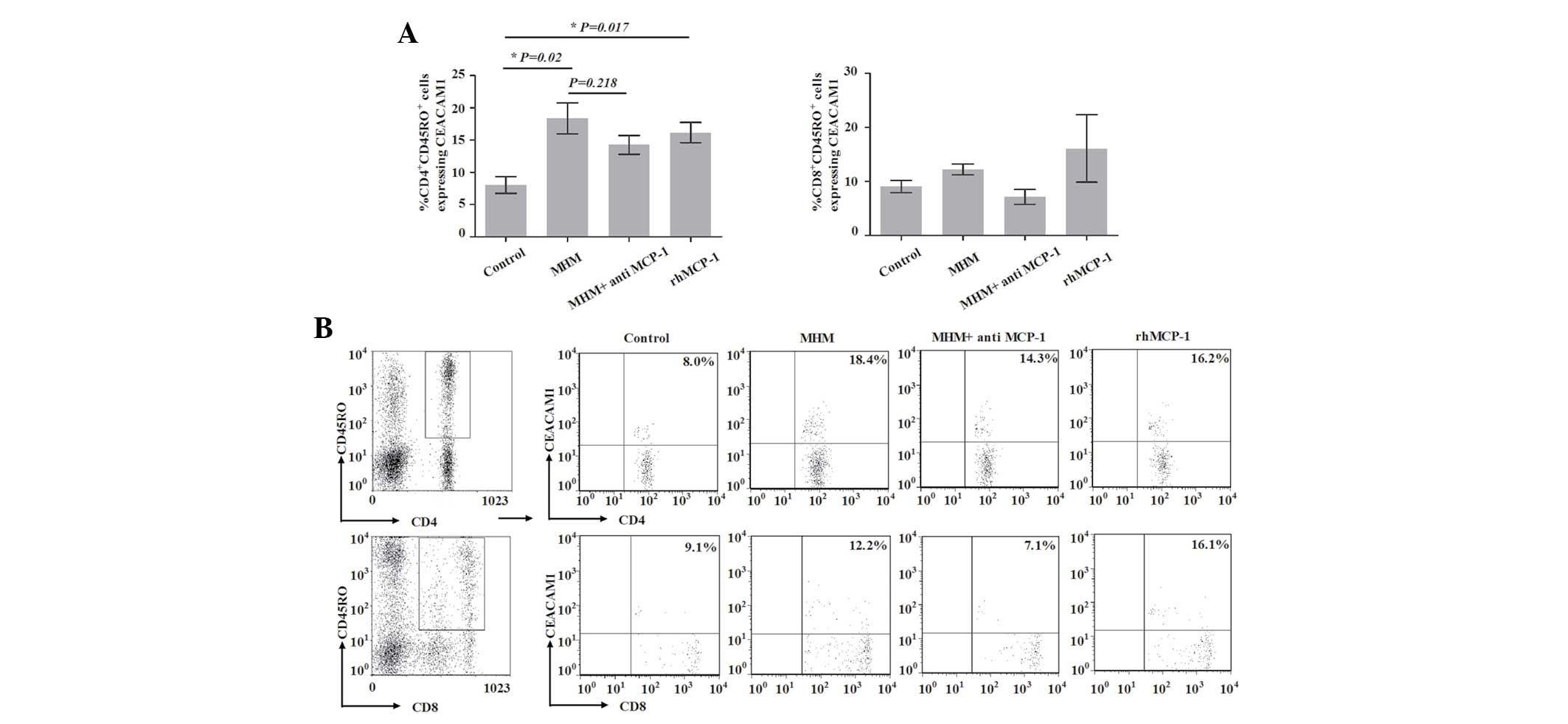
|
1
|
Burrows TD, King A and Loke YW:
Trophoblast migration during human placental implantation. Hum
Reprod Update. 2:307–321. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
King A, Gardner L and Loke YW:
Co-stimulation of human decidual natural killer cells by
interleukin-2 and stromal cells. Hum Reprod. 14:656–663. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sindram-Trujillo A, Scherjon S, Kanhai H,
Roelen D and Claas F: Increased T-cell activation in decidua
parietalis compared to decidua basalis in uncomplicated human term
pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 49:261–268. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Trundley A and Moffett A: Human uterine
leukocytes and pregnancy. Tissue Antigens. 63:1–12. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saito S, Nishikawa K, Morii T, et al: A
study of CD45RO, CD45RA and CD29 antigen expression on human
decidual T cells in an early stage of pregnancy. Immunol Lett.
40:193–197. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slukvin II, Merkulova AA, Vodyanik MA and
Chernyshov VP: Differential expression of CD45RA and CD45RO
molecules on human decidual and peripheral blood lymphocytes at
early stage of pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 35:16–22.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schumacher A, Brachwitz N, Sohr S, et al:
Human chorionic gonadotropin attracts regulatory T cells into the
fetal-maternal interface during early human pregnancy. J Immunol.
182:5488–5497. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tsuda H, Michimata T, Hayakawa S, et al: A
Th2 chemokine, TARC, produced by trophoblasts and endometrial gland
cells, regulates the infiltration of CCR4+ T lymphocytes
into human decidua at early pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 48:1–8.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Carlino C, Stabile H, Morrone S, et al:
Recruitment of circulating NK cells through decidual tissues: a
possible mechanism controlling NK cell accumulation in the uterus
during early pregnancy. Blood. 111:3108–3115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qu X, Yang M, Zhang W, et al: Osteopontin
expression in human decidua is associated with decidual natural
killer cells recruitment and regulated by progesterone. In Vivo.
22:55–61. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vacca P, Cantoni C, Vitale M, et al:
Crosstalk between decidual NK and CD14+ myelomonocytic
cells results in induction of Tregs and immunosuppression. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:11918–11923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanna J, Wald O, Goldman-Wohl D, et al:
CXCL12 expression by invasive trophoblasts induces the specific
migration of CD16-human natural killer cells. Blood. 102:1569–1577.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang Y, Zhu XY, Du MR and Li DJ: Human
trophoblasts recruited T lymphocytes and monocytes into decidua by
secretion of chemokine CXCL16 and interaction with CXCR6 in the
first-trimester pregnancy. J Immunol. 180:2367–2375. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
King A, Gardner L and Loke YW: Human
decidual leukocytes do not proliferate in response to either
extravillous trophoblast or allogeneic peripheral blood
lymphocytes. J Reprod Immunol. 30:67–74. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fest S, Aldo PB, Abrahams VM, et al:
Trophoblast-macrophage interactions: a regulatory network for the
protection of pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 57:55–66. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang T, Dai H, Wan N, Moore Y and Dai Z:
The role for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the generation
and function of memory CD8+ T cells. J Immunol.
180:2886–2893. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hammarström S: The carcinoembryonic
antigen (CEA) family: structures, suggested functions and
expression in normal and malignant tissues. Semin Cancer Biol.
9:67–81. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagaishi T, Iijima H, Nakajima A, Chen D
and Blumberg RS: Role of CEACAM1 as a regulator of T cells. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1072:155–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moller MJ, Kammerer R, Grunert F and von
Kleist S: Biliary glycoprotein (BGP) expression on T cells and on a
natural-killer-cell sub-population. Int J Cancer. 65:740–745. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kammerer R, Hahn S, Singer BB, Luo JS and
von Kleist S: Biliary glycoprotein (CD66a), a cell adhesion
molecule of the immunoglobulin superfamily, on human lymphocytes:
structure, expression and involvement in T cell activation. Eur J
Immunol. 28:3664–3674. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Donda A, Mori L, Shamshiev A, et al:
Locally inducible CD66a (CEACAM1) as an amplifier of the human
intestinal T cell response. Eur J Immunol. 30:2593–2603. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morales VM, Christ A, Watt SM, et al:
Regulation of human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte cytolytic
function by biliary glycoprotein (CD66a). J Immunol. 163:1363–1370.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koga K and Mor G: Toll-like receptors at
the maternal-fetal interface in normal pregnancy and pregnancy
disorders. Am J Reprod Immunol. 63:587–600. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mor G and Cardenas I: The immune system in
pregnancy: a unique complexity. Am J Reprod Immunol. 63:425–433.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saito S, Nishikawa K, Morii T, Narita N,
Enomoto M and Ichijo M: Expression of activation antigens CD69,
HLA-DR, interleukin-2 receptor-alpha (IL-2R alpha) and IL-2R beta
on T cells of human decidua at an early stage of pregnancy.
Immunology. 75:710–712. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Markel G, Wolf D, Hanna J, et al: Pivotal
role of CEACAM1 protein in the inhibition of activated decidual
lymphocyte functions. J Clin Invest. 110:943–953. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakajima A, Iijima H, Neurath MF, et al:
Activation-induced expression of carcinoembryonic antigen-cell
adhesion molecule 1 regulates mouse T lymphocyte function. J
Immunol. 168:1028–1035. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boulton IC and Gray-Owen SD: Neisserial
binding to CEACAM1 arrests the activation and proliferation of
CD4+ T lymphocytes. Nat Immunol. 3:229–236. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen CJ and Shively JE: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule carcinoembryonic antigen-related cellular
adhesion molecule 1 inhibits IL-2 production and proliferation in
human T cells by association with Src homology protein-1 and
down-regulates IL-2 receptor. J Immunol. 172:3544–3552. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Geiselhart A, Dietl J, Marzusch K, et al:
Comparative analysis of the immunophenotypes of decidual and
peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes and T cells during
early human pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 33:315–322. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ho HN, Chao KH, Chen CK, Yang YS and Huang
SC: Activation status of T and NK cells in the endometrium
throughout menstrual cycle and normal and abnormal early pregnancy.
Hum Immunol. 49:130–136. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gray-Owen SD and Blumberg RS: CEACAM1:
contact-dependent control of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:433–446.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bamberger AM, Sudahl S, Löning T, et al:
The adhesion molecule CEACAM1 (CD66a, C-CAM, BGP) is specifically
expressed by the extravillous intermediate trophoblast. Am J
Pathol. 156:1165–1170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Briese J, Oberndörfer M, Pätschenik C, et
al: Osteopontin is colocalized with the adhesion molecule CEACAM1
in the extravillous trophoblast of the human placenta and enhances
invasion of CEACAM1-expressing placental cells. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 90:5407–5413. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bamberger AM, Minas V, Kalantaridou SN, et
al: Corticotropin-releasing hormone modulates human trophoblast
invasion through carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion
molecule-1 regulation. Am J Pathol. 168:141–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|