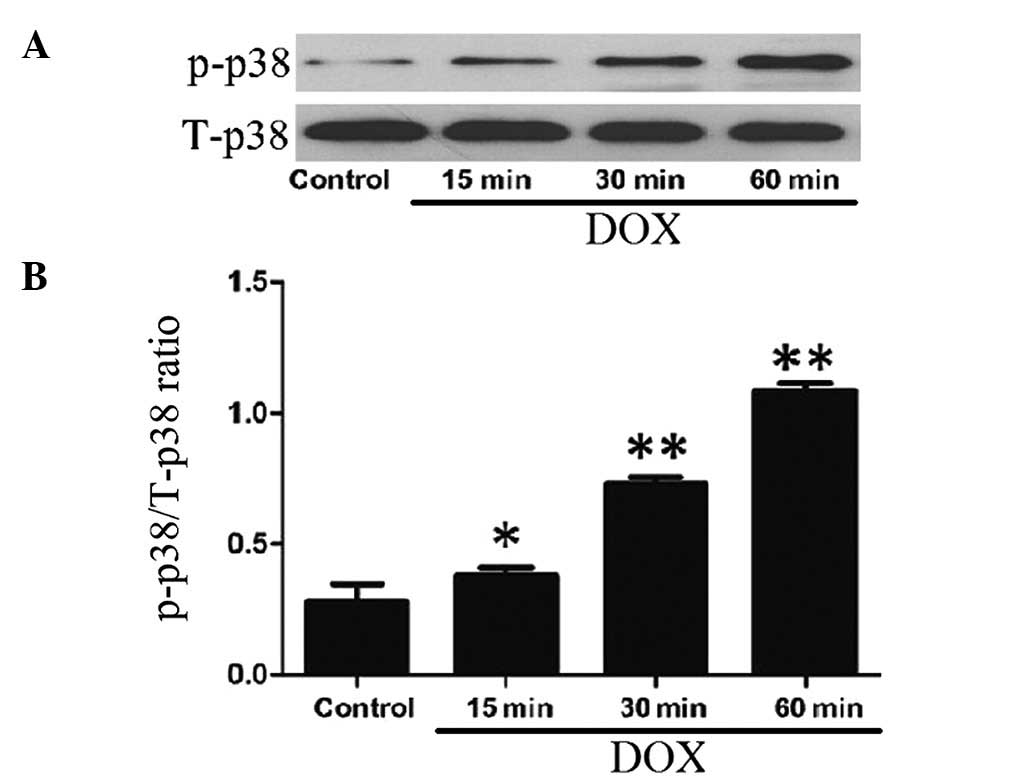
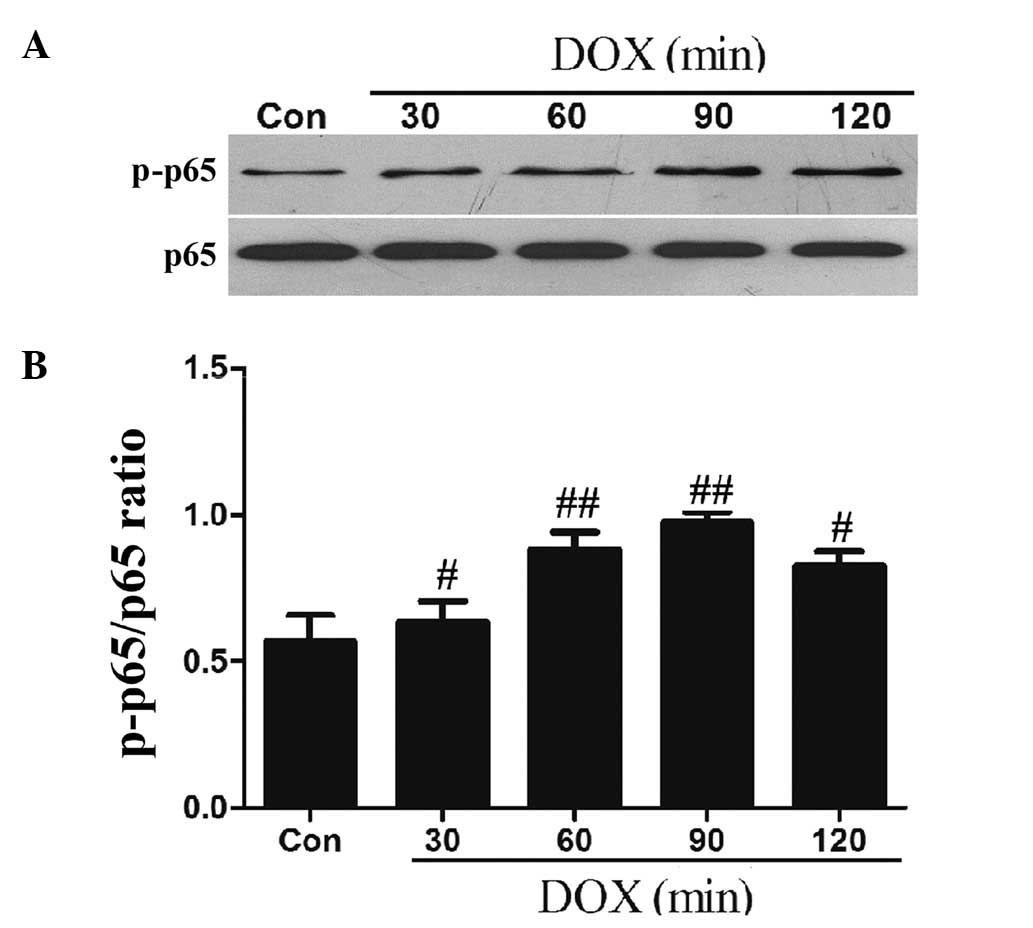
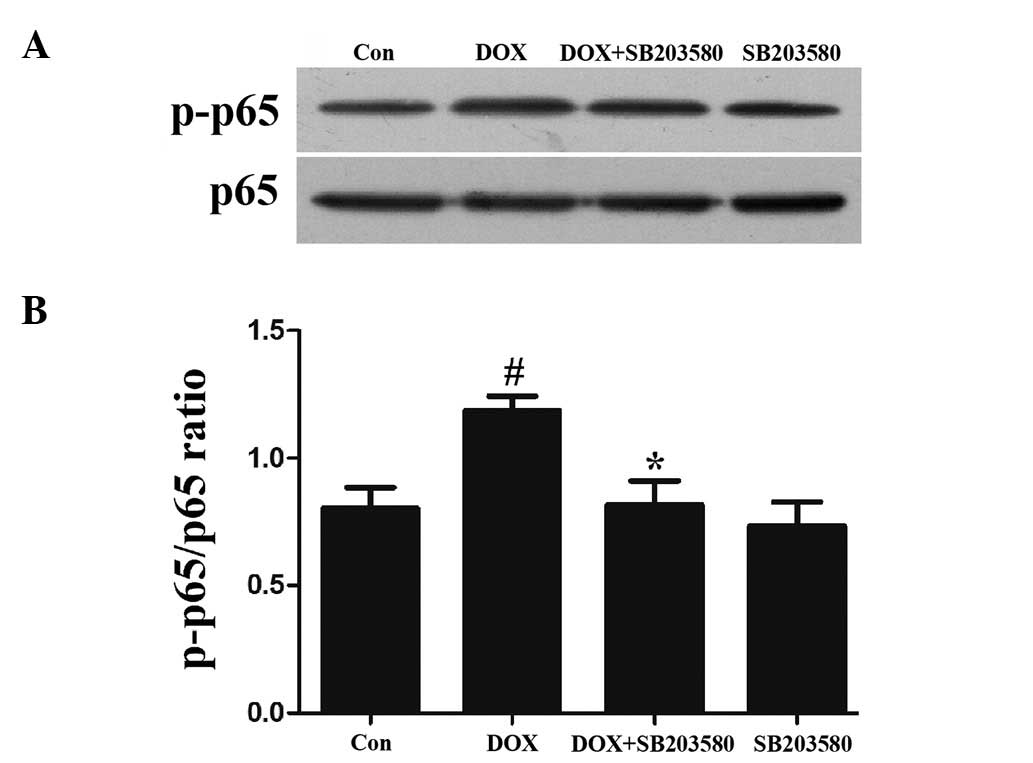
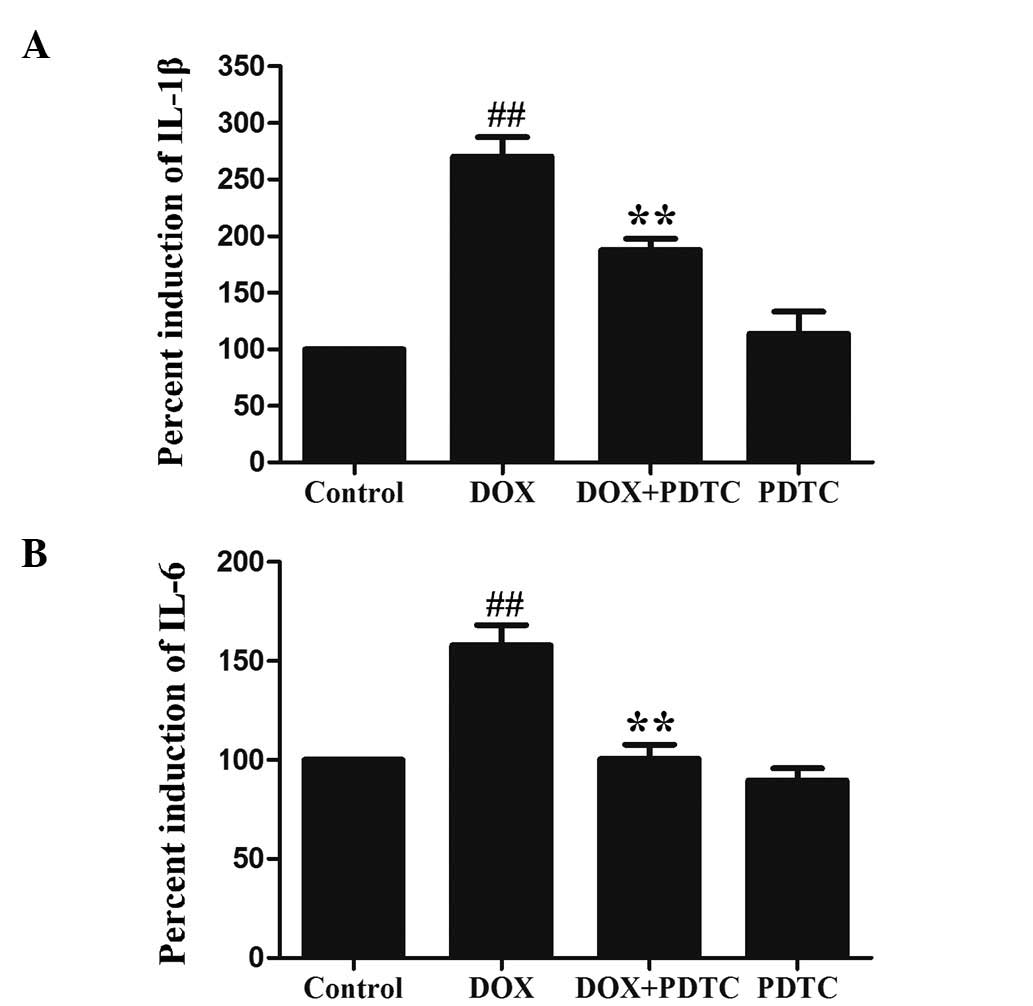
|
1
|
Danesi R, Fogli S, Gennari A, Conte P and
Del Tacca M: Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic relationships of the
anthracycline anticancer drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 41:431–444.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hrdina R, Gersl V, Klimtová I, Simůnek T,
Machácková J and Adamcová M: Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity.
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 43:75–82. 2000.
|
|
3
|
Scully RE and Lipshultz SE: Anthracycline
cardiotoxicity in long-term survivors of childhood cancer.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 7:122–128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zucchi R and Danesi R: Cardiac toxicity of
antineoplastic anthracyclines. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
3:151–171. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Morsi MI, Hussein AE, Mostafa M, El-Abd E
and El-Moneim NA: Evaluation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha,
soluble P-selectin, gamma-glutamyl transferase, glutathione
S-transferase-pi and alpha-fetoprotein in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma before and during chemotherapy. Br J
Biomed Sci. 63:74–78. 2006.
|
|
6
|
Mukherjee S, Banerjee SK, Maulik M, Dinda
AK, Talwar KK and Maulik SK: Protection against acute
adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity by garlic: role of endogenous
antioxidants and inhibition of TNF-alpha expression. BMC Pharmacol.
3:162003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Riad A, Bien S, Westermann D, et al:
Pretreatment with statin attenuates the cardiotoxicity of
Doxorubicin in mice. Cancer Res. 69:695–699. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zordoky BN, Anwar-Mohamed A, Aboutabl ME
and El-Kadi AO: Acute doxorubicin toxicity differentially alters
cytochrome P450 expression and arachidonic acid metabolism in rat
kidney and liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 39:1440–1450. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang CC, Chen PC, Huang CW and Yu J:
Aristolochic Acid induces heart failure in zebrafish embryos that
is mediated by inflammation. Toxicol Sci. 100:486–494. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Delgado RM 3rd, Nawar MA, Zewail AM, et
al: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor treatment improves left ventricular
function and mortality in a murine model of doxorubicin-induced
heart failure. Circulation. 109:1428–1433. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang CY, Fujimura M, Noshita N, Chang YY
and Chan PH: SOD1 down-regulates NF-kappaB and c-Myc expression in
mice after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:163–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang YJ, Wingerd BA, Arakawa T and Smith
WL: Cyclooxygenase-2 gene transcription in a macrophage model of
inflammation. J Immunol. 177:8111–8122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin X, Li Q, Wang YJ, et al: Morphine
inhibits doxorubicin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and
nuclear factor kappaB transcriptional activation in neuroblastoma
SH-SY5Y cells. Biochem J. 406:215–221. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Riganti C, Doublier S, Costamagna C, et
al: Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B pathway by simvastatin and
RhoA silencing increases doxorubicin cytotoxicity in human colon
cancer HT29 cells. Mol Pharmacol. 74:476–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu HG, Ai YW, Yu LL, et al:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway plays an important role in
chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells against etoposide and
doxorubicin induced cell death. Int J Cancer. 122:433–443. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang C, Ling H, Zhang M, et al: Oxidative
stress mediates chemical hypoxia-induced injury and inflammation by
activating NF-κb-COX-2 pathway in HaCaT cells. Mol Cells.
31:531–538. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang C, Yang Z, Zhang M, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and
inflammation in HaCaT cells through inhibition of ROS/NF-κB/COX-2
pathway. PLoS One. 6:e219712011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang YJ, Zhou ZX, Wang GW, Buridi A and
Klein JB: Suppression by metallothionein of doxorubicin-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 275:13690–13698. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lou H, Danelisen I and Singal PK:
Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinases in
adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
288:H1925–H1930. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lou H, Kaur K, Sharma AK and Singal PK:
Adriamycin-induced oxidative stress, activation of MAP kinases and
apoptosis in isolated cardiomyocytes. Pathophysiology. 13:103–109.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poizat C, Puri PL, Bai Y and Kedes L:
Phosphorylation-dependent degradation of p300 by
doxorubicin-activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in
cardiac cells. Mol Cell Biol. 25:2673–2687. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lechner C, Zahalka MA, Giot JF, Møller NP
and Ullrich A: ERK6, a mitogen-activated protein kinase involved in
C2C12 myoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:4355–4359. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Young PR, McLaughlin MM, Kumar S, et al:
Pyridinyl imidazole inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase bind in the ATP site. J Biol Chem. 272:12116–12121. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Puri PL and Sartorelli V: Regulation of
muscle regulatory factors by DNA-binding, interacting proteins, and
post-transcriptional modifications. J Cell Physiol. 185:155–173.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lan AP, Xiao LC, Yang ZL, et al:
Interaction between ROS and p38MAPK contributes to chemical
hypoxia-induced injuries in PC12 cells. Mol Med Report. 5:250–255.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hensley ML, Hagerty KL, Kewalramani T, et
al: American Society of Clinical Oncology 2008 clinical practice
guideline update: use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy
protectants. J Clin Oncol. 27:127–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Sandri MT, et al:
Prevention of high-dose chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in
high-risk patients by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition.
Circulation. 114:2474–2481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalay N, Basar E, Ozdogru I, et al:
Protective effects of carvedilol against anthracycline-induced
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:2258–2262. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Berthiaume JM, Oliveira PJ, Fariss MW and
Wallace KB: Dietary vitamin E decreases doxorubicin-induced
oxidative stress without preventing mitochondrial dysfunction.
Cardiovasc Toxicol. 5:257–267. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sauter KA, Wood LJ, Wong J, Iordanov M and
Magun BE: Doxorubicin and daunorubicin induce processing and
release of interleukin-1beta through activation of the NLRP3
inflammasome. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:1008–1016. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi Y, Moon M, Dawood S, McManus B and Liu
PP: Mechanisms and management of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Herz.
36:296–305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bankers-Fulbright JL, Kalli KR and McKean
DJ: Interleukin-1 signal transduction. Life Sci. 59:61–83. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dinarello CA: IL-1: discoveries,
controversies and future directions. Eur J Immunol. 40:599–606.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
MacEwan DJ: TNF ligands and receptors - a
matter of life and death. Br J Pharmacol. 135:855–875. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gilliam LA, Moylan JS, Ferreira LF and
Reid MB: TNF/TNFR1 signaling mediates doxorubicin-induced diaphragm
weakness. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 300:L225–L231. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Riad A, Bien S, Gratz M, et al: Toll-like
receptor-4 deficiency attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy
in mice. Eur J Heart Fail. 10:233–243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boland MP, Foster SJ and O’Neill LA:
Daunorubicin activates NFkappaB and induces kappaB-dependent gene
expression in HL-60 promyelocytic and Jurkat T lymphoma cells. J
Biol Chem. 272:12952–12960. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|