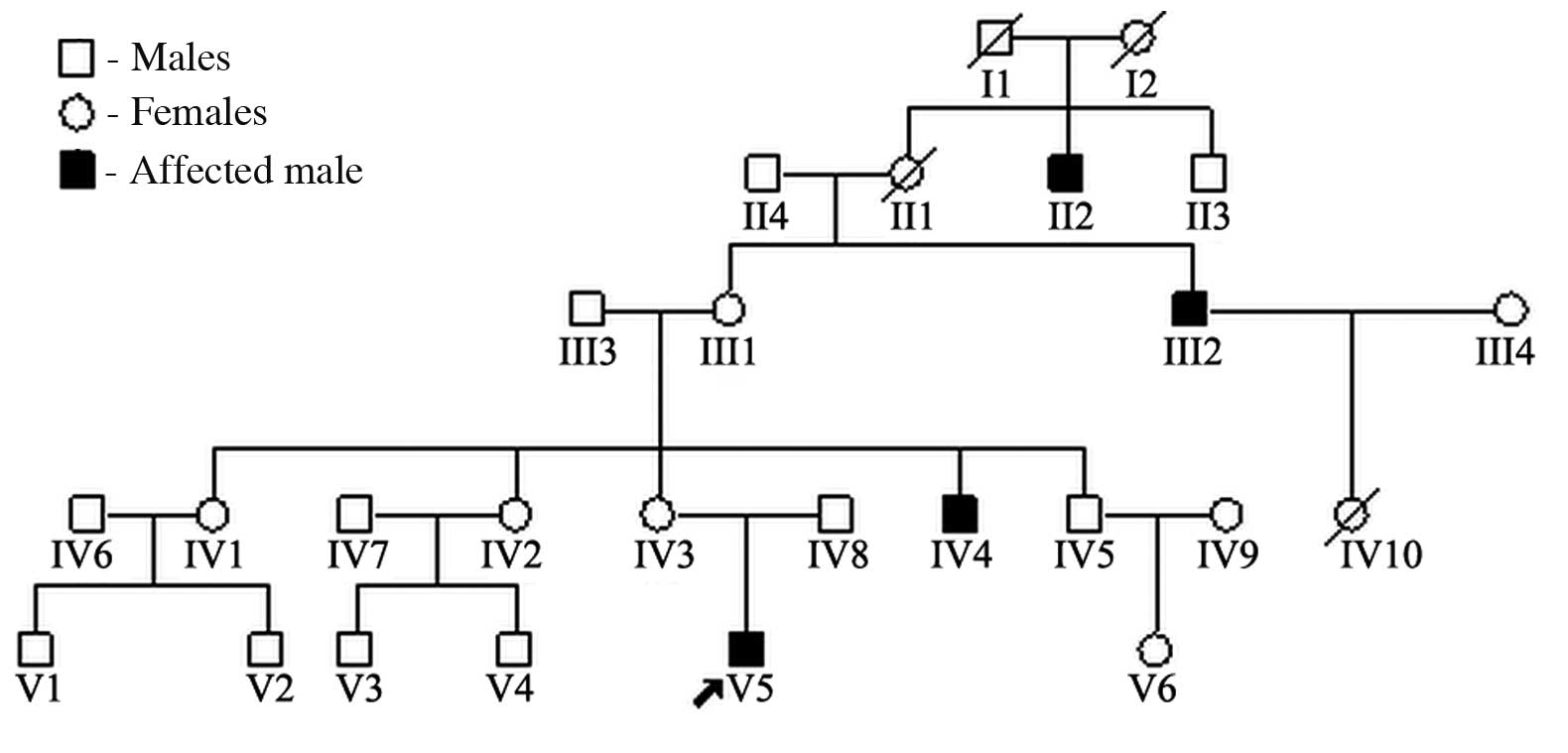
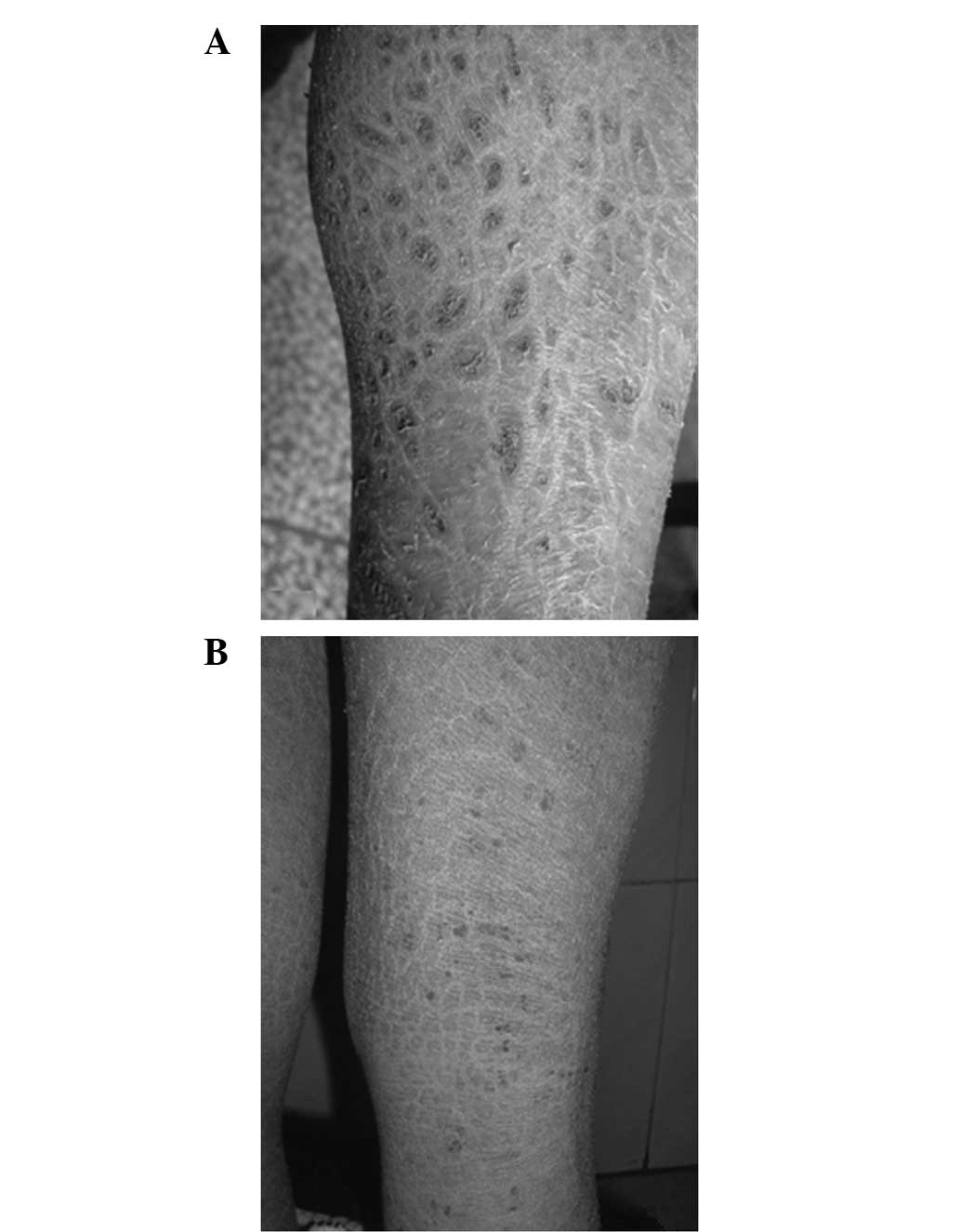
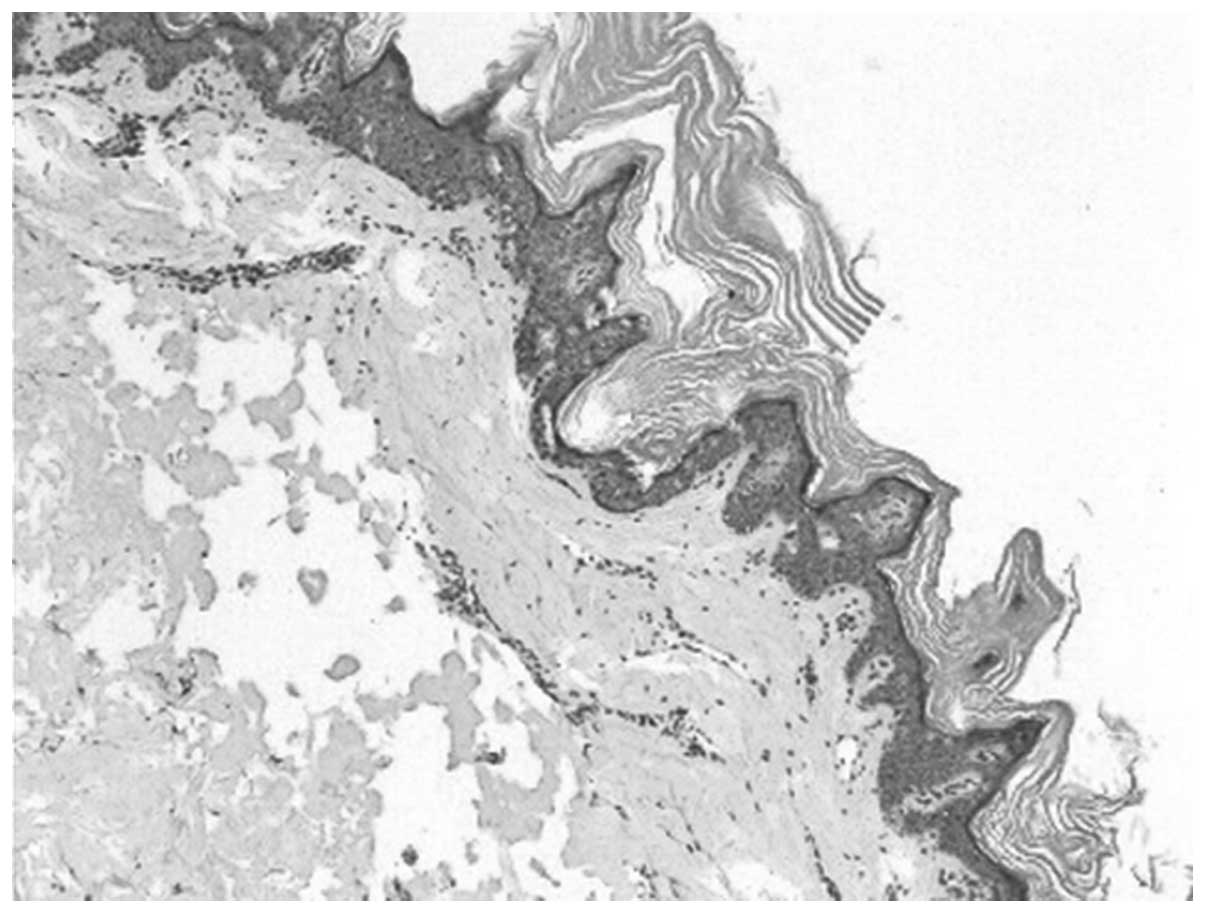
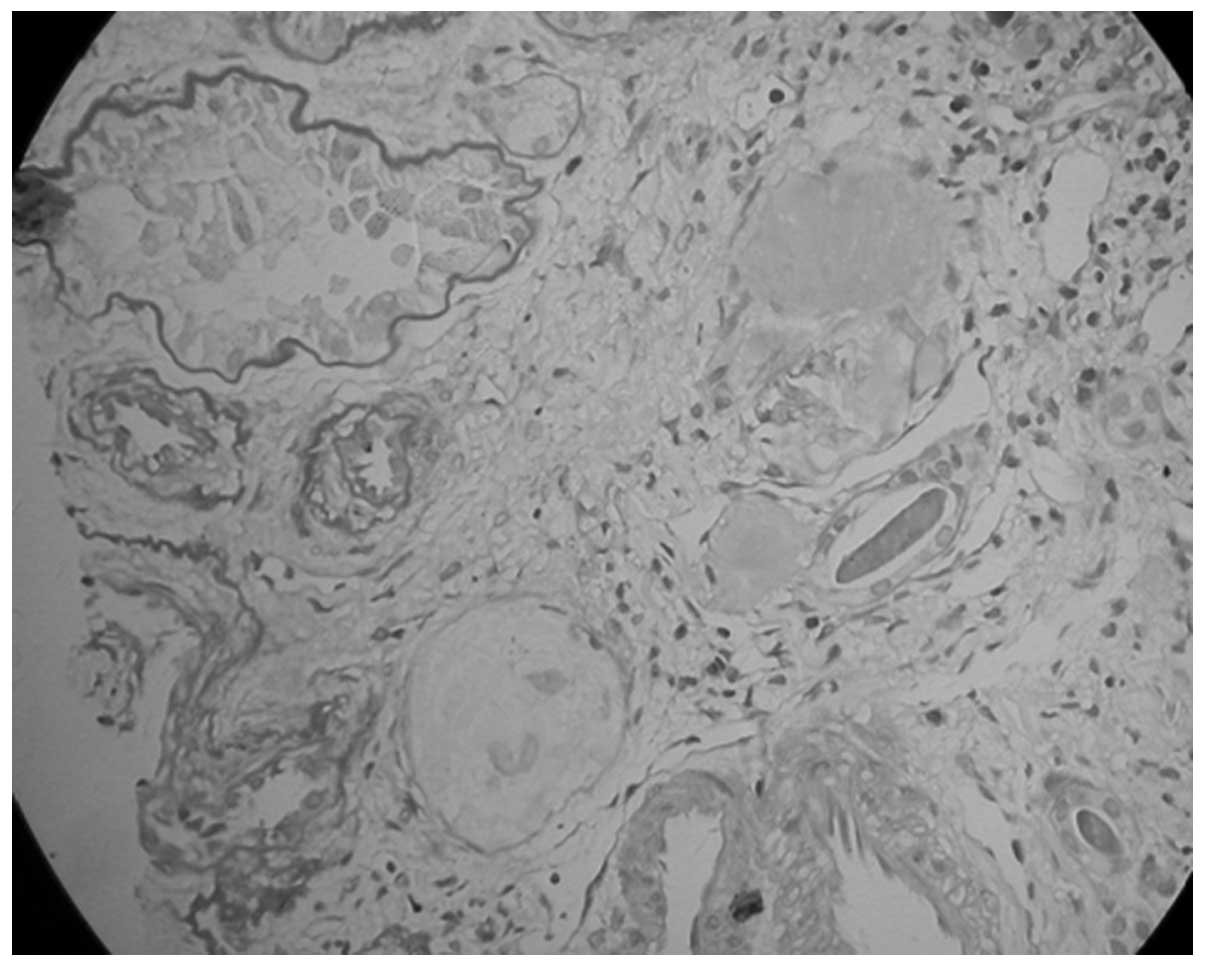
|
1
|
Webster D, France JT, Shapiro LJ and Weiss
R: X-linked ichthyosis due to steroid sulphatase deficiency.
Lancet. 1:70–72. 1978.
|
|
2
|
Paige DG, Emilion GG, Bouloux PM and
Harper JI: A clinical and genetic study of X-linked recessive
ichthyosis and contiguous gene defects. Br J Dermatol. 131:622–629.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gohlke BC, Haug K, Fukami M, et al:
Interstitial deletion in Xp22.3 is associated with X linked
ichthyosis, mental retardation, and epilepsy. J Med Genet.
37:600–602. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hernández-Martin A, González-Sarmiento R
and De Unamuno P: X-linked ichthyosis: an update. Br J Dermatol.
141:617–627. 1999.
|
|
5
|
Richard G: Molecular genetics of the
ichthyoses. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 131C:32–44. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ballabio A, Sebastio G, Carrozzo R, et al:
Deletions of the steroid sulphatase gene in ‘classical’ X-linked
ichthyosis and in X-linked ichthyosis associated with Kallmann
syndrome. Hum Genet. 77:338–341. 1987.
|
|
7
|
Bonifas JM, Morley BJ, Oakey RE, Kan YW
and Epstein EJ Jr: Cloning of a cDNA for steroid sulfatase:
Frequent occurrence of gene deletions in patients with recessive X
chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:9248–9251.
1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu YM, Jiang ZF and Zhu FT: Practical
Paediatrics. 7th edition. People’s Medical Publishing House;
Beijing: pp. 23–31. 2002
|
|
9
|
Yang XG, Li YP, Ma GS, et al: Study on
weight and height of the Chinese people and the differences between
1992 and 2002. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 26:489–493.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Ballabio A, Ranier JE, Chamberlain JS,
Zollo M and Caskey CT: Screening for steroid sulfatase (STS) gene
deletion by multiplex DNA amplification. Hum Genet. 84:571–573.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schaefer L, Ferrero GB, Grillo A, et al: A
high resolution deletion map of human chromosome Xp22. Nat Genet.
4:272–279. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valdes-Flores M, Kofman-Alfaro SH, Jimenez
Vaca AL and Cuevas-Covarrubias SA: Mutation report: a novel partial
deletion of exons 2–10 of the STS gene in recessive X-linked
ichthyosis. J Invest Dermatol. 114:591–593. 2000.
|
|
13
|
Goyer RA, Reynolds J Jr, Burke J and
Burkholder P: Hereditary renal disease with neurosensory hearing
loss, prolinuria and ichthyosis. Am J Med Sci. 256:166–179. 1968.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rayner A, Lampert RP and Rennert OM:
Familial ichthyosis, dwarfism, mental retardation, and renal
disease. J Pediatr. 92:766–768. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deal JE, Barratt TM and Dillon MJ: Fanconi
syndrome, ichthyosis, dysmorphism, jaundice and diarrhoea - a new
syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 4:308–313. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laiho E, Ignatius J, Mikkola H, et al:
Transglutaminase 1 mutations in autosomal recessive congenital
ichthyosis: private and recurrent mutations in an isolated
population. Am J Hum Genet. 61:529–538. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Martul P, Pineda J, Levilliers J, et al:
Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism with hyposmia, X-linked ichthyosis,
and renal malformation syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
42:121–128. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsukura H, Fuchizawa T, Ohtsuki A, et
al: End-stage renal failure in a child with X-linked ichthyosis.
Pediatr Nephrol. 18:297–300. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Krishnamurthy S, Kapoor S and Yadav S:
Nephrotic syndrome with X-linked ichthyosis, Kallmann Syndrome and
unilateral renal agenesis. Indian Pediatr. 44:301–303.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mishra K, Batra VV, Basu S, et al:
Steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome associated with steroid
sulfatase deficiency-x-linked recessive ichthyosis: a case report
and review of literature. Eur J Pediatr. 171:847–850. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ballabio A, Carrozzo R, Parenti G, et al:
Molecular heterogeneity of steroid sulfatase deficiency: A
multicenter study on 57 unrelated patients at DNA and protein
levels. Genomics. 4:36–40. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saeki H, Kuwata S, Nakagawa H, Shimada S,
Tamaki K and Ishibashi Y: Deletion pattern of steroid sulphatase
gene in Japanese patients with X-linked ichthyosis. Br J Dermatol.
139:96–98. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jimenez Vaca AL, Valdes-Flores Mdel R,
Rivera-Vega MR, González-Huerta LM, Kofman-Alfaro SH and
Cuevas-Covarrubias SA: Deletion pattern of the STS gene in X-linked
ichthyosis in a Mexican population. Mol Med. 7:845–849.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aviram-Goldring A, Goldman B,
Netanelov-Shapira I, et al: Deletion patterns of the STS gene and
flanking sequences in Israeli X-linked ichthyosis patients and
carriers: analysis by polymerase chain reaction and fluorescence in
situ hybridization techniques. Int J Dermatol. 39:182–187. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Valdes-Flores M, Kofman-Alfaro SH, Vaca AL
and Cuevas-Covarrubias SA: Deletion of exons 1–5 of the STS gene
causing X-linked ichthyosis. J Invest Dermatol. 116:456–458.
2001.
|
|
26
|
Russell L, DiGiovanna J, Rogers G, et al:
Mutations in the gene for transglutaminase 1 in autosomal recessive
lamellar ichthyosis. Nat Genet. 9:279–283. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nemes Z, Demény M, Marekov LN, Fésüs L and
Steinert PM: Cholesterol 3-sulfate interferes with cornified
envelope assembly by diverting transglutaminase 1 activity from the
formation of cross-links and esters to the hydrolysis of glutamine.
J Biol Chem. 275:2636–2646. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hiiragi T, Sasaki H, Nagafuchi A, et al:
Transglutaminase type 1 and its cross-linking activity are
concentrated at adherens junctions in simple epithelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 274:34148–34154. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reiser J, Kriz W, Kretzler M and Mundel P:
The glomerular slit diaphragm is a modified adherens junction. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 11:1–8. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|