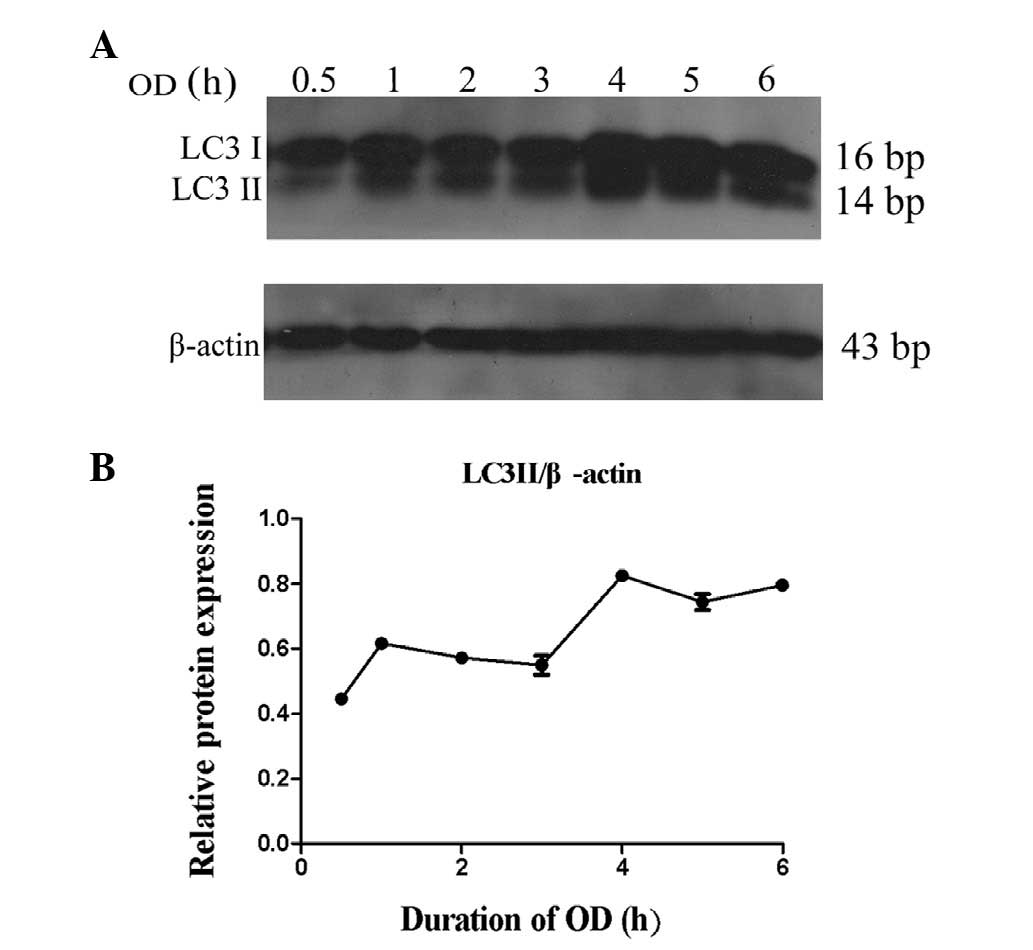
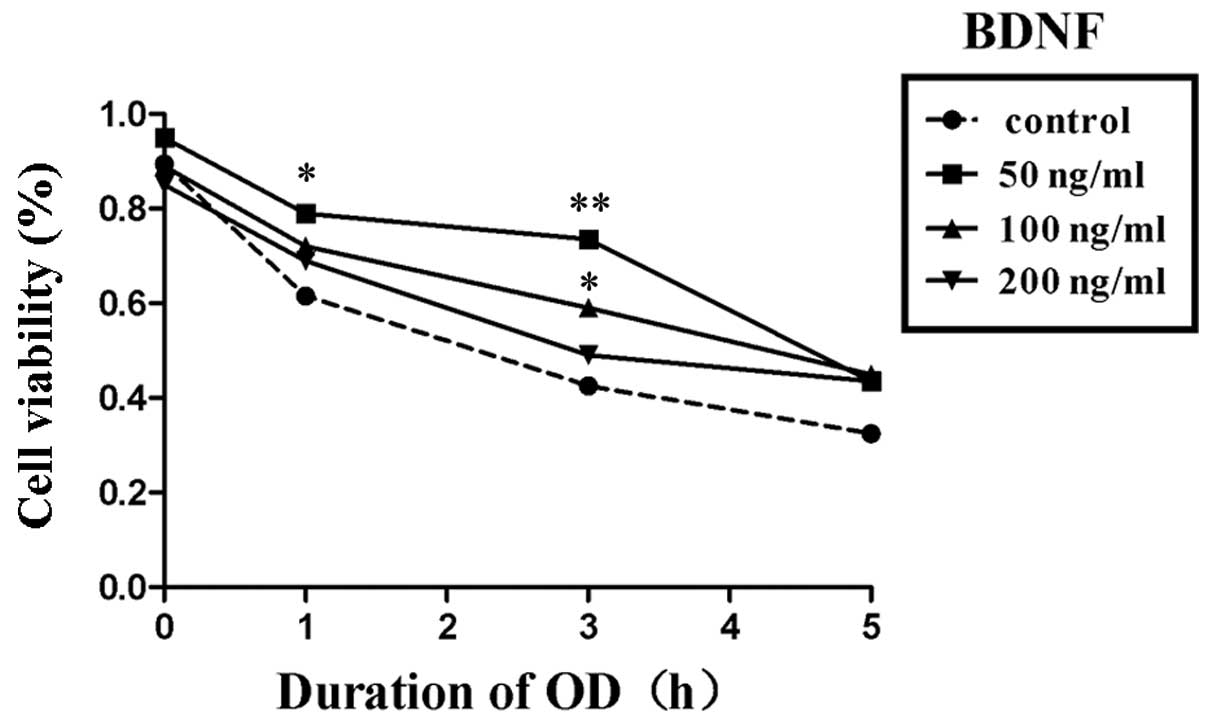
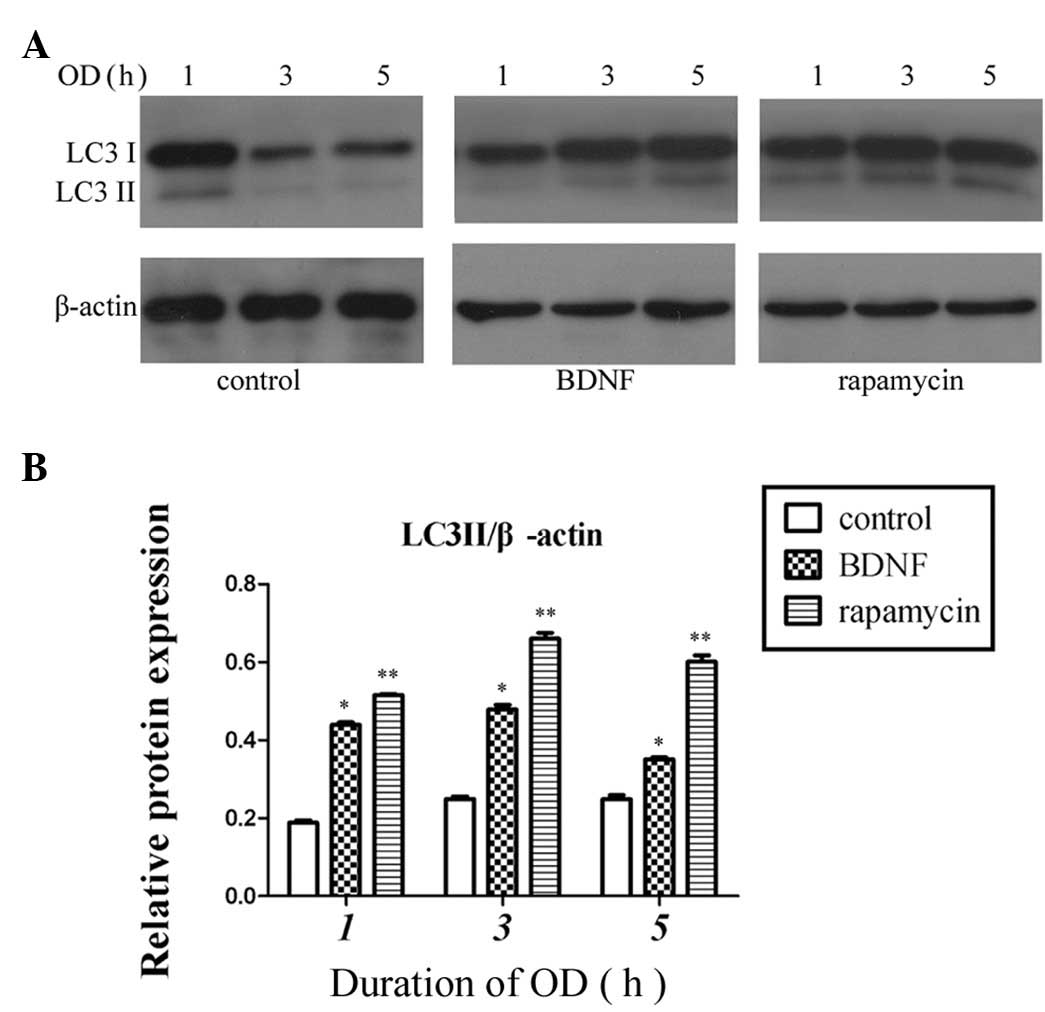
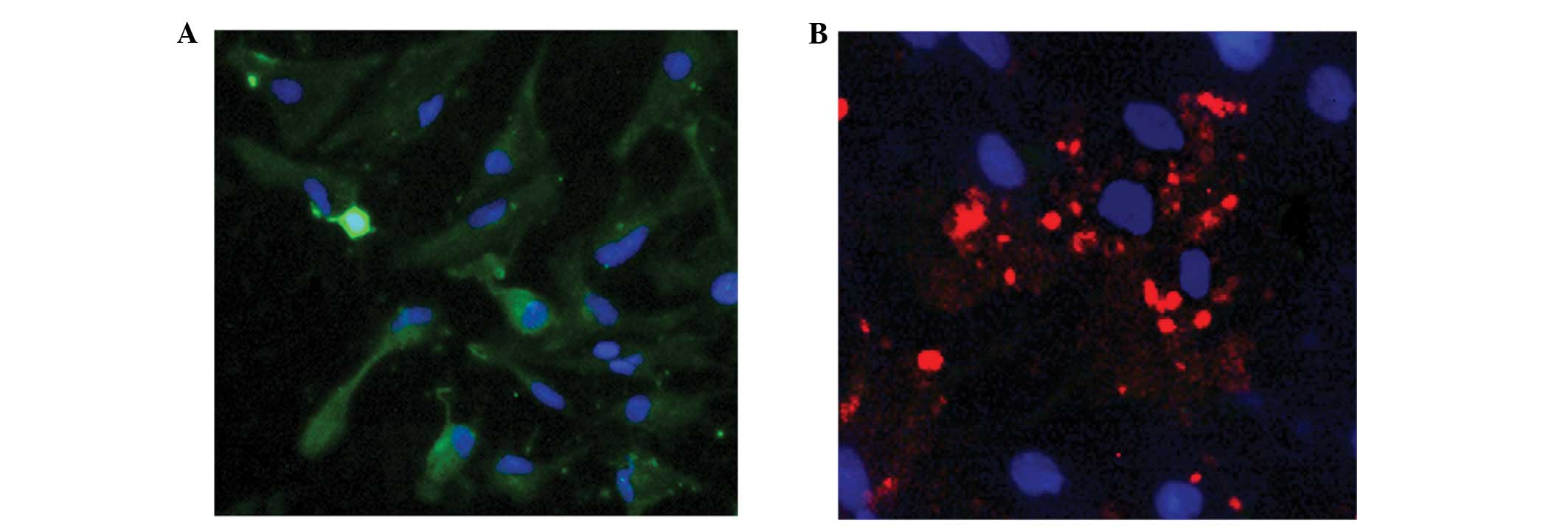
|
1
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H, et
al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for
monitoring autophagy. Autophagy. 8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Carloni S, Girelli S, Scopa C, Buonocore
G, Longini M and Balduini W: Activation of autophagy and Akt/CREB
signaling play an equivalent role in the neuroprotective effect of
rapamycin in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Autophagy. 6:366–377. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan W, Zhang H, Bai X, Lu Y, Dong H and
Xiong L: Autophagy activation is involved in neuroprotection
induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 1402:109–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lessmann V and Brigadski T: Mechanisms,
locations, and kinetics of synaptic BDNF secretion: an update.
Neurosci Res. 65:11–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Massa SM, Yang T, Xie Y, et al: Small
molecule BDNF mimetics activate TrkB signaling and prevent neuronal
degeneration in rodents. J Clin Invest. 120:1774–1785. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meng M, Zhiling W, Hui Z, Shengfu L, Dan Y
and Jiping H: Cellular levels of TrkB and MAPK in the
neuroprotective role of BDNF for embryonic rat cortical neurons
against hypoxia in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 23:515–521. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhou H, Mao M, Liu W, Li S and Wang H:
Expression of BDNF Receptor TrkBmRNA in hypoxia-induced fetal
cortical neurons. J West China Univ Med Sci. 33:573–576. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Sun X, Zhou H, Luo X, et al:
Neuroprotection of brain-derived neurotrophic factor against
hypoxic injury in vitro requires activation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Int J
Dev Neurosci. 26:363–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu YT, Tan HL, Huang Q, Ong CN and Shen
HM: Activation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway promotes
necrotic cell death via suppression of autophagy. Autophagy.
5:824–834. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, et al:
Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen M, Du Y, Qui M, et al: Ophiopogonin
B-induced autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer cells via
inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
29:430–436. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo H, Ma J, Tong Y, Qu Y, Mu DZ and Mao
M: A comparative study on three models of co-culture of neurons and
astrocytes. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 12:984–987. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Zeng W, Tong Y, Li H, Luo R and Mao M:
P2X7 receptor modulation of the viability of radial glial clone
L2.3 cells during hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Mol Med Rep.
5:1357–1361. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kubota C, Torii S, Hou N, Saito N,
Yoshimoto Y, Imai H and Takeuchi T: Constitutive reactive oxygen
species generation from autophagosome/lysosome in neuronal
oxidative toxicity. J Biol Chem. 285:667–674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, et al: Neuronal
injury in rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is
associated with activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways.
Autophagy. 4:762–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi R, Weng J, Zhao L, Li XM, Gao TM and
Kong J: Excessive autophagy contributes to neuron death in cerebral
ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:250–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF and
Miao CY: Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection
of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia.
Autophagy. 8:77–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Balduini W, Carloni S and Buonocore G:
Autophagy in hypoxia-ischemia induced brain injury. J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 25(Suppl 1): 30–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Siao CJ, Nagappan G, et al:
Neuronal release of proBDNF. Nat Neurosci. 12:113–115. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yao RQ, Qi DS, Yu HL, Liu J, Yang LH and
Wu XX: Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral
ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurochem Res. 37:2777–2786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Casalbore P, Barone I, Felsani A, D’Agnano
I, Michetti F, Maira G and Cenciarelli C: Neural stem cells
modified to express BDNF antagonize trimethyltin-induced
neurotoxicity through PI3K/Akt and MAP kinase pathways. J Cell
Physiol. 224:710–721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang W, Han Q, Jin W, et al: The
promotion of neurological recovery in the rat spinal cord crushed
injury model by collagen-binding BDNF. Biomaterials. 31:8634–8641.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blurton-Jones M, Kitazawa M,
Martinez-Coria H, et al: Neural stem cells improve cognition via
BDNF in a transgenic model of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:13594–13599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu YT, Tan HL, Shui G, et al: Dual role of
3-methyladenine in modulation of autophagy via different temporal
patterns of inhibition on class I and III phosphoinositide
3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 285:10850–10861. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
LoPiccolo J, Blumenthal GM, Bernstein WB
and Dennis PA: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway: effective
combinations and clinical considerations. Drug Resist Updat.
11:32–50. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang J and Manning BD: A complex
interplay between Akt, TSC2 and the two mTOR complexes. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:217–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Wang S:
mTOR: on target for novel therapeutic strategies in the nervous
system. Trends Mol Med. 19:51–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin L, Ye S, Chen Z and Zeng Y: Rapamycin
preconditioning attenuates transient focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Int J Neurosci. 122:748–756.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abe N, Borson SH, Gambello MJ, Wang F and
Cavalli V: Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) activation
increases axonal growth capacity of injured peripheral nerves. J
Biol Chem. 285:28034–28043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen AI, Xiong LJ, Tong Y and Mao M: The
neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury
(Review). Biomed Rep. 1:167–176. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang YP, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL and Qin ZH:
Molecular mechanism and regulation of autophagy. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 26:1421–1434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|