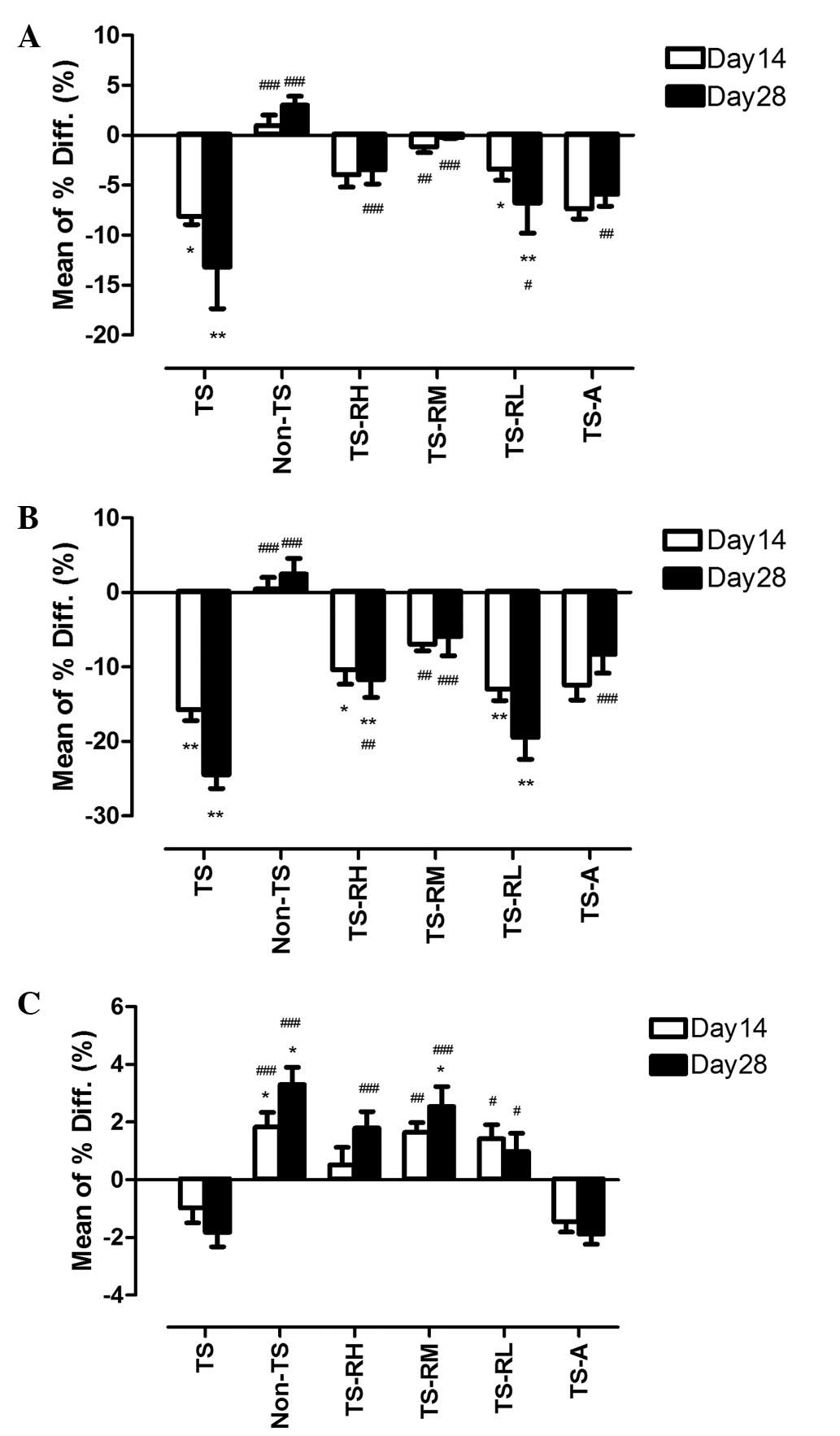
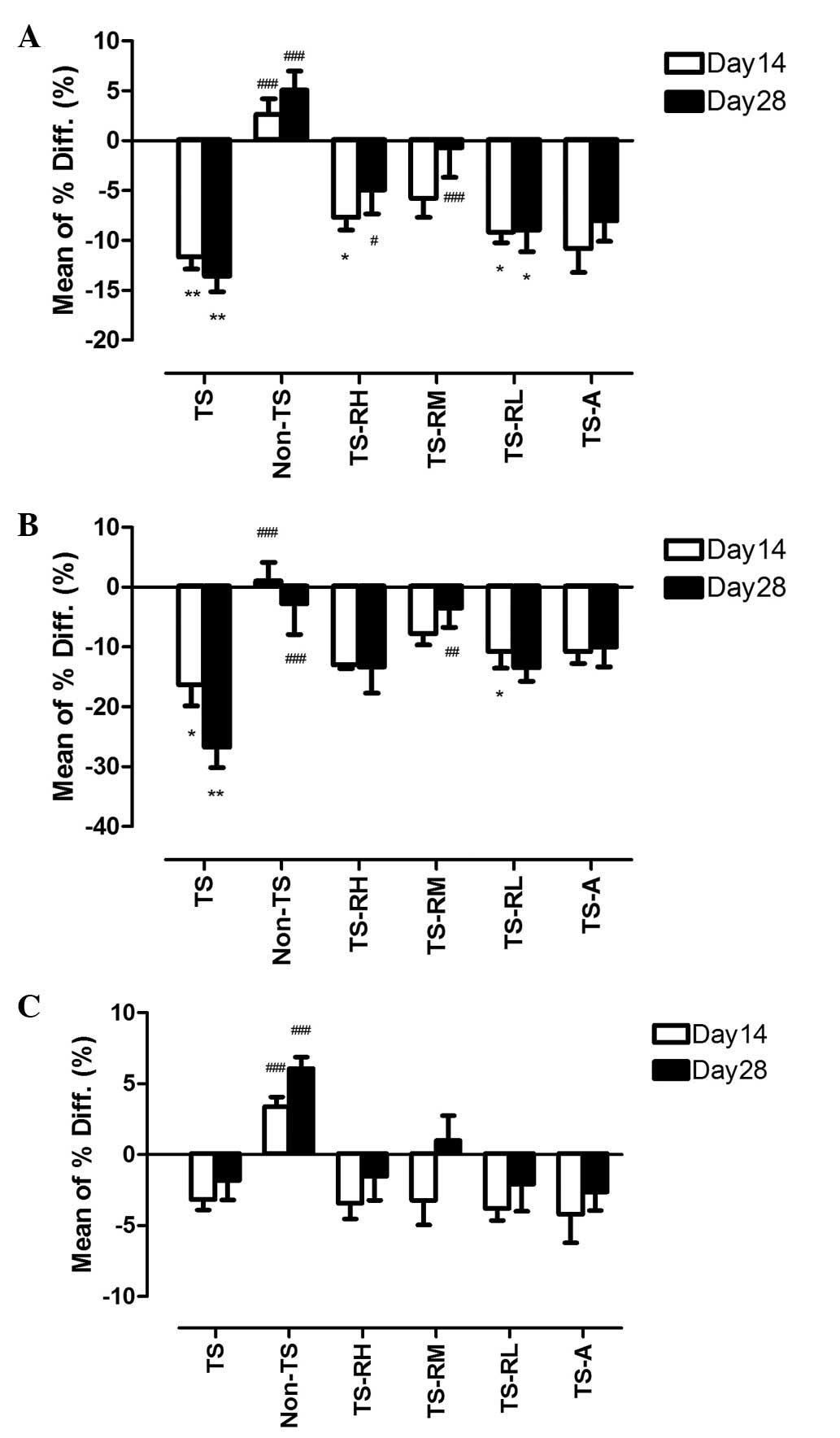
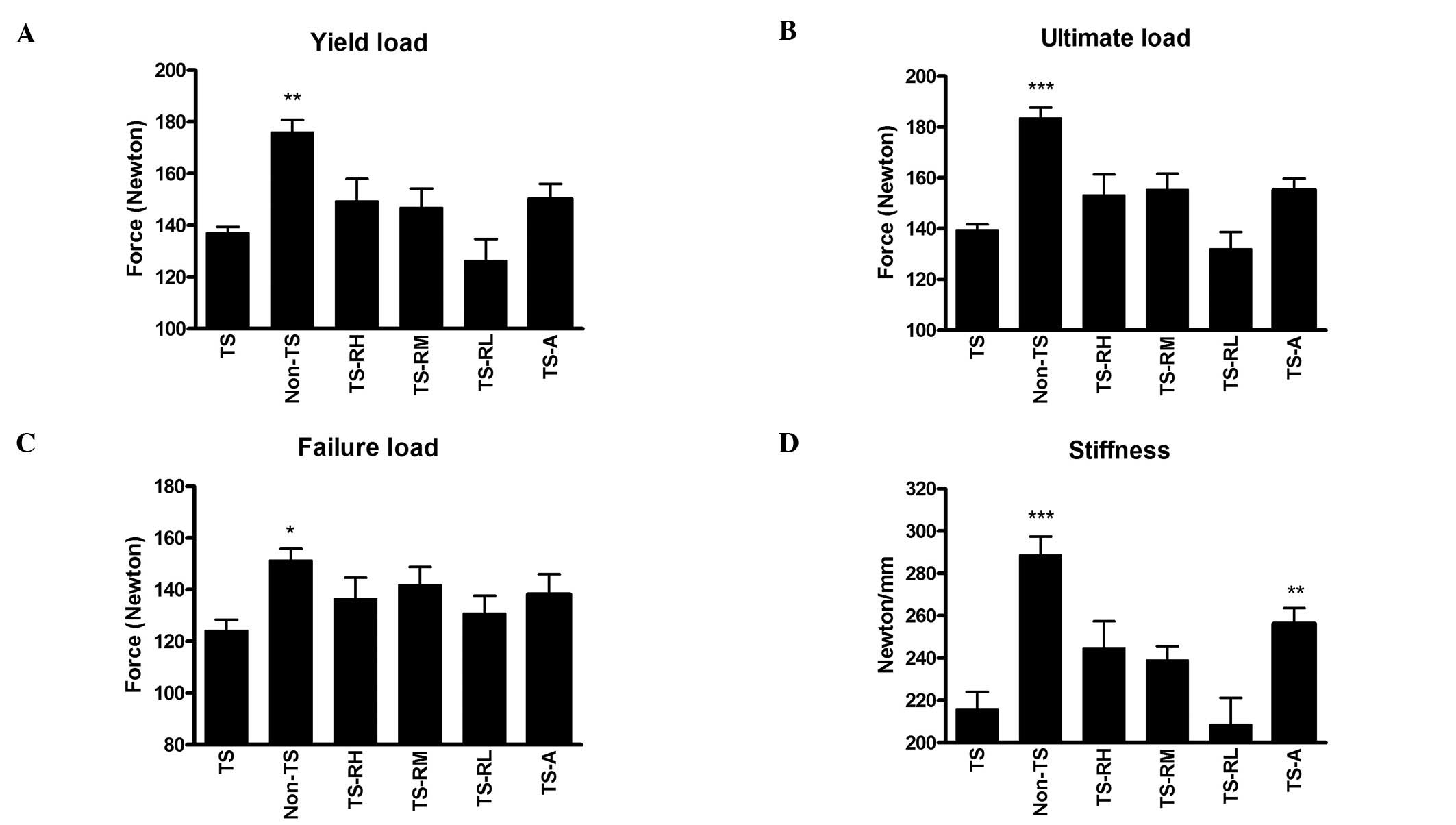
|
1
|
Takata S and Yasui N: Disuse osteoporosis.
J Med Invest. 48:147–156. 2001.
|
|
2
|
Karlsson MK, Nordqvist A and Karlsson C:
Physical activity increases bone mass during growth. Food Nutr Res.
52:2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wilsgaard T, Emaus N, Ahmed LA, Grimnes G,
Joakimsen RM, Omsland TK and Berntsen GR: Lifestyle impact on
lifetime bone loss in women and men: the Tromso Study. Am J
Epidemiol. 169:877–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ehrlich PJ and Lanyon LE: Mechanical
strain and bone cell function: a review. Osteoporos Int.
13:688–700. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bikle DD, Sakata T and Halloran BP: The
impact of skeletal unloading on bone formation. Gravit Space Biol
Bull. 6:45–54. 2003.
|
|
6
|
Tilton FE, Degioanni JJ and Schneider VS:
Long-term follow-up of Skylab bone demineralization. Aviat Space
Environ Med. 51:1209–1213. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith SM, Wastney ME, O’Brien KO, Morukov
BV, Larina IM, Abrams SA, Davis-Street JE, Oganov V and Shackelford
LC: Bone markers, calcium metabolism, and calcium kinetics during
extended-duration space flight on the mir space station. J Bone
Miner Res. 20:208–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Vico L, Collet P, Guignandon A,
Lafage-Proust MH, Thomas T, Rehaillia M and Alexandre C: Effects of
long-term microgravity exposure on cancellous and cortical
weight-bearing bones of cosmonauts. Lancet. 355:1607–1611. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sibonga JD, Evans HJ, Sung HG, Spector ER,
Lang TF, Oganov VS, Bakulin AV, Shackelford LC and LeBlanc AD:
Recovery of spaceflight-induced bone loss: bone mineral density
after long-duration missions as fitted with an exponential
function. Bone. 41:973–978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Michaëlsson K, Bergström R, Mallmin H,
Holmberg L, Wolk A and Ljunghall S: Screening for osteopenia and
osteoporosis: selection by body composition. Osteoporos Int.
6:120–126. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nayak S, Roberts MS and Greenspan SL:
Factors associated with diagnosis and treatment of osteoporosis in
older adults. Osteoporos Int. 20:1963–1967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nelson RE, Nebeker JR, Sauer BC and
LaFleur J: Factors associated with screening or treatment
initiation among male United States veterans at risk for
osteoporosis fracture. Bone. 50:983–988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morey-Holton ER and Globus RK: Hindlimb
unloading of growing rats: a model for predicting skeletal changes
during space flight. Bone. 22:S83–S88. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bloomfield SA, Allen MR, Hogan HA and Delp
MD: Site- and compartment-specific changes in bone with hindlimb
unloading in mature adult rats. Bone. 31:149–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shimano MM and Volpon JB: Biomechanics and
structural adaptations of the rat femur after hindlimb suspension
and treadmill running. Braz J Med Biol Res. 42:330–338. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saxon LK, Robling AG, Castillo AB, Mohan S
and Turner CH: The skeletal responsiveness to mechanical loading is
enhanced in mice with a null mutation in estrogen receptor-beta. Am
J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E484–E491. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lanyon LE: Using functional loading to
influence bone mass and architecture: objectives, mechanisms, and
relationship with estrogen of the mechanically adaptive process in
bone. Bone. 18:37S–43S. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ehrlich PJ, Noble BS, Jessop HL, Stevens
HY, Mosley JR and Lanyon LE: The effect of in vivo mechanical
loading on estrogen receptor alpha expression in rat ulnar
osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 17:1646–1655. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Licata AA, Ciaccia AV, Wong M and Draper
MW: Raloxifene: a new choice for treating and preventing
osteoporosis. Cleve Clin J Med. 67:273–280. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morii H, Ohashi Y, Taketani Y, Fukunaga M,
Nakamura T, Itabashi A, Sarkar S and Harper K: Effect of raloxifene
on bone mineral density and biochemical markers of bone turnover in
Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis: results from a
randomized placebo-controlled trial. Osteoporos Int. 14:793–800.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Morey-Holton ER and Globus RK: Hindlimb
unloading rodent model: technical aspects. J Appl Physiol.
92:1367–1377. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Laib A, Barou O, Vico L, Lafage-Proust MH,
Alexandre C and Rügsegger P: 3D micro-computed tomography of
trabecular and cortical bone architecture with application to a rat
model of immobilisation osteoporosis. Med Biol Eng Comput.
38:326–332. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fitts JM, Klein RM and Powers CA:
Comparison of tamoxifen and testosterone propionate in male rats:
differential prevention of orchidectomy effects on sex organs, bone
mass, growth, and the growth hormone-IGF-I axis. J Androl.
25:523–534. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Urasopon N, Hamada Y, Asaoka K,
Cherdshewasart W and Malaivijitnond S: Pueraria mirifica, a
phytoestrogen-rich herb, prevents bone loss in orchidectomized
rats. Maturitas. 56:322–331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Barou O, Lafage-Proust MH, Martel C,
Thomas T, Tirode F, Laroche N, Barbier A, Alexandre C and Vico L:
Bisphosphonate effects in rat unloaded hindlimb bone loss model:
three-dimensional microcomputed tomographic, histomorphometric, and
densitometric analyses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 291:321–328.
1999.
|
|
26
|
Neviaser AS, Lane JM, Lenart BA,
Edobor-Osula F and Lorich DG: Low-energy femoral shaft fractures
associated with alendronate use. J Orthop Trauma. 22:346–350. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abrahamsen B, Eiken P and Eastell R:
Subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femur fractures in patients treated
with alendronate: A register-based national cohort study. J Bone
Miner Res. 24:1095–1102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Migliorati CA, Siegel MA and Elting LS:
Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis: a long-term complication
of bisphosphonate treatment. Lancet Oncol. 7:508–514. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vieillard MH, Maes JM, Penel G, Facon T,
Magro L, Bonneterre J and Cortet B: Thirteen cases of jaw
osteonecrosis in patients on bisphosphonate therapy. Joint Bone
Spine. 75:34–40. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li CY, Price C, Delisser K, Nasser P,
Laudier D, Clement M, Jepsen KJ and Schaffler MB: Long-term disuse
osteoporosis seems less sensitive to bisphosphonate treatment than
other osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 20:117–124. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heringa M: Review on raloxifene: profile
of a selective estrogen receptor modulator. Int J Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 41:331–345. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Russell RG, Watts NB, Ebetino FH and
Rogers MJ: Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: similarities
and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy.
Osteoporos Int. 19:733–759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Riggs BL and Hartmann LC: Selective
estrogen-receptor modulators – mechanisms of action and application
to clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 348:618–629. 2003.
|