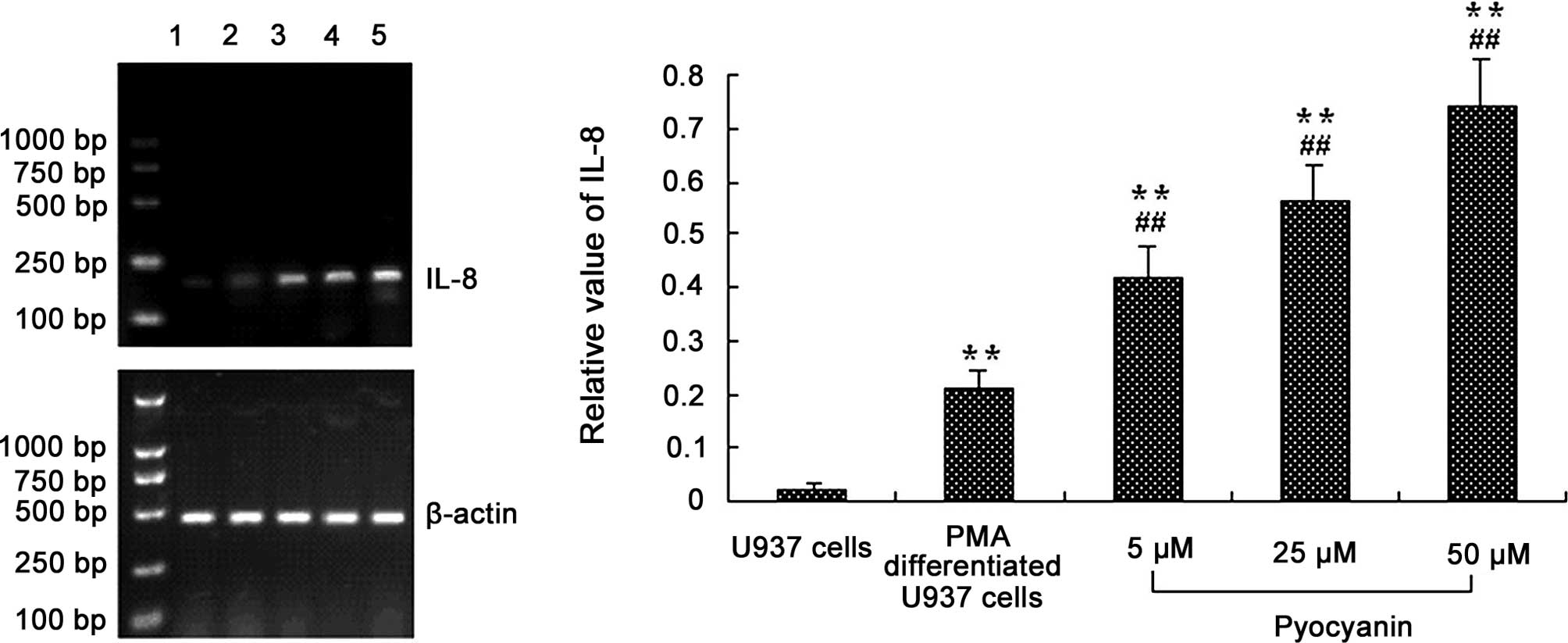
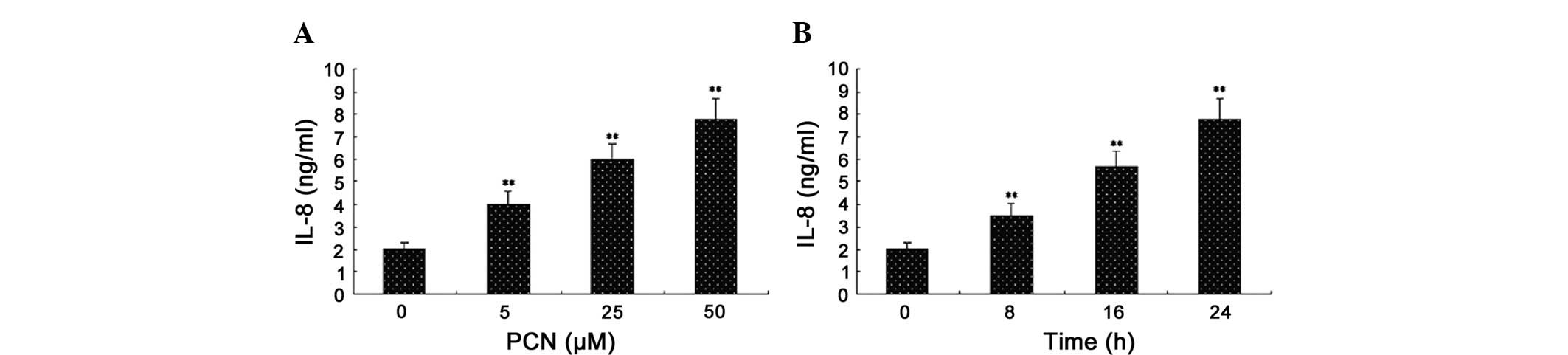
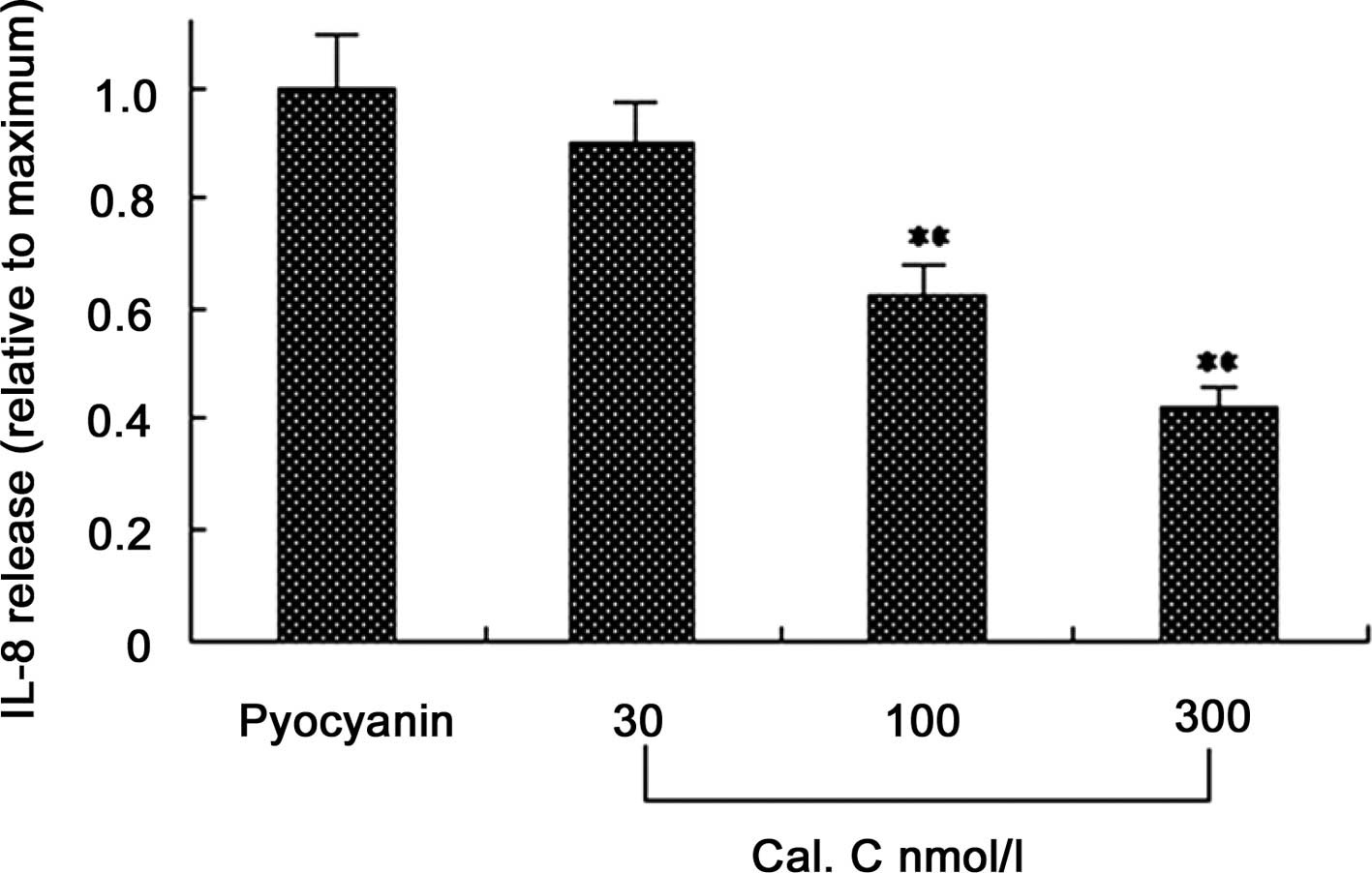
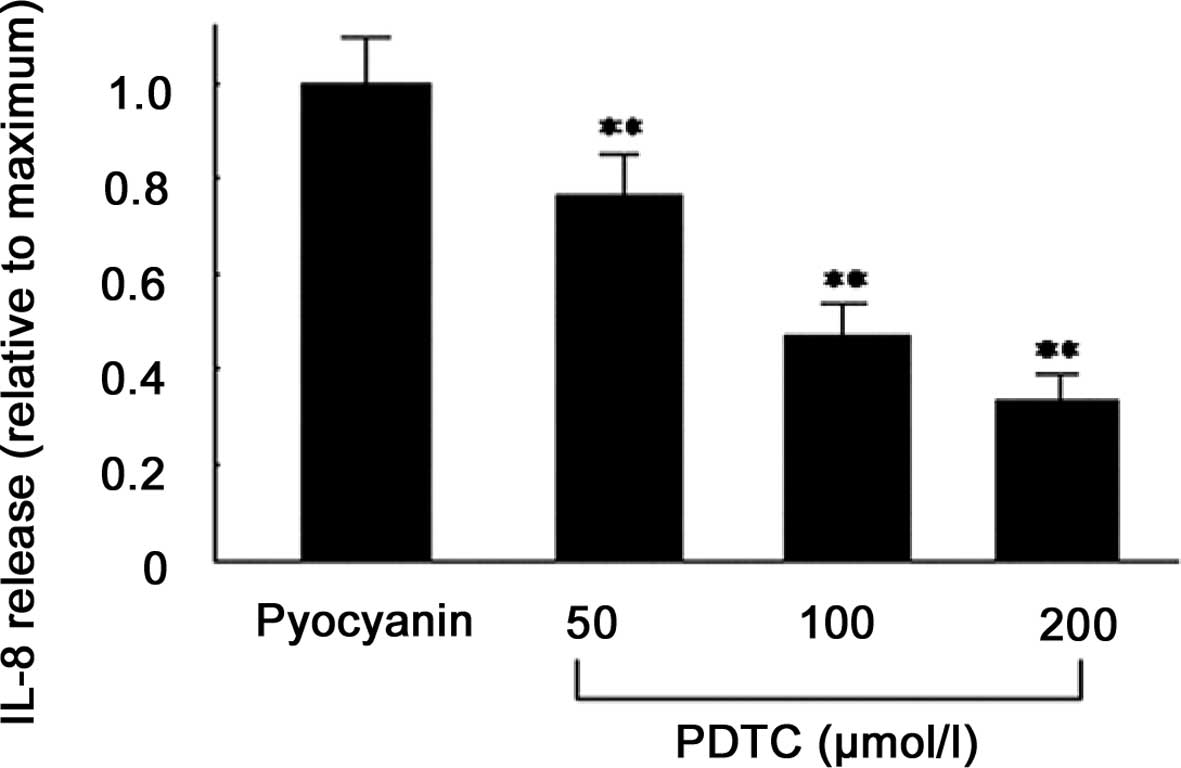
|
1
|
Aloush V, Navon-Venezia S, Seigman-Igra Y,
Cabili S and Carmeli Y: Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas
aeruginosa: risk factors and clinical impact. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 50:43–48. 2006.
|
|
2
|
Tam VH, Chang KT, Abdelraouf K, et al:
Prevalence, resistance mechanisms, and susceptibility of
multidrug-resistant bloodstream isolates of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 54:1160–1164. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS, Christman JW and
Prince AS: Pathogen-host interactions in Pseudomonas
aeruginosa pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 171:1209–1223.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vinckx T, Wei Q, Matthijs S and Cornelis
P: The Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidative stress regulator
OxyR influences production of pyocyanin and rhamnolipids:
protective role of pyocyanin. Microbiology. 156:678–686. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Look DC, Stoll LL, Romig SA, Humlicek A,
Britigan BE and Denning GM: Pyocyanin and its precursor
phenazine-1-carboxylic acid increase IL-8 and intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 expression in human airway epithelial cells by
oxidant-dependent mechanisms. J Immunol. 175:4017–4023. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
O’Malley YQ, Abdalla MY, McCormick ML,
Reszka KJ, Denning GM and Britigan BE: Subcellular localization of
Pseudomonas pyocyanin cytotoxicity in human lung epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 284:L420–L430. 2003.
|
|
7
|
O’Malley YQ, Reszka KJ, Rasmussen GT,
Abdalla MY, Denning GM and Britigan BE: The Pseudomonas
secretory product pyocyanin inhibits catalase activity in human
lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
285:L1077–L1086. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Prince LR, Bianchi SM, Vaughan KM, et al:
Subversion of a lysosomal pathway regulating neutrophil apoptosis
by a major bacterial toxin, pyocyanin. J Immunol. 180:3502–3511.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bianchi SM, Prince LR, McPhillips K, et
al: Impairment of apoptotic cell engulfment by pyocyanin, a toxic
metabolite of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 177:35–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Farberman MM, Ibricevic A, Joseph TD, et
al: Effect of polarized release of CXC-chemokines from wild-type
and cystic fibrosis murine airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 45:221–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mackay CR: Chemokines: immunology’s high
impact factors. Nat Immunol. 2:95–101. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Power CA and Proudfoot AE: The chemokine
system: novel broad-spectrum therapeutic targets. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 1:417–424. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pan NY, Hui WS, Tipoe GL, et al:
Inhibition of pyocyanin-potentiated IL-8 release by steroids in
bronchial epithelial cells. Respir Med. 100:1614–1622. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rada B, Gardina P, Myers TG and Leto TL:
Reactive oxygen species mediate inflammatory cytokine release and
EGFR-dependent mucin secretion in airway epithelial cells exposed
to Pseudomonas pyocyanin. Mucosal Immunol. 4:158–171. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Elswaifi SF, Palmieri JR, Hockey KS and
Rzigalinski BA: Antioxidant nanoparticles for control of infectious
disease. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 9:445–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chomczynski P: A reagent for the
single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from
cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 15:532–537. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maceyka M, Payne SG, Milstien S and
Spiegel S: Sphingosine kinase, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1585:193–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shidham VB, Qi D, Rao RN, et al: Improved
immunohistochemical evaluation of micrometastases in sentinel lymph
nodes of cutaneous melanoma with ‘MCW melanoma cocktail’ - a
mixture of monoclonal antibodies to MART-1, Melan-A, and
tyrosinase. BMC Cancer. 3:152003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lauredo IT, Sabater JR, Ahmed A,
Botvinnikova Y and Abraham WM: Mechanism of pyocyanin- and
1-hydroxyphenazine-induced lung neutrophilia in sheep airways. J
Appl Physiol. 85:2298–2304. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Denning GM, Iyer SS, Reszka KJ, O’Malley
Y, Rasmussen GT and Britigan BE: Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, a
secondary metabolite of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, alters
expression of immunomodulatory proteins by human airway epithelial
cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 285:L584–L592.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sundström C and Nilsson K: Establishment
and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line
(U-937). Int J Cancer. 17:565–577. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang ZL and Failla ML: Copper deficiency
suppresses effector activities of differentiated U937 cells. J
Nutr. 130:1536–1542. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harris P and Ralph P: Human leukemic
models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and
U937 cell lines. J Leukocyte Biol. 37:407–422. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hewison M, Brennan A, Singh-Ranger R,
Walters JC, Katz DR and O’Riordan JL: The comparative role of
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol and phorbol esters in the
differentiation of the U937 cell line. Immunology. 77:304–311.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Delgado MA, Poschet JF and Deretic V:
Nonclassical pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa DNA-induced
interleukin-8 secretion in cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells.
Infect Immun. 74:2975–2984. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Venza I, Cucinotta M, Visalli M, De Grazia
G, Oliva S and Teti D: Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces
interleukin-8 (IL-8) gene expression in human conjunctiva through
the recruitment of both RelA and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
beta to the IL-8 promoter. J Biol Chem. 284:4191–4199. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hessle CC, Andersson B and Wold AE:
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria elicit different patterns
of pro-inflammatory cytokines in human monocytes. Cytokine.
30:311–318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Steinberg SF: Structural basis of protein
kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev. 88:1341–1378. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tak PP and Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: a key
role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 107:7–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|