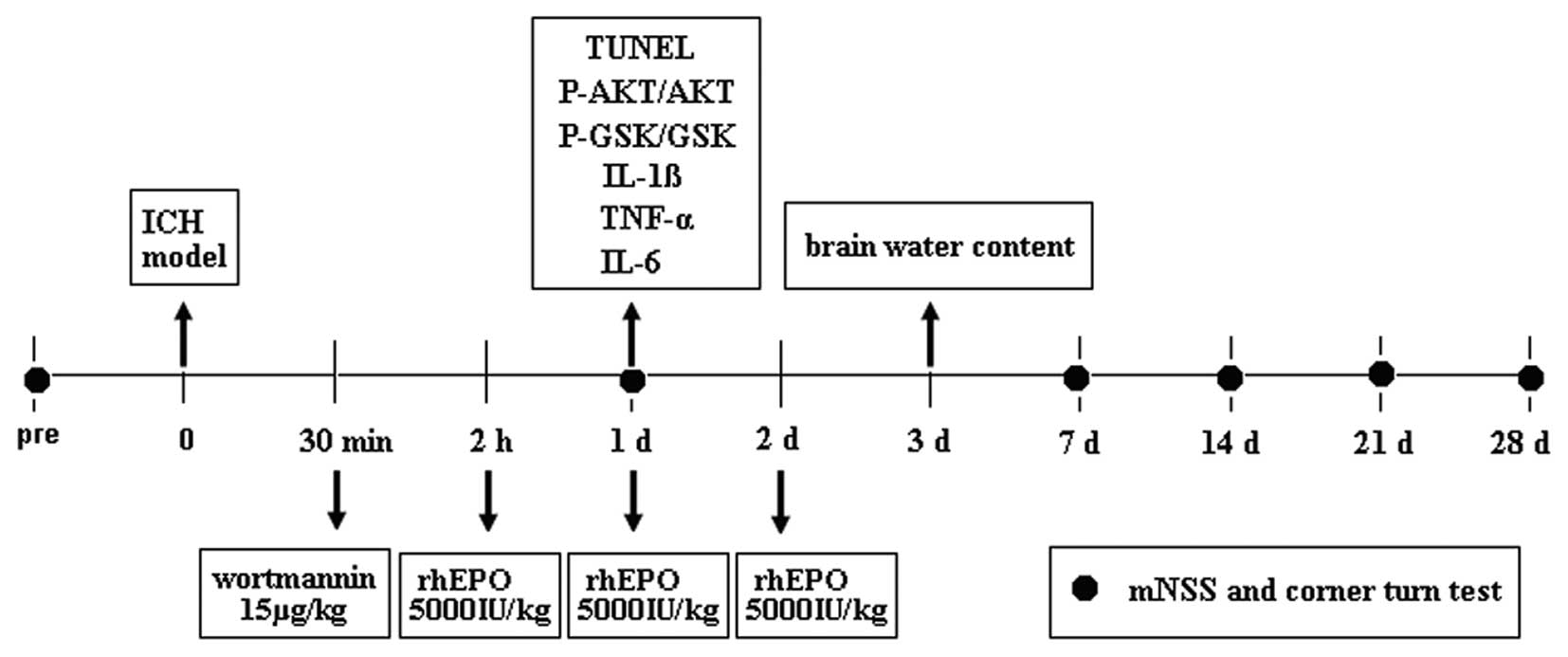
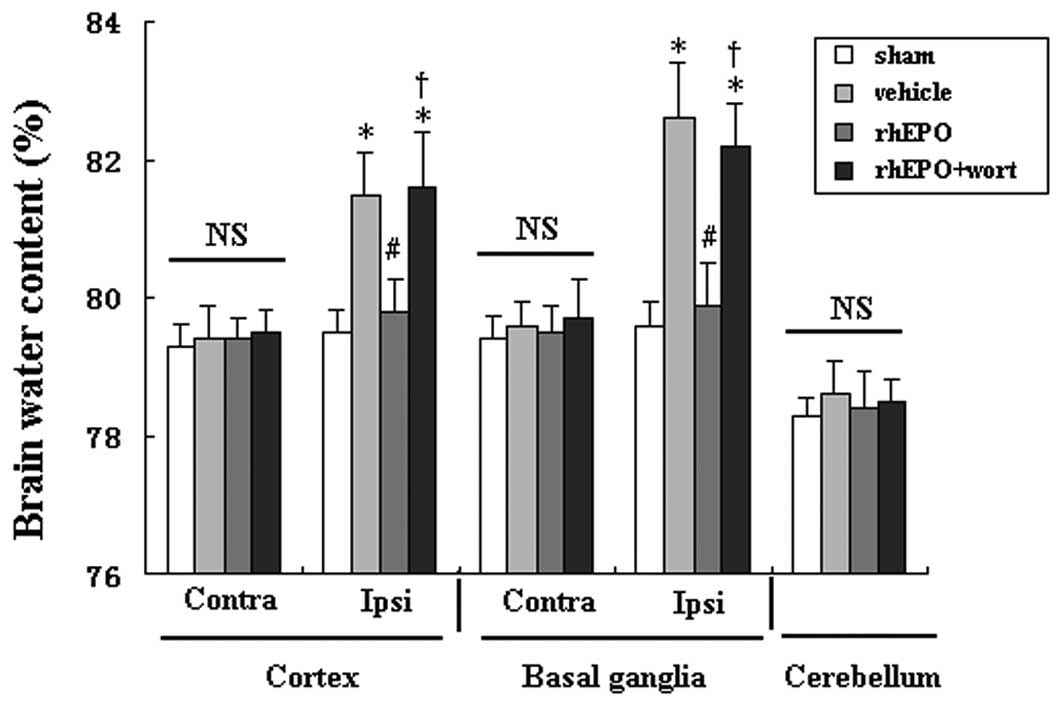
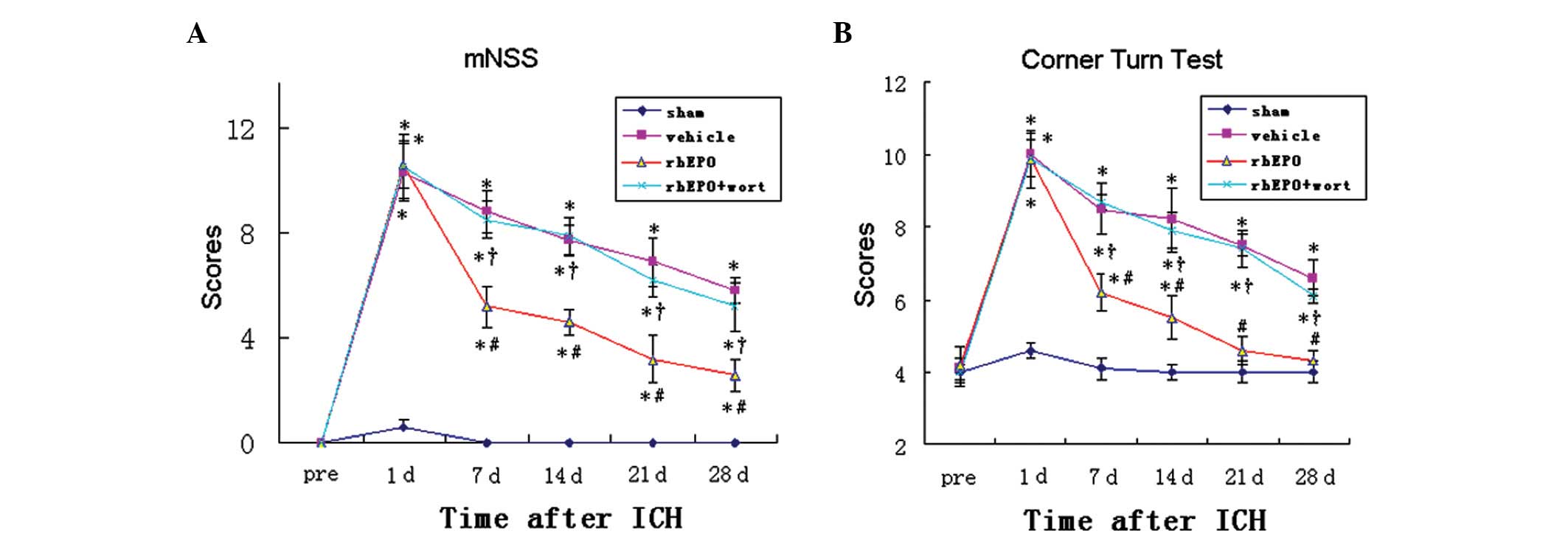
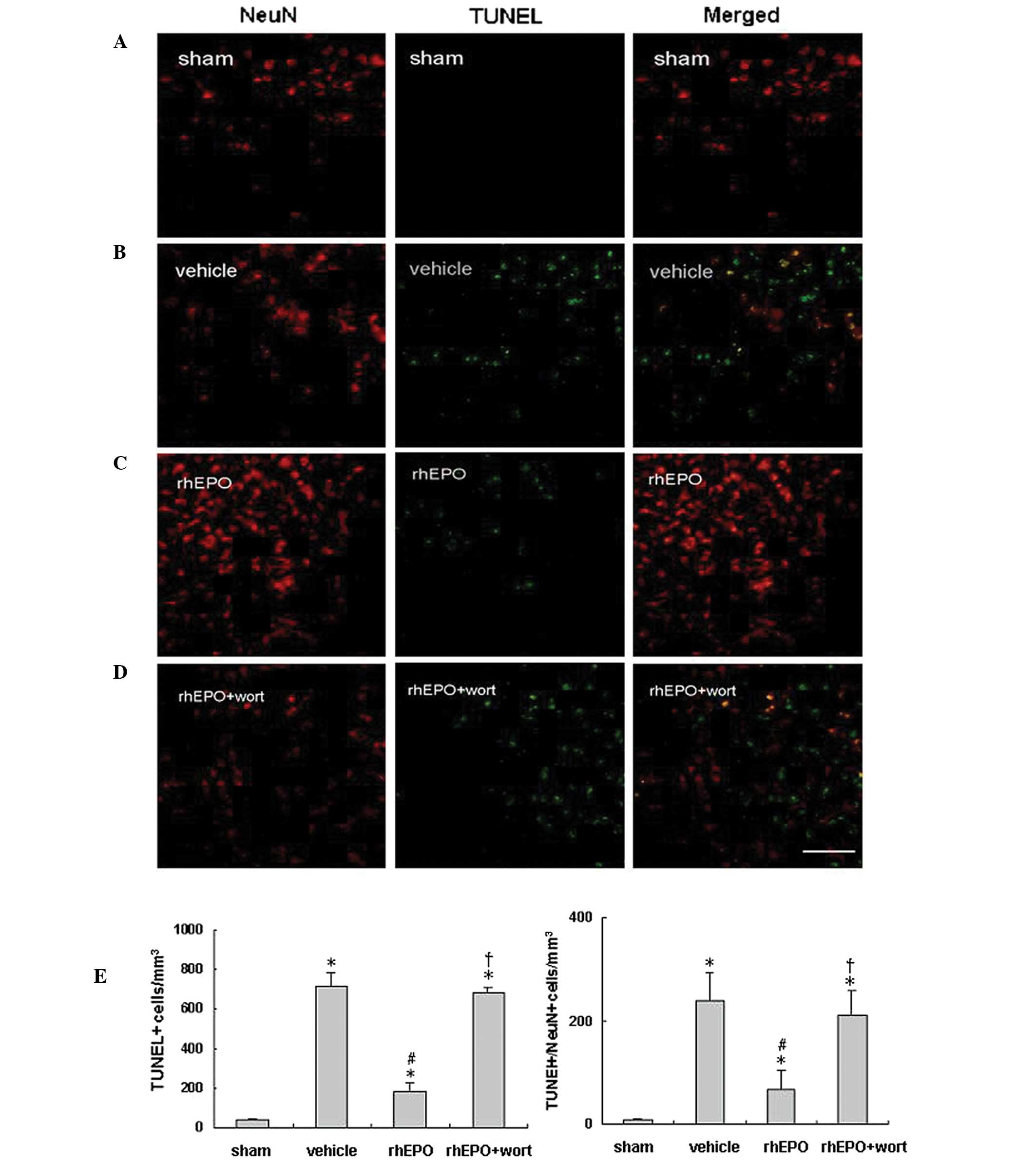
|
1
|
Ostrowski RP, Colohan AR and Zhang JH:
Mechanisms of hyperbaric oxygen-induced neuroprotection in a rat
model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
25:554–571. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lyden PD and Zivin JA: Hemorrhagic
transformation after cerebral ischemia: mechanisms and incidence.
Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 5:1–16. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng JS, Zheng P, Xu JF, et al: Prediction
of motor function by diffusion tensor tractography in patients with
basal ganglion haemorrhage. Arch Med Sci. 7:310–314. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E,
Hanley D, Kase C, Krieger D, et al: Guidelines for the management
of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: a
guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke
Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council,
and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary
Working Group. Stroke. 38:2001–2023. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Daverat P, Castel JP, Dartigues JF and
Orgogozo JM: Death and functional outcome after spontaneous
intracerebral hemorrhage. A prospective study of 166 cases using
multivariate analysis. Stroke. 22:1–6. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cotena S, Piazza O and Tufano R: The use
of erythropoietin in cerebral diseases. Panminerva Med. 50:185–192.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li L, Jiang Q, Ding G, et al: MRI
identification of white matter reorganization enhanced by
erythropoietin treatment in a rat model of focal ischemia. Stroke.
40:936–941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruscher K, Freyer D, Karsch M, et al:
Erythropoietin is a paracrine mediator of ischemic tolerance in the
brain: evidence from an in vitro model. J Neurosci. 22:10291–10301.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sirén AL, Fratelli M, Brines M, et al:
Erythropoietin prevents neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia
and metabolic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:4044–4049.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Celik M, Gökmen N, Erbayraktar S, et al:
Erythropoietin prevents motor neuron apoptosis and neurologic
disability in experimental spinal cord ischemic injury. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:2258–2263. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hwang J, Huh J, Kim J, Jeon Y, Cho S and
Han S: Pretreatment with erythropoietin attenuates the neurological
injury after spinal cord ischaemia. Spinal Cord. 50:208–212. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiong Y, Mahmood A, Meng Y, Zhang Y, Qu C,
Schallert T and Chopp M: Delayed administration of erythropoietin
reducing hippocampal cell loss, enhancing angiogenesis and
neurogenesis, and improving functional outcome following traumatic
brain injury in rats: comparison of treatment with single and
triple dose. J Neurosurg. 113:598–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xiong Y, Mahmood A, Lu D, et al:
Histological and functional outcomes after traumatic brain injury
in mice null for the erythropoietin receptor in the central nervous
system. Brain Res. 1230:247–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen G, Zhang S, Shi J, Ai J and Hang C:
Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) on JAK2/STAT3
pathway and endothelial apoptosis in the rabbit basilar artery
after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cytokine. 45:162–168. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Grasso G, Buemi M, Alafaci C, et al:
Beneficial effects of sys- temic administration of recombinant
human erythropoietin in rabbits subjected to subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:5627–5631. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tseng MY, Hutchinson PJ, Richards HK, et
al: Acute systemic erythropoietin therapy to reduce delayed
ischemic deficits following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a
Phase II randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J
Neurosurg. 111:171–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chau M, Chen D and Wei L: Erythropoietin
attenuates inflammatory factors and cell death in neonatal rats
with intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 111:299–305.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seyfried DM, Han Y, Yang D, Ding J and
Chopp M: Erythropoietin promotes neurological recovery after
intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Int J Stroke. 4:250–256. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grasso G, Graziano F, Sfacteria A, et al:
Neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin and darbepoetin alfa after
experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 65:763–770.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Sinn DI, et al:
Erythropoietin reduces perihematomal inflammation and cell death
with eNOS and STAT3 activations in experimental intracerebral
hemorrhage. J Neurochem. 96:1728–1739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seyfried D, Han Y, Lu D, Chen J, Bydon A
and Chopp M: Improvement in neurological outcome after
administration of atorvastatin following experimental intracerebral
hemorrhage in rats. J Neurosurg. 101:104–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Duris K, Manaenko A, Suzuki H, Rolland WB,
Krafft PR and Zhang JH: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist
pnu-282987 attenuates early brain injury in a perforation model of
subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 42:3530–3536. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Wishka DG, Walker DP, Yates KM, Reitz SC,
Jia S, Myers JK, et al: Discovery of
N-[(3R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl]furo[2,3-c]pyridine-5-carboxamide,
an agonist of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, for the
potential treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia:
synthesis and structure--activity relationship. J Med Chem.
49:4425–4436. 2006.
|
|
24
|
Aronowski J and Hall CE: New horizons for
primary intracerebral hemorrhage treatment: experience from
preclinical studies. Neurol Res. 27:268–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al: Therapeutic
benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells
after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 32:1005–1011. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma Q, Manaenko A, Khatibi NH, Chen W,
Zhang JH and Tang J: Vascular adhesion protein-1 inhibition
provides antiinflammatory protection after an intracerebral
hemorrhagic stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 31:881–893.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Del Bigio MR, Yan HJ, Buist R and Peeling
J: Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Magnetic
resonance imaging and histopathological correlates. Stroke.
27:2312–2319. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
van der Kooij MA, Groenendaal F, Kavelaars
A, et al: Neuroprotective properties and mechanisms of
erythropoietin in in vitro and in vivo experimental models for
hypoxia/ischemia. Brain Res Rev. 59:22–33. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loftspring MC, McDole J, Lu A, Clark JF
and Johnson AJ: Intracerebral hemorrhage leads to infiltration of
several leukocyte populations with concomitant pathophysiological
changes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:137–143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang J: Preclinical and clinical research
on inflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Prog Neurobiol.
92:463–477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hanisch UK: Microglia as a source and
target of cytokines. Glia. 40:140–155. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Allan SM and Rothwell NJ: Cytokines and
acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:734–744. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Masada T, Hua Y, Xi G, Yang GY, Hoff JT
and Keep RF: Attenuation of intracerebral hemorrhage and
thrombin-induced brain edema by overexpression of interleukin-1
receptor antagonist. J Neurosurg. 95:680–686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xi G, Keep RF and Hoff JT: Mechanisms of
brain injury after intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol.
5:53–63. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zazulia AR, Diringer MN, Derdeyn CP and
Powers WJ: Progression of mass effect after intracerebral
hemorrhage. Stroke. 30:1167–1173. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jung KH, Chu K, Jeong SW, et al: HMG-CoA
reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes sensorimotor recovery,
suppressing acute inflammatory reaction after experimental
intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke. 35:1744–1749. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Villa P, Bigini P, Mennini T, Agnello D,
et al: Erythropoietin selectively attenuates cytokine production
and inflammation in cerebral ischemia by targeting neuronal
apoptosis. J Exp Med. 198:971–975. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu X, Shen J, Jin Y, Duan M and Xu J:
Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) preconditioning on nuclear
factor-kappa B (NF-kB) activation & proinflammatory cytokines
induced by myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion. Indian J Med Res.
124:343–354. 2006.
|
|
39
|
Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Zhao W, et al:
Neuroprotective effect of darbepoetin alfa, a novel recombinant
erythropoietic protein, in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke.
36:1071–1076. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Brines ML, Ghezzi P, Keenan S, et al:
Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against
experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:10526–10531.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Valerio A, Bertolotti P, Delbarba A, et
al: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition reduces ischemic cerebral
damage, restores impaired mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents ROS
production. J Neurochem. 116:1148–1159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yano S, Morioka M, Fukunaga K, et al:
Activation of Akt/protein kinase B contributes to induction of
ischemic tolerance in the CA1 subfield of gerbil hippocampus. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 21:351–360. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|