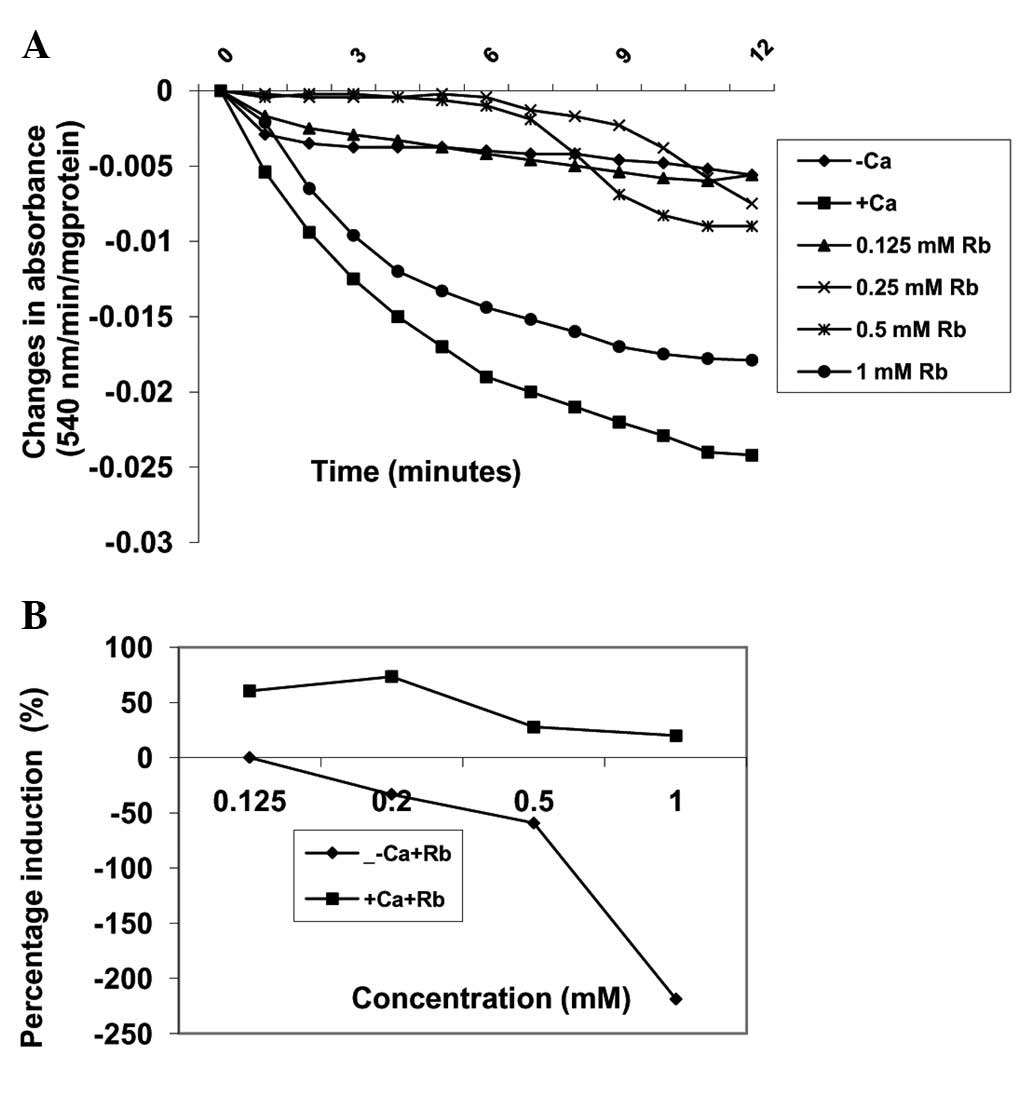
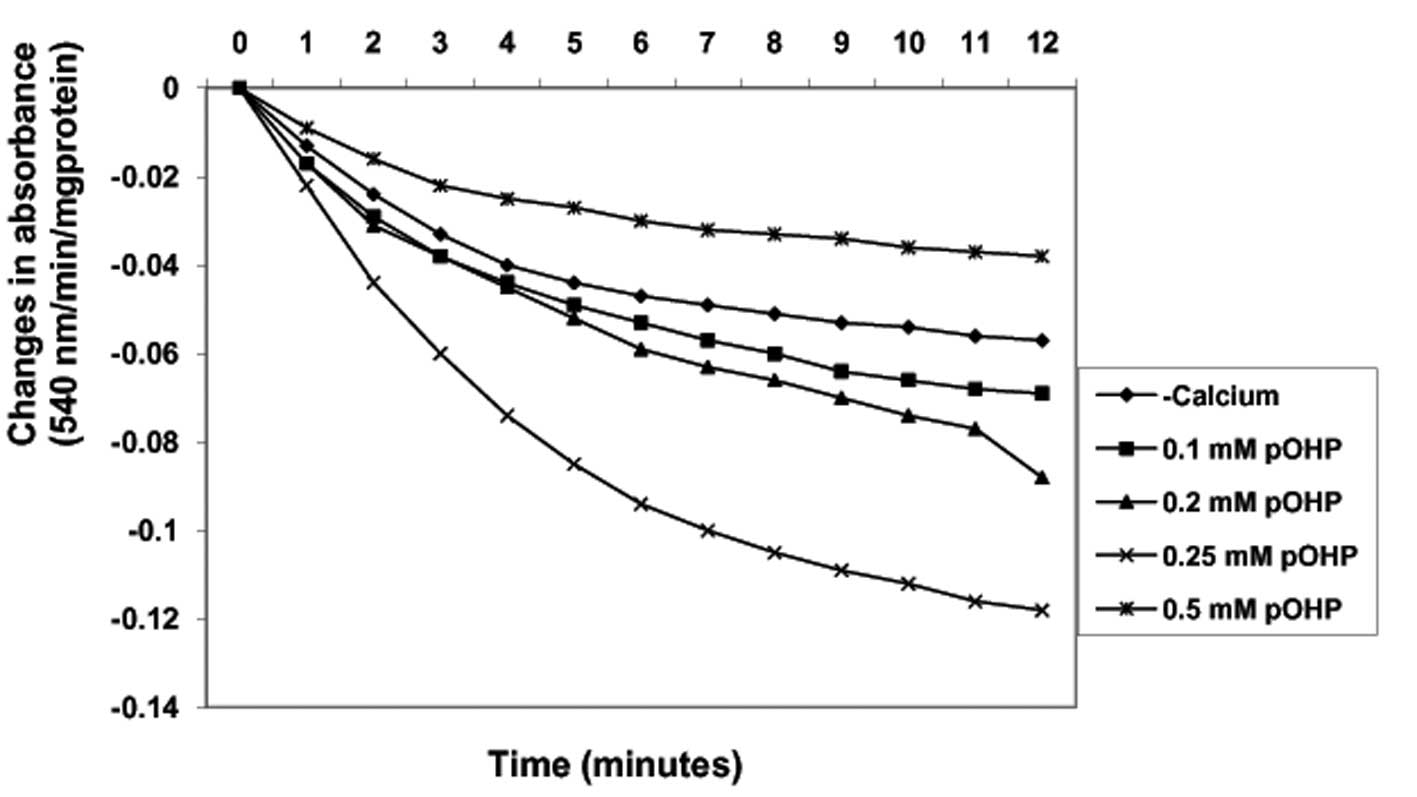
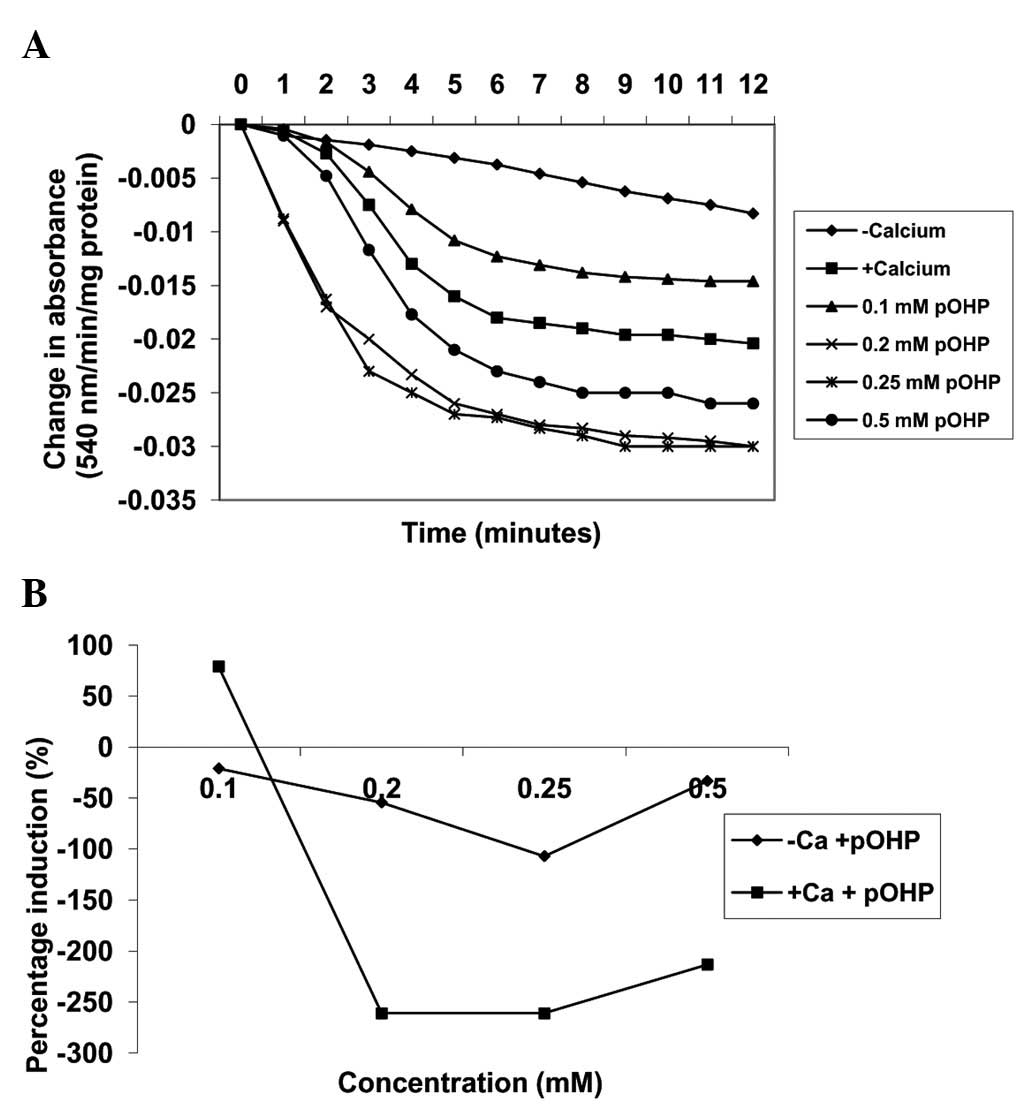
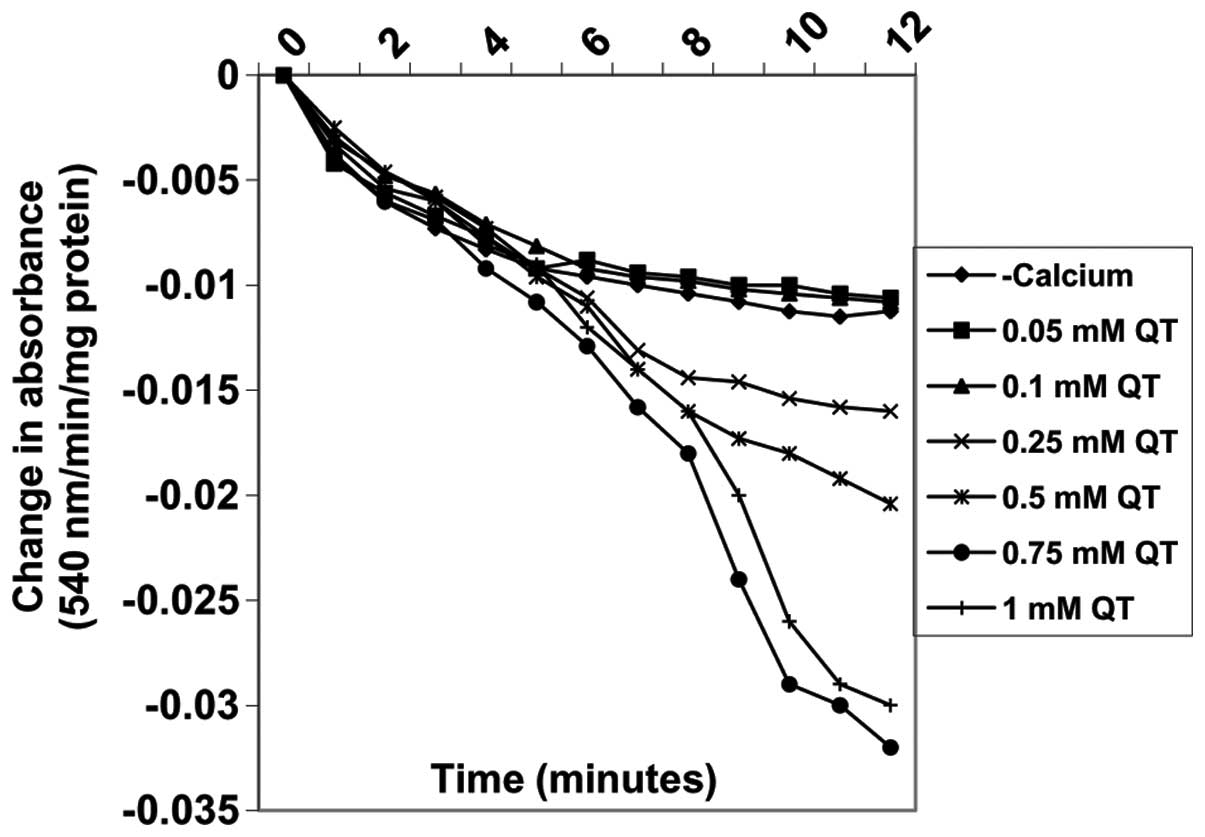
|
1
|
Critchfield JW, Welsh CJ, Phang JM and Yeh
GC: Modulation of adriamycin accumulation and efflux by flavonoids
in HCT-15 colon cells. Activation of P-glycoprotein as a putative
mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol. 48:1437–1445. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Briviba K and Sies H: Nonenzymatic
antioxidant defense systems. Natural Antioxidants in Human Health
and Disease. Frei B: Academic Press; San Diego, CA: pp. 107–128.
1994, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Halliwell B and Gutteridge JM: Role of
free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease: an
overview. Methods Enzymol. 186:1–85. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dargel R: Lipid peroxidation - a common
pathogenetic mechanism? Exp Toxicol Pathol. 44:169–181. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kehrer JP and Smith CV: Free radicals in
biology: sources, reactivities, and roles in the etiology of human
diseases. Natural Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Frei B:
Academic Press; San Diego, CA: pp. 25–62. 1994
|
|
6
|
Bors W, Michel C and Stettmaier K:
Antioxidant effects of flavonoids. Biofactors. 6:399–402. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Halliwell B: Drug antioxidant effects. A
basis for drug selection? Drugs. 42:569–605. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahmed AS, Nakamura N, Meselhy MR, Makhboul
MA, El-Emary N and Hattori M: Phenolic constituents from
Grevillea robusta. Phytochemistry. 53:149–154. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
He QQ, Liu MS, Jin DJ and Kong LY:
Phenolic glycosides from leaves of Hopiciopsis lobata. J
Asian Natur Prod Res. 8:373–377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Adisa RA, Abass Khan A, Oladosu I, Ajaz A,
Choudhary MI, Olorunsogo OO and Ur Rahman A: Purification and
characterization of phenolic compounds from the leaves of
Cnestis ferruginea (De Candolle): Investigation of
antioxidant property. Res J Phytochem. 5:177–189. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boakye-Yiadom K and Konning GH: Incidence
of antibacterial activity in the Connaraceae. Planta Med.
28:397–400. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Akiu S, Suzuki Y, Fujinuma Y, Asahara T
and Fukada M: Inhibitory effect of Arbutin on melanogenesis:
Biochemical study in cultured B16 cells and effect on the
UV-induced pigmentation in human skin. Proc Jpn Soc Invest
Dermatol. 12:138–139. 1988.(In Japanese).
|
|
13
|
World Health Organization. Cause-specific
mortality and morbidity. http://www.who.int/whosis/whostat/EN_WHS09_Table2.pdf.
Accessed July 10, 2013
|
|
14
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grever MCB: Cancer drug discovery and
development. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. De Vita
VT Jr, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA: Lippincott Raven; Philadelphia,
PA: pp. 328–339. 2001
|
|
16
|
Peters GJ, Backus HH, Freemantle S, Van
Triest B, Codacci-Pisanelli PG, et al: Induction of thymidylate
synthase as a 5-fluorouracil resistance mechanism. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1587:194–205. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Desagher S and Martinou JC: Mitochondria
as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
10:369–377. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bernardi P: Mitochondrial transport of
cations: channels, exchangers and permeability transition. Physiol
Rev. 79:1127–1155. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crompton M: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 341:233–249.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Halestrap AP, McStay GP and Clarke SJ: The
permeability transition pore complex: another view. Biochimie.
84:153–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rasola A, Sciacovelli M, Pantic B and
Bernardi P: Signal transduction to the permeability transition
pore. FEBS Lett. 584:1989–1996. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fadeel B, Orrenius S and Zhivotovsky B:
Apoptosis in human disease: a new skin for the old ceremony?
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 266:699–717. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Endrini S, Jaksa S, Marsiati H, Othman F
and Rahmat A: Effects of cola nut (Cola nitida) on the
apoptotic cell of human breast carcinoma cell lines. J Medicinal
Plant Res. 5:2393–2397. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Martin KR: Targeting apoptosis with
dietary bioactive agents. Exper Biol Med (Maywood). 231:117–129.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Berridge MV, Herst PM and Lawen A:
Targeting mitochondrial permeability in cancer drug development.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 53:76–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salako TA, Adisa RA, Alao OO, Adeniran OO,
Atanu FO and Olorunsogo OO: Effects of methanolic and chloroform
extracts of leaves of Alstonia boonei on rat liver
mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore. Afr J Med Med
Sci. 39(Suppl 1): 109–116. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Johnson D and Lardy H: Isolation of liver
or kidney mitochondria. Methods Enzymol. 10:94–96. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol
Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varshney R and Kale RK: Effect of
calmodulin antagonists on radiation induced-lipid peroxidation in
microsomes. Internatl J Radiat Biol. 58:733–743. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Farombi EO, Ogundipe OO, Samuel Uhunwangho
E, Adeyanju MA and Olarenwaju Moody J: Antioxidant properties of
extracts from Alchornea laxiflora (Benth) Pax and Hoffman.
Phytother Res. 17:713–716. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lapidus RG and Sokolove PM: Inhibition by
spermine of the inner membrane permeability transition of isolated
rat heart mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 313:314–318. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shawi AA, Rasul A, Khan M, Iqbal F and
Tonghui M: Eupatilin: A flavonoid compound isolated from the
artemisia plant induces apoptosis and G2/M phase cell cycle arrest
in human melanoma A375 cells. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 5:582–588.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nugraheni M, Santoso U, Suparmo H and
Wuryastuti H: Potential of Coleus tuberosus as an
antioxidant and cancer chemoprevention agent. Int Food Res J.
18:1471–1480. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Choi S, Jang HJ, Choi JY, Kim MS, Lee YR,
Kim HS, et al: Antioxidant and anticancer activity of fractions of
the ethanol extracts of Naematoloma sublateritium. J Med
Plant Res. 6:1344–1352. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Stadtman ER: Metal ion-catalyzed oxidation
of proteins: biochemical mechanism and biological consequences.
Free Radical Biol Med. 9:315–325. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lapidus RG and Sokolove PM: Spermine
inhibition of the permeability transition of isolated rat liver
mitochondria: an investigation of mechanism. Arch Biochem Biohphys.
306:246–253. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|