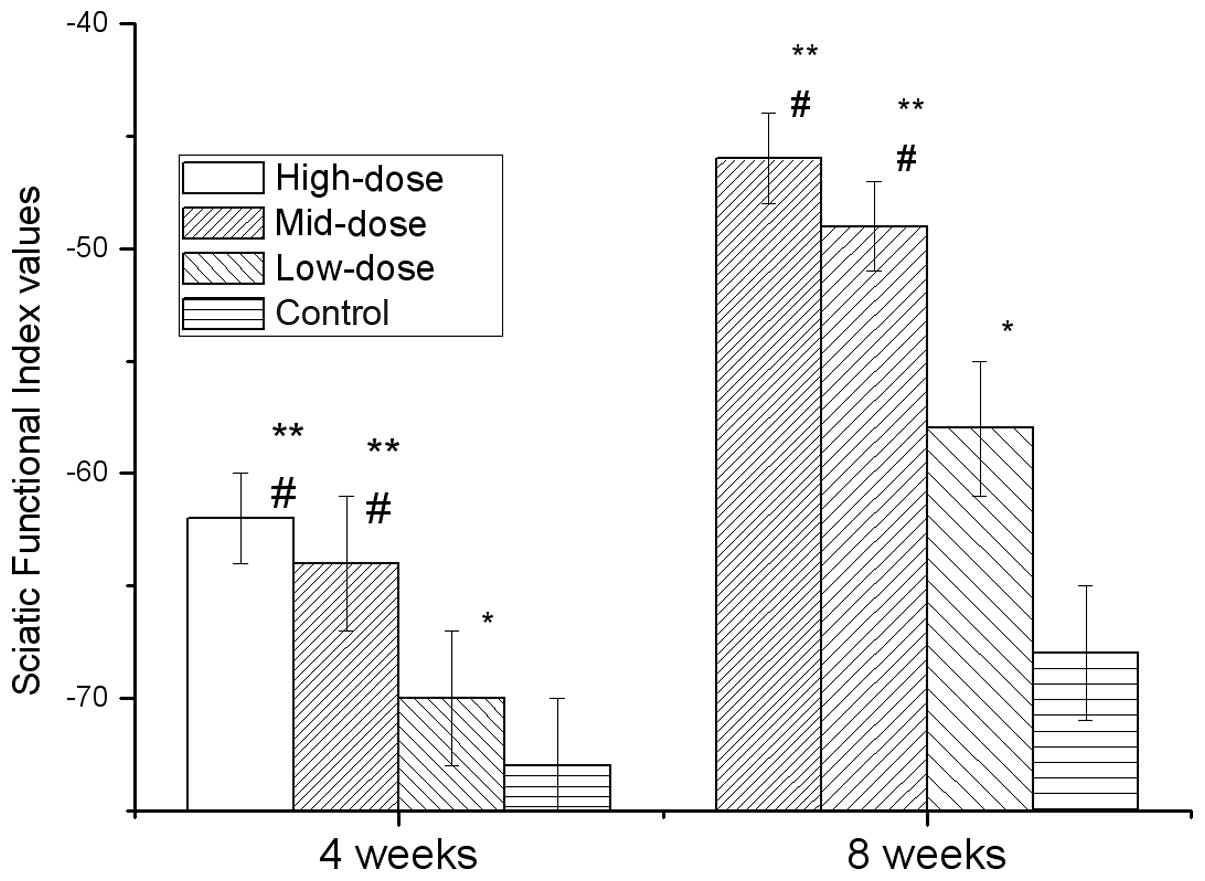
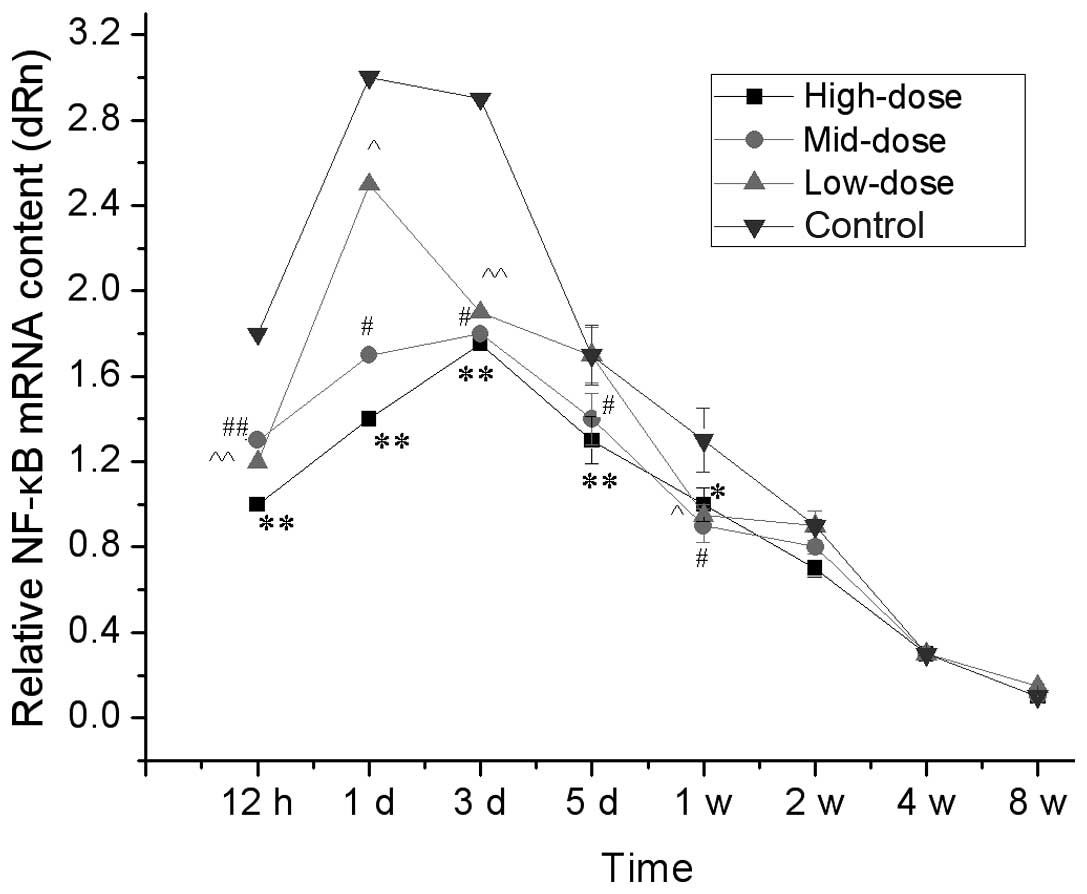
|
1
|
Iwatsuki K, Arai T, Ota H, Kato S, Natsume
T, Kurimoto S, Yamamoto M and Hirata H: Targeting anti-inflammatory
treatment can ameliorate injury-induced neuropathic pain. PLoS One.
8:e577212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Camara-Lemarroy CR, Gonzalez-Moreno EI,
Guzman-de la Garza FJ and Fernandez-Garza NE: Arachidonic acid
derivatives and their role in peripheral nerve degeneration and
regeneration. ScientificWolrdJournal. 2012:1689532012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stern S, Sinske D and Knöll B: Serum
response factor modulates neuron survival during peripheral axon
injury. J Neuroinflammation. 9:782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Que J, Cao Q, Sui T, Du S, Kong D and Cao
X: Effect of FK506 in reducing scar formation by inducing
fibroblast apoptosis after sciatic nerve injury in rats. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e5262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Azizi S, Mohammadi R, Amini K and Fallah
R: Effects of topically administered FK506 on sciatic nerve
regeneration and reinnervation after vein graft repair of short
nerve gaps. Neurosurg Focus. 32:E52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan Y, Sun HH, Hunter DA, Mackinnon SE and
Johnson PJ: Efficacy of short-term FK506 administration on
accelerating nerve regeneration. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.
26:570–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li X, Wang W, Wei G, Wang G, Zhang W and
Ma X: Immunophilin FK506 loaded in chitosan guide promotes
peripheral nerve regeneration. Biotechnol Lett. 32:1333–1337. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang MS and Gold BG: FK506 increase the
regeneration of spinal cord axons in a predegenerated peripheral
nerve autograft. J Spinal Cord Med. 22:287–296. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jost SC, Doolabh VB, Mackinnon SE, Lee M
and Hunter D: Acceleration of peripheral nerve regeneration
following FK506 administration. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 17:39–44.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Phan DQ and Schuind F: Tolerance and
effects of FK506 (tacrolimus) on nerve regeneration: a pilot study.
J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 37:537–543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jifeng H, Dezhong L, Qiongjiao Y, Huayong
Z and Shipu L: Evaluation of PRGD/FK506/NGF conduits for peripheral
nerve regeneration in rats. Neurol India. 58:384–391. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rustemeyer J and Dicke U: Allografting
combined with systemic FK506 produces greater functional recovery
than conduit implantation in a rat model of sciatic nerve injury. J
Reconstr Microsurg. 26:123–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sibilia J and Griscelli C: Immunotherapy
of inflammatory diseases, 2005. Expert Opin Biol Ther. (Suppl 1):
S1–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zheng BR, Shen JP, Zhuang HF, Lin SY, Shen
YP and Zhou YH: Treatment of severe aplastic anemia by
immunosuppressor anti-lymphocyte globulin/anti-thymus globulin as
the chief medicine in combination with Chinese drugs. Chin J Integr
Med. 15:145–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xue B, Jiao J, Zhang L, Li KR, Gong YT,
Xie JX and Wang XM: Triptolide upregulates NGF synthesis in rat
astrocyte cultures. Neurochem Res. 32:1113–1119. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang G: Trends of research on immunology
of Chinese materia medica. Zhongguo Chong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
19:259–260. 1999.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Cao J, Niu Z, Wang Y, Jiang Y, et al:
Immune reactions and nerve repair in mice with sciatic nerve injury
14 days after intraperitoneal injection of Brazil. Neural Regen
Res. 7:675–679. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan L, Zhou X, Zhou X, Zhang Z and Luo HM:
Neurotrophic effects of 7,8-dihydroxycoumarin in primary cultured
rat cortical neurons. Neurosci Bull. 28:493–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Du J, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Wang Y and Ma M:
7,8-dihydroxycoumarin improves neurological function in a mouse
model of sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 7:445–450.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ojala T, Remes S, Haansuu P, Vuorela H,
Hiltunen R, Haahtela K and Vuorela P: Antimicrobial activity of
some coumarin containing herbal plants growing in Finland. J
Ethnopharmacol. 73:299–305. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang CH, Wang B, Wendu RL, Bi HE, Cao GF,
Ji C, Jiang Q and Yao J: Protective role of Wallerian degeneration
slow (Wlds) gene against retinal ganglion cell body damage in a
Wallerian degeneration model. Exp Ther Med. 5:621–625.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Guo W, Zhang P, Li H, Gu X and Yao
D: Signal flow and pathways in response to early Wallerian
degeneration after rat sciatic nerve injury. Neurosci Lett.
536:56–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun SC, Ganchi PA, Ballard DW and Greene
WC: NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha:
evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science.
259:1912–1915. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Castranova V and Shi X: New
insights into the role of nuclear factor-kappa B in cell growth
regulation. Am J Pathol. 159:387–397. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meffert MK, Chang JM, Wiltgen BJ, Fanselow
MS and Baltimore D: NF-kappa B functions in synaptic signaling and
behavior. Nat Neurosci. 6:1072–1078. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brambilla R, Bracchi-Ricard V, Hu WH,
Frydel B, Bramwell A, Karmally S, Green EJ and Bethea JR:
Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation
and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp
Med. 202:145–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
The Ministry of Science and Technology of
the People’s Republic of China. Guidance suggestions for the care
and use of Laboratory Animals. 2006.
|
|
28
|
Huang JH, Huang XZ, Chen ZY, Zheng QS and
Sun RY: Dose conversion among different animals and healthy
volunteers in pharmacological study. Chin J Clin Pharmacol
Therapeut. 9:1069–1072. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Chen G, Gong M, Yan M and Zhang X:
Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis
in hippocampal neurons of aging rats. PLoS One. 8:e578702013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|