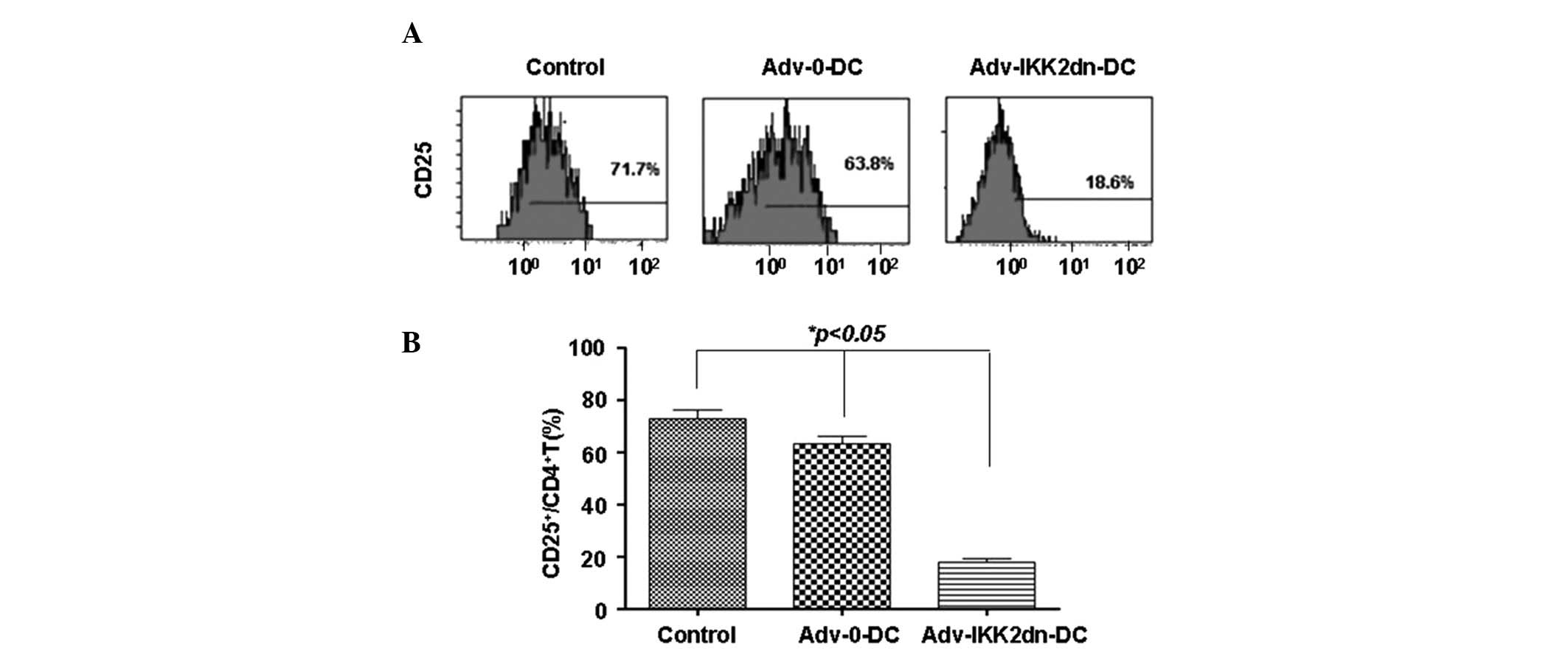
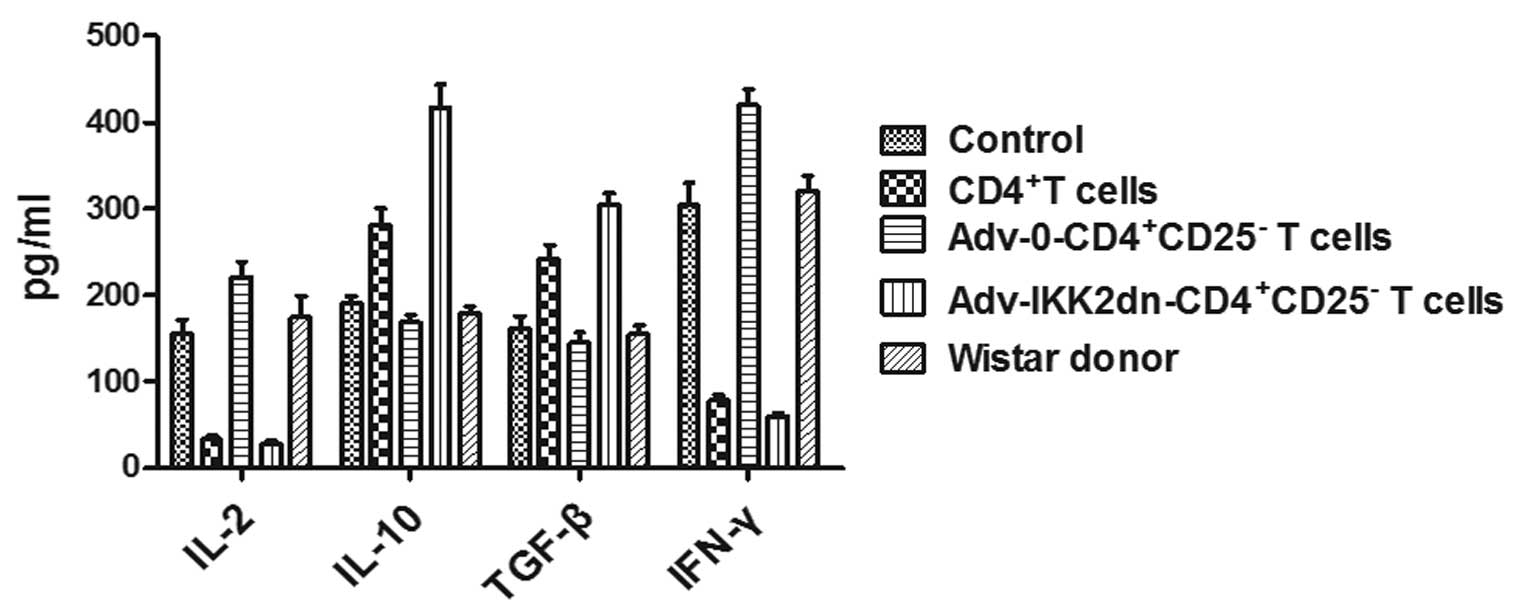
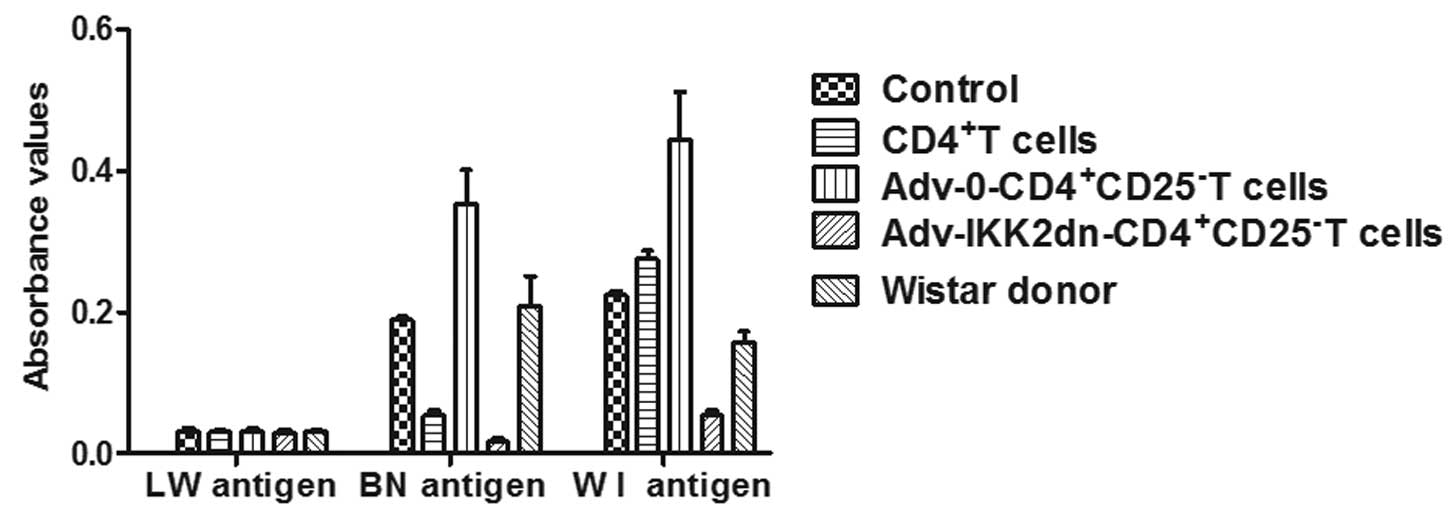
|
1
|
van Duivenvoorde LM, van Mierlo GJ,
Boonman ZF and Toes RE: Dendritic cells: vehicles for tolerance
induction and prevention of autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology.
211:627–632. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moser M: Dendritic cells in immunity and
tolerance-do they display opposite functions? Immunity. 19:5–8.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morelli AE and Thomson AW: Dendritic
cells: regulators of alloimmunity and opportunities for tolerance
induction. Immunol Rev. 196:125–146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muth S, Schütze K, Schild H and Probst HC:
Release of dendritic cells from cognate CD4+ T-cell
recognition results in impaired peripheral tolerance and fatal
cytotoxic T-cell mediated autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:9059–9064. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Camirand G, Caron NJ, Turgeon NA, Rossini
AA and Tremblay JP: Treatment with anti-CD154 antibody and
donor-specific transfusion prevents acute rejection of myoblast
transplantation. Transplantation. 73:453–461. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sela U, Olds P, Park A, Schlesinger SJ and
Steinman RM: Dendritic cells induce antigen-specific regulatory T
cells that prevent graft versus host disease and persist in mice. J
Exp Med. 208:2489–2496. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Karin M, Yamamoto Y and Wang QM: The IKK
NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 3:17–26. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng H, Guerau-de-Arellano M, Mehta VB,
Yang Y, Huss DJ, Papenfuss TL, Lovett-Racke AE and Racke MK:
Dimethyl fumarate inhibits dendritic cell maturation via nuclear
factor κB (NF-κB) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2
(ERK1/2) and mitogen stress-activated kinase 1 (MSK1) signaling. J
Biol Chem. 287:28017–28026. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jimenez F, Quinones MP, Martinez HG,
Estrada CA, Clark K, Garavito E, Ibarra J, Melby PC and Ahuja SS:
CCR2 plays a critical role in dendritic cell maturation: possible
role of CCL2 and NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 184:5571–5581. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cosulich SC, James NH, Needham MR, Newham
PP, Bundell KR and Roberts RA: A dominant negative form of IKK2
prevents suppression of apoptosis by the peroxisome proliferator
nafenopin. Carcinogenesis. 21:1757–1760. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tomasoni S, Aiello S, Cassis L, Noris M,
Longaretti L, Cavinato RA, Azzollini N, Pezzotta A, Remuzzi G and
Benigni A: Dendritic cells genetically engineered with adenoviral
vector encoding dnIKK2 induce the formation of potent
CD4+ T-regulatory cells. Transplantation. 79:1056–1061.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ouyang J, Fan C, Wen D, Hou J, Du Y, Wang
Y and Shi G: Donor antigen loaded IKK2dn gene-modified dendritic
cells prolong allograft survival. Scand J Immunol. 71:336–344.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aiello S, Cassis P, Cassis L, Tomasoni S,
Benigni A, Pezzotta A, Cavinato RA, Cuqini D, Azzollini N, Mister
M, et al: DnIKK2-transfected dendritic cells induce a novel
population of inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing
CD4+CD25− cells with tolerogenic properties.
Transplantation. 83:474–484. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fan CB, Zhang DX, Wen DG, Hou JQ, Ouyang J
and Du KL: Screening and function identifying of
CD4+CD25− T cells induced by immature
dendritic cells transfected with IKK2dn. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 29:1076–1079. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Du KL, Fan CB, Wen DG, Hou JQ, Ouyang J
and Zhang DX: Dominant negative form of IκB kinases 2-transfected
recipient immature dendritic cells induce
CD4+CD25− T cells with tolerogenic
properties. Zhonghua Shi Yan Wai Ke Za Zhi. 29:2439–2441. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Schumacher M, Van Vliet BN and Ferrari P:
Kidney transplantation in rats: an appraisal of surgical techniques
and outcome. Microsurgery. 23:387–394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wood KJ and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in transplantation tolerance. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:199–210.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yates SF, Paterson AM, Nolan KF, Cobbold
SP, Saunders NJ, Waldmann H and Fairchild PJ: Induction of
regulatory T cells and dominant tolerance by dendritic cells
incapable of full activation. J Immunol. 179:967–976. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamazaki S, Inaba K, Tarbell KV and
Steinman RM: Dendritic cells expand antigen-specific
Foxp3+ CD25+CD4+ regulatory T
cells including suppressors of alloreactivity. Immunol Rev.
212:314–329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang H, Cheng EY, Sharma VK, Lagman M,
Chang C, Song P, Ding R, Muthukumar T and Suthanthiran M: Dendritic
cells with TGF-β1 and Il-2 differentiate naive CD4+ T
cells into alloantigen-specific and allograft protective
Foxp3+ regulatory T Cells. Transplantation. 93:580–588.
2012.
|
|
21
|
Brennan TV, Tang Q, Liu FC, Hoang V, Bi M,
Bluestone JA and Kang SM: Requirements for prolongation of
allograft survival with regulatory T cell infusion in
lymphosufficient hosts. J Surg Res. 169:e69–e75. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Di Ianni M, Falzetti F, Carotti A, Terenzi
A, Castellino F, Bonifacio E, Del Papa B, Zei T, Ostini RI,
Cecchini D, et al: Tregs prevent GVHD and promote immune
reconstitution in HLA-haploidentical transplantation. Blood.
117:3921–3928. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sagoo P, Ali N, Garg G, Nestle FO, Lechler
RI and Lombardi G: Human regulatory T cells with alloantigen
specificity are more potent inhibitors of alloimmune skin graft
damage than polyclonal regulatory T cells. Sci Transl Med.
3:83ra422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wakkach A, Fournier N, Brun V, Breittmayer
JP, Cottrez F and Groux H: Characterization of dendritic cells that
induce tolerance and T regulatory 1 cell differentiation in vivo.
Immunity. 18:605–617. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fahlén L, Read S, Gorelik L, Hurst SD,
Coffman RL, Flavell RA and Powrie F: T cells that cannot respond to
TGF-beta escape control by CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells. J Exp
Med. 201:737–746. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marie JC, Letterio JJ, Gavin M and
Rudensky AY: TGF-beta1 maintains suppressor function and Foxp3
expression in CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J
Exp Med. 201:1061–1067. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kearley J, Barker JE, Robinson DS and
Lloyd CM: Resolution of airway inflammation and hyperreactivity
after in vivo transfer of CD4+ D25+
regulatory T cells is interleukin 10 dependent. J Exp Med.
202:1539–1547. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Darrah PA, Hegde ST, Patel DT, Lindsay RW,
Chen L, Roederer M and Seder RA: Il-10 production differentially
influences the magnitude, quality, and protective capacity of Th1
responses depending on the vaccine platform. J Exp Med.
207:1421–1433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao Q, Wang Y, Zheng D, Sun Y, Wang Y, Lee
VW, Zheng G, Tan TK, Ince J, Alexander SI and Harris DC:
Il-10/TGF-beta-modified macrophages induce regulatory T cells and
protect against adriamycin nephrosis. J AM Soc Nephrol. 21:933–942.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang S, Golshayan D, Tsang J, Lombardi G
and Lechler RI: In vitro expanded alloantigen-specific
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell treatment for the
induction of donor-specific transplantation tolerance. Int
Immunopharmacol. 6:1879–1882. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Velásquez-Lopera MM, Eaton VL, Lerret NM,
Correa LA, Decresce RP, García LF and Jaramillo A: Induction of
transplantation tolerance by allogeneic donor-derived
CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Transpl Immunol.
19:127–135. 2008.
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Wang YL, Liu YW, Li Q, Yuan YH,
Niu WY, Sun LY, Zhu ZJ, Shen ZY and Han RF: Change of peripheral
blood mononuclear cells IFN-gamma, Il-10, and TGF-beta1 mRNA
expression levels with active human cytomegalovirus infection in
orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 41:1767–1769.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tomasoni S, Azzollini N, Casiraghi F,
Capogrossi MC, Remuzzi G and Benigni A: CTLA4Ig gene transfer
prolongs survival and induces donor-specific tolerance in a rat
renal allograft. J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:747–752. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kurlberg G, Haglind E, Schön K, Törnqvist
H and Lycke N: Blockade of the B7-CD28 pathway by CTLA4-Ig
counteracts rejection and prolongs survival in small bowel
transplantation. Scand J Immunol. 51:224–230. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|