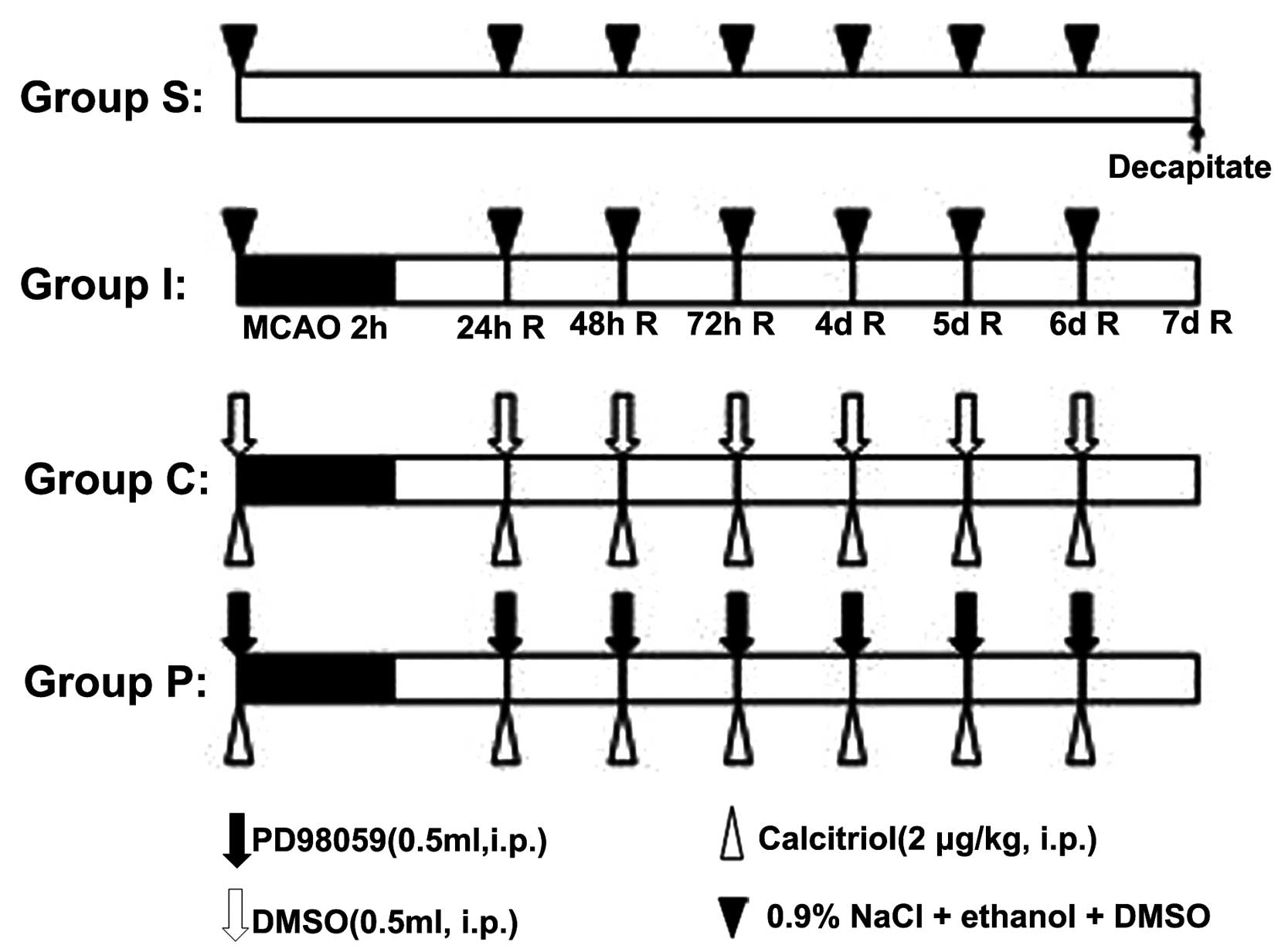
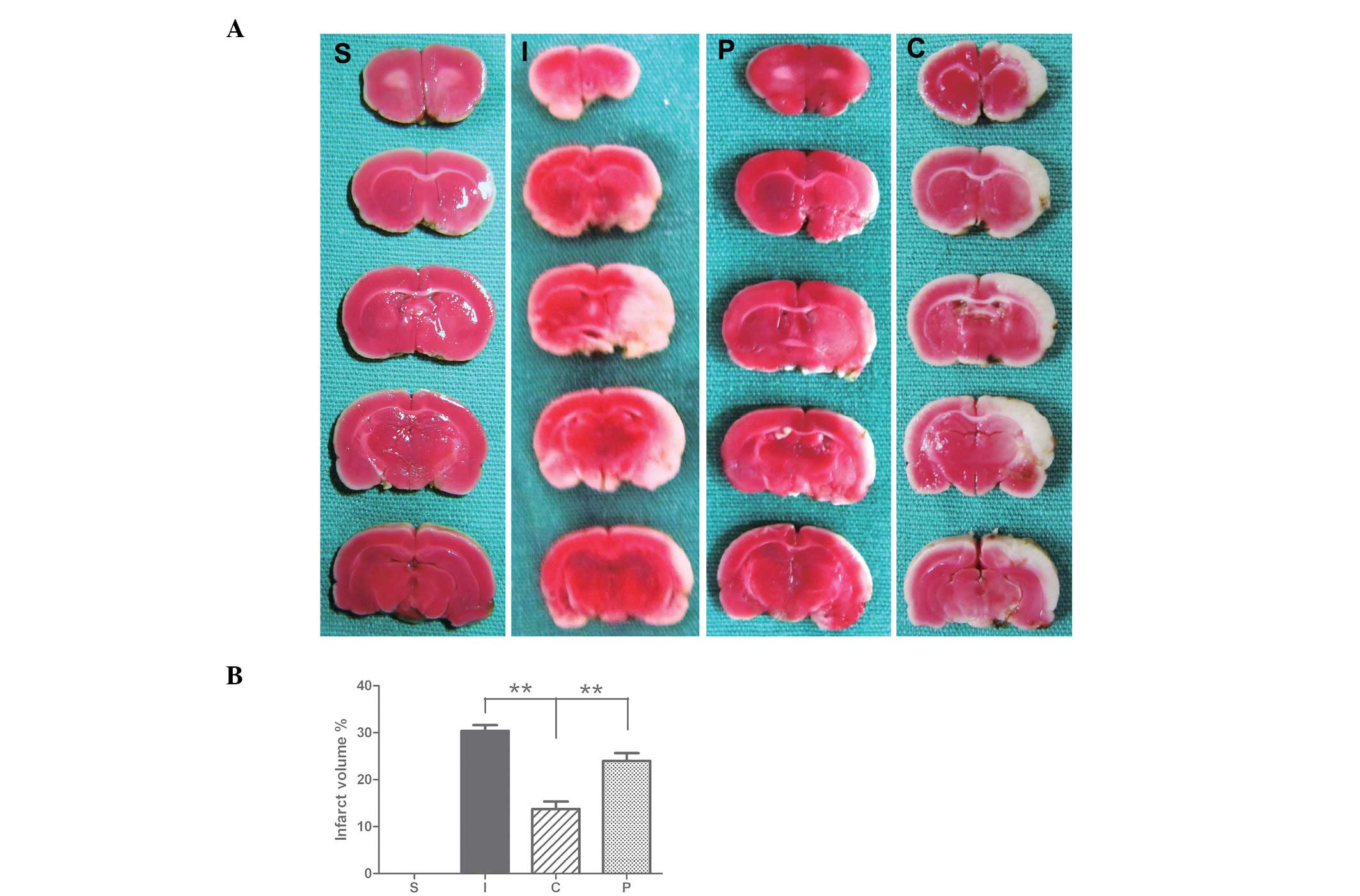
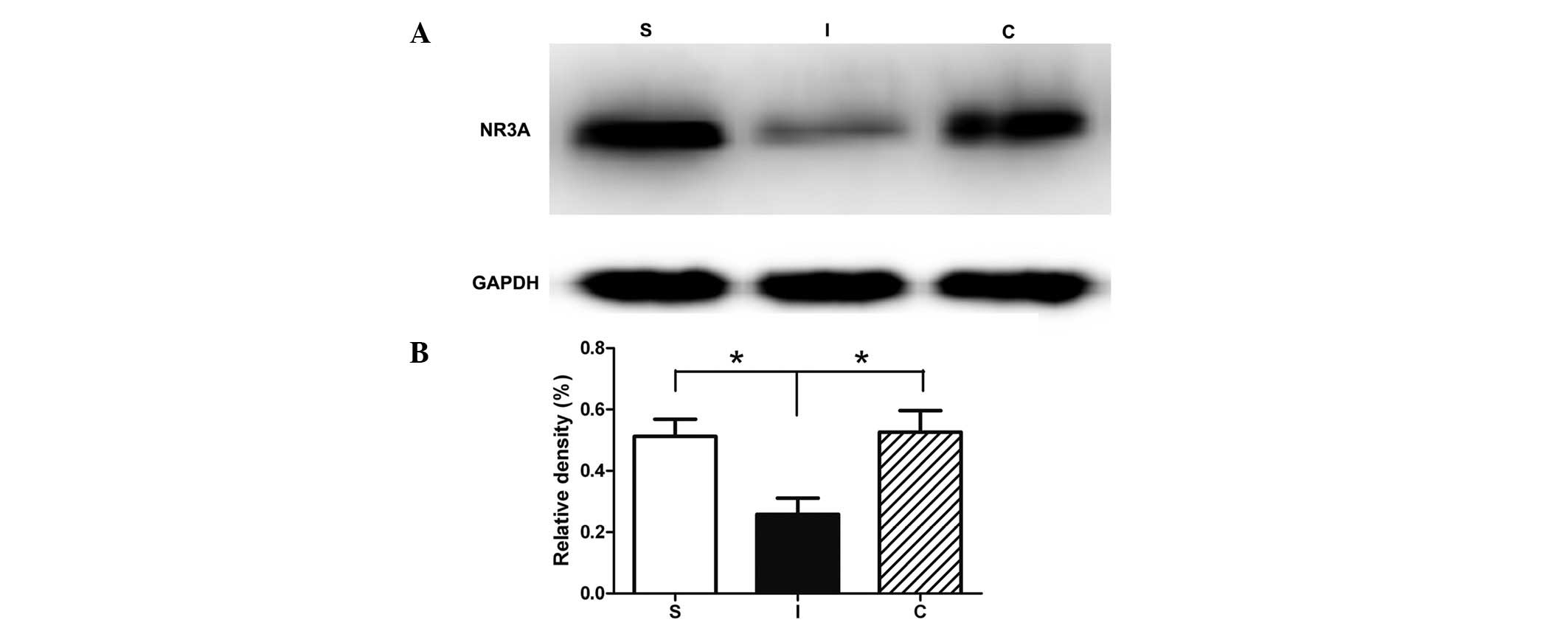
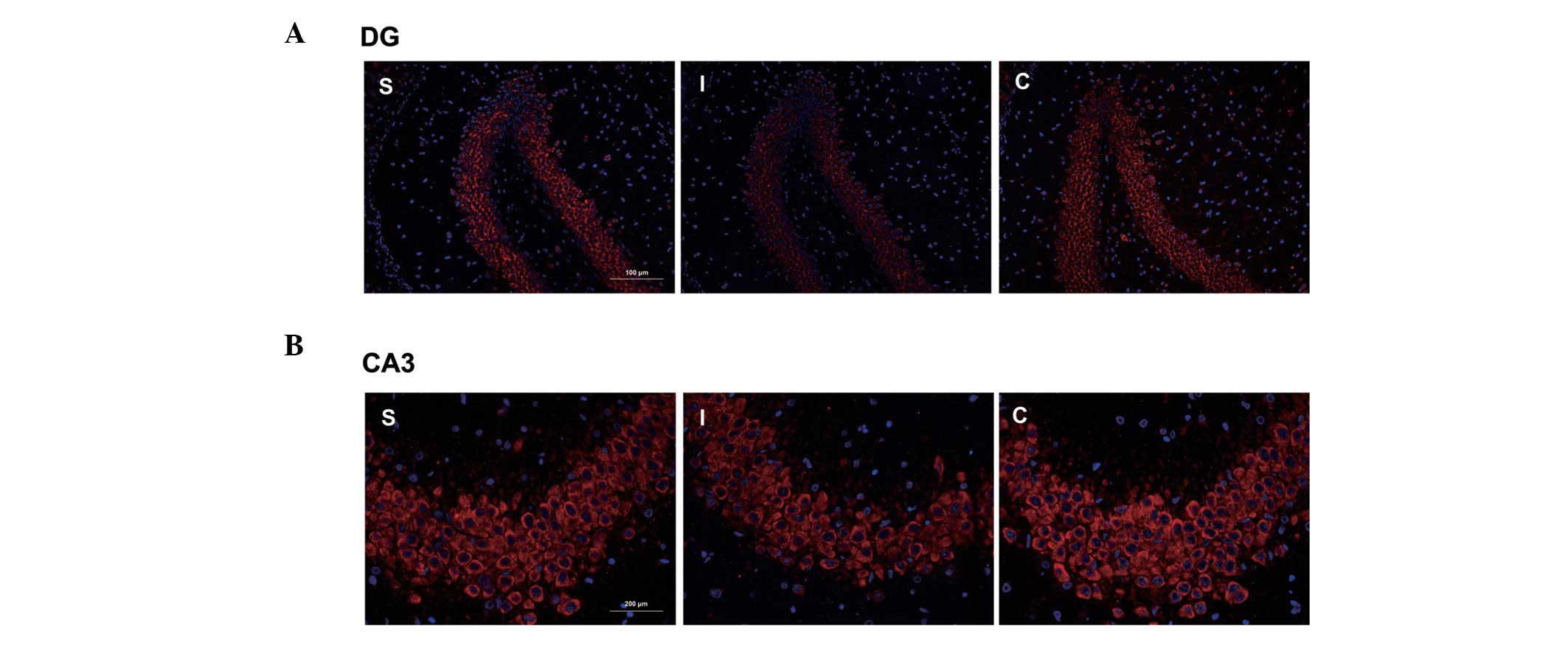
|
1
|
Feigin VL: Stroke epidemiology in the
developing world. Lancet. 365:2160–2161. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fisher M, Feuerstein G, Howells DW, et al:
Update of the stroke therapy academic industry roundtable
preclinical recommendations. Stroke. 40:2244–2250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grotta JC, Burgin WS, El-Mitwalli A, et
al: Intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy for
ischemic stroke: Houston experience 1996 to 2000. Arch Neurol.
58:2009–2013. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McBain CJ and Mayer ML:
N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor structure and function. Physiol
Rev. 74:723–760. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dingledine R, Borges K, Bowie D and
Traynelis SF: The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol Rev.
51:7–61. 1999.
|
|
6
|
Sucher NJ, Akbarian S, Chi CL, et al:
Developmental and regional expression pattern of a novel NMDA
receptor-like subunit (NMDAR-L) in the rodent brain. J Neurosci.
15:6509–6520. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chatterton JE, Awobuluyi M, Premkumar LS,
et al: Excitatory glycine receptors containing the NR3 family of
NMDA receptor subunits. Nature. 415:793–798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Das S, Sasaki YF, Rothe T, et al:
Increased NMDA current and spine density in mice lacking the NMDA
receptor subunit NR3A. Nature. 393:377–381. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Perez-Otano I, Schulteis CT, Contractor A,
et al: Assembly with the NR1 subunit is required for surface
expression of NR3A-containing NMDA receptors. J Neurosci.
21:1228–1237. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sasaki YF, Rothe T, Premkumar LS, et al:
Characterization and comparison of the NR3A subunit of the NMDA
receptor in recombinant systems and primary cortical neurons. J
Neurophysiol. 87:2052–2063. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ciabarra AM, Sullivan JM, Gahn LG, Pecht
G, Heinemann S and Sevarino KA: Cloning and characterization of
chi-1: a developmentally regulated member of a novel class of the
ionotropic glutamate receptor family. J Neurosci. 15:6498–6508.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
DeLuca HF and Zierold C: Mechanisms and
functions of vitamin D. Nutr Rev. 56:S4–S10, (discussion S54–S75).
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brown AJ, Dusso A and Slatopolsky E:
Vitamin D. Am J Physiol. 277:F157–F175. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Landfield PW and Cadwallader-Neal L:
Long-term treatment with calcitriol (1,25(OH)2 vit D3) retards a
biomarker of hippocampal aging in rats. Neurobiol Aging.
19:469–477. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Chiang YH, Su TP, et al: Vitamin
D(3) attenuates cortical infarction induced by middle cerebral
arterial ligation in rats. Neuropharmacology. 39:873–880. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brewer LD, Thibault V, Chen KC, Langub MC,
Landfield PW and Porter NM: Vitamin D hormone confers
neuroprotection in parallel with downregulation of L-type calcium
channel expression in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 21:98–108.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kostandy BB: The role of glutamate in
neuronal ischemic injury: the role of spark in fire. Neurol Sci.
33:223–237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Szydlowska K and Tymianski M: Calcium,
ischemia and excitotoxicity. Cell Calcium. 47:122–129. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Henson MA, Roberts AC, Pérez-Otaño I and
Philpot BD: Influence of the NR3A subunit on NMDA receptor
functions. Prog Neurobiol. 91:23–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shen H, Chen GJ, Harvey BK, Bickford PC
and Wang Y: Inosine reduces ischemic brain injury in rats. Stroke.
36:654–659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shen H, Kuo CC, Chou J, et al: Astaxanthin
reduces ischemic brain injury in adult rats. FASEB J. 23:1958–1968.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y and Bading H:
Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB
shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci. 5:405–414.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoyte L, Barber PA, Buchan AM and Hill MD:
The rise and fall of NMDA antagonists for ischemic stroke. Curr Mol
Med. 4:131–136. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Wong TP, Aarts M, et al: NMDA
receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic
neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 27:2846–2857.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terasaki Y, Sasaki T, Yagita Y, et al:
Activation of NR2A receptors induces ischemic tolerance through
CREB signaling. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1441–1449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cavara NA and Hollmann M: Shuffling the
deck anew: how NR3 tweaks NMDA receptor function. Mol Neurobiol.
38:16–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stys PK and Lipton SA: White matter NMDA
receptors: an unexpected new therapeutic target? Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 28:561–566. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Piña-Crespo JC, Talantova M, Micu I, et
al: Excitatory glycine responses of CNS myelin mediated by NR1/NR3
‘NMDA’ receptor subunits. J Neurosci. 30:11501–11505.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chatterton JE, Awobuluyi M, Premkumar LS,
et al: Excitatory glycine receptors containing the NR3 family of
NMDA receptor subunits. Nature. 415:793–798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fukumori R, Takarada T, Nakamichi N, et
al: Requirement of both NR3A and NR3B subunits for dominant
negative properties on Ca2+ mobilization mediated by
acquired N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels into mitochondria.
Neurochem Int. 57:730–737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakanishi N, Tu S, Shin Y, et al:
Neuroprotection by the NR3A subunit of the NMDA receptor. J
Neurosci. 29:5260–5265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu DY, Lau L, Liu SH, Wei JS and Lu YM:
Activation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) after
focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult
dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9453–9457. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Walton MR and Dragunow I: Is CREB a key to
neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 23:48–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Finkbeiner S: CREB couples neurotrophin
signals to survival messages. Neuron. 25:11–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|