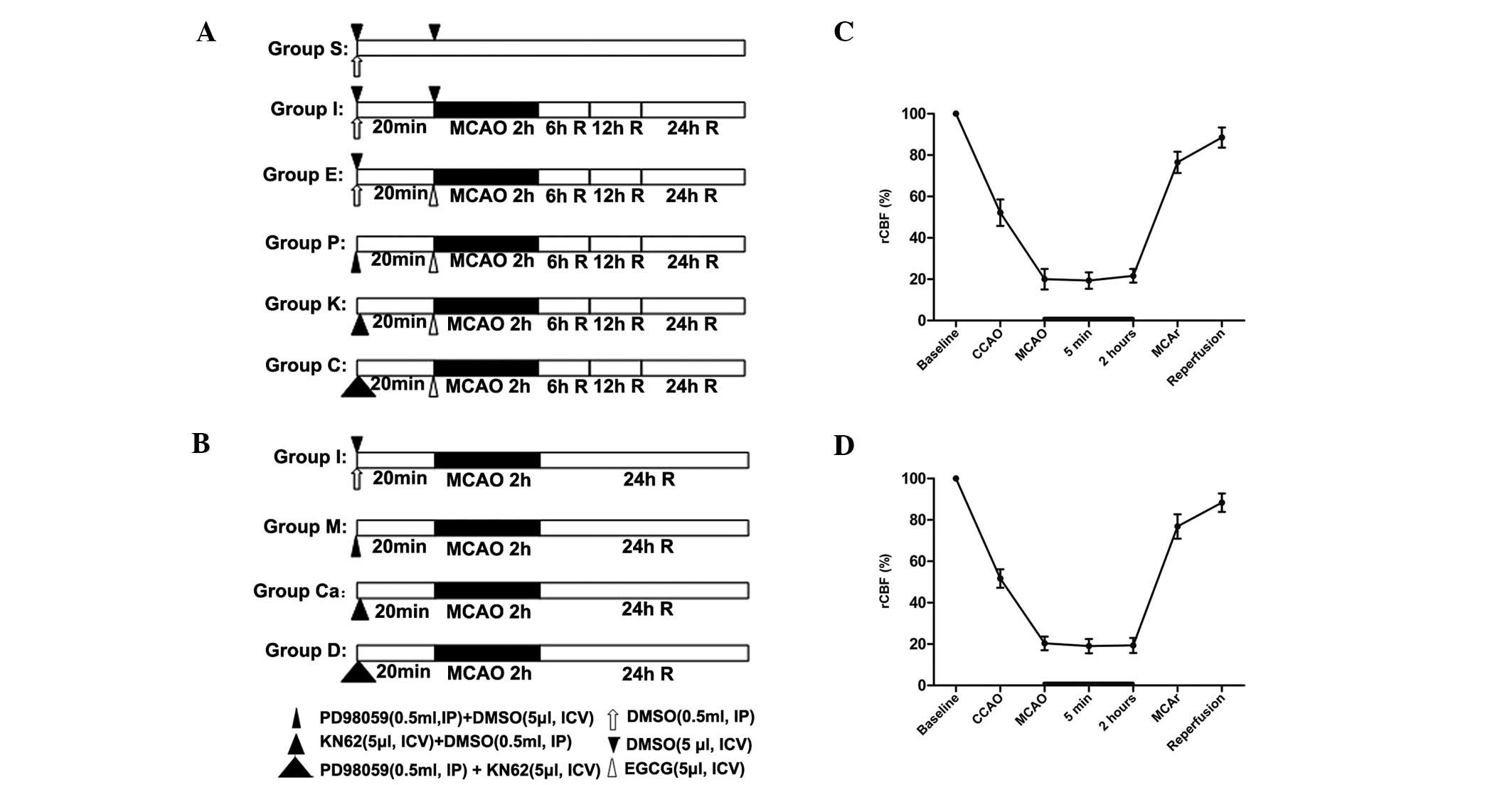
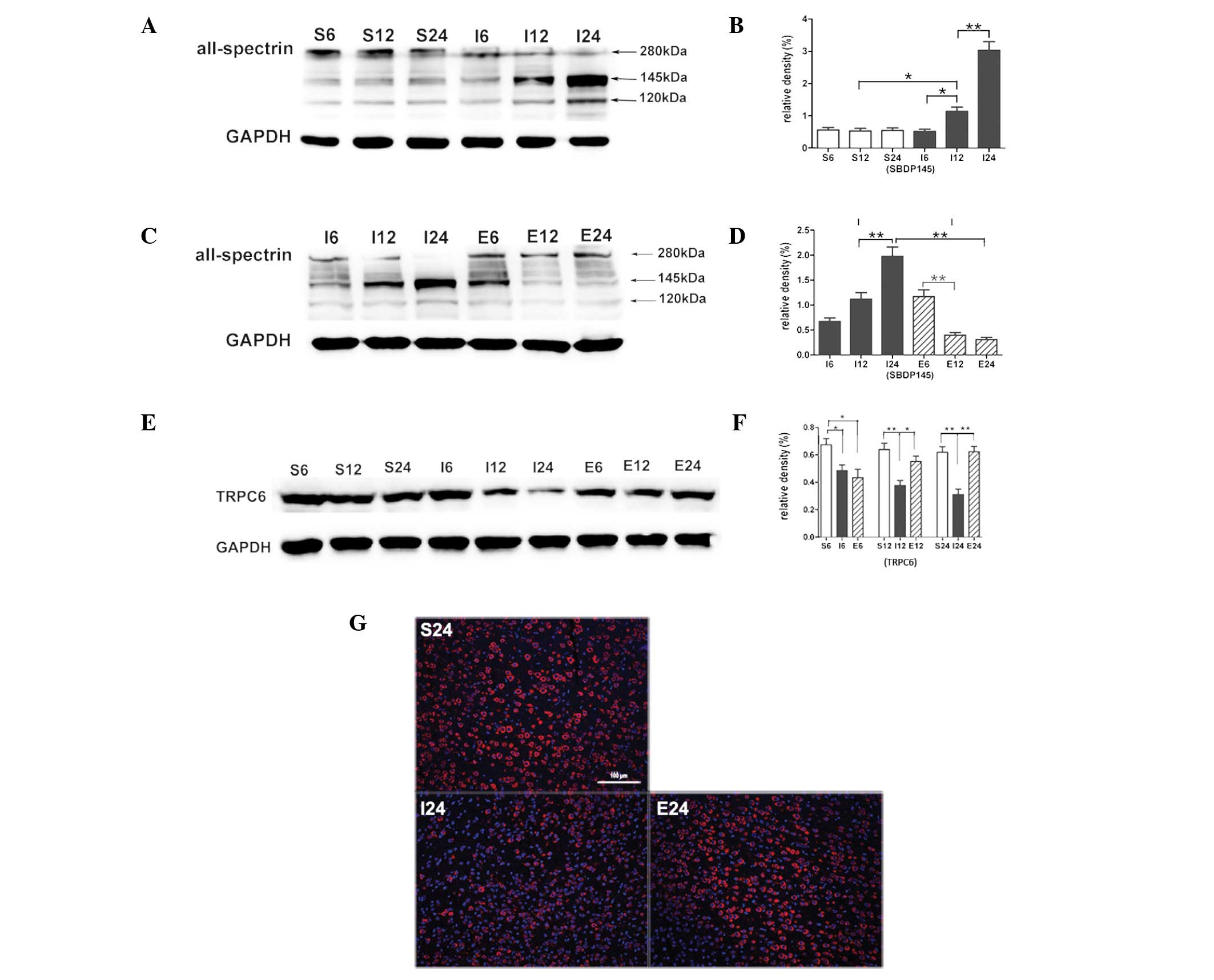
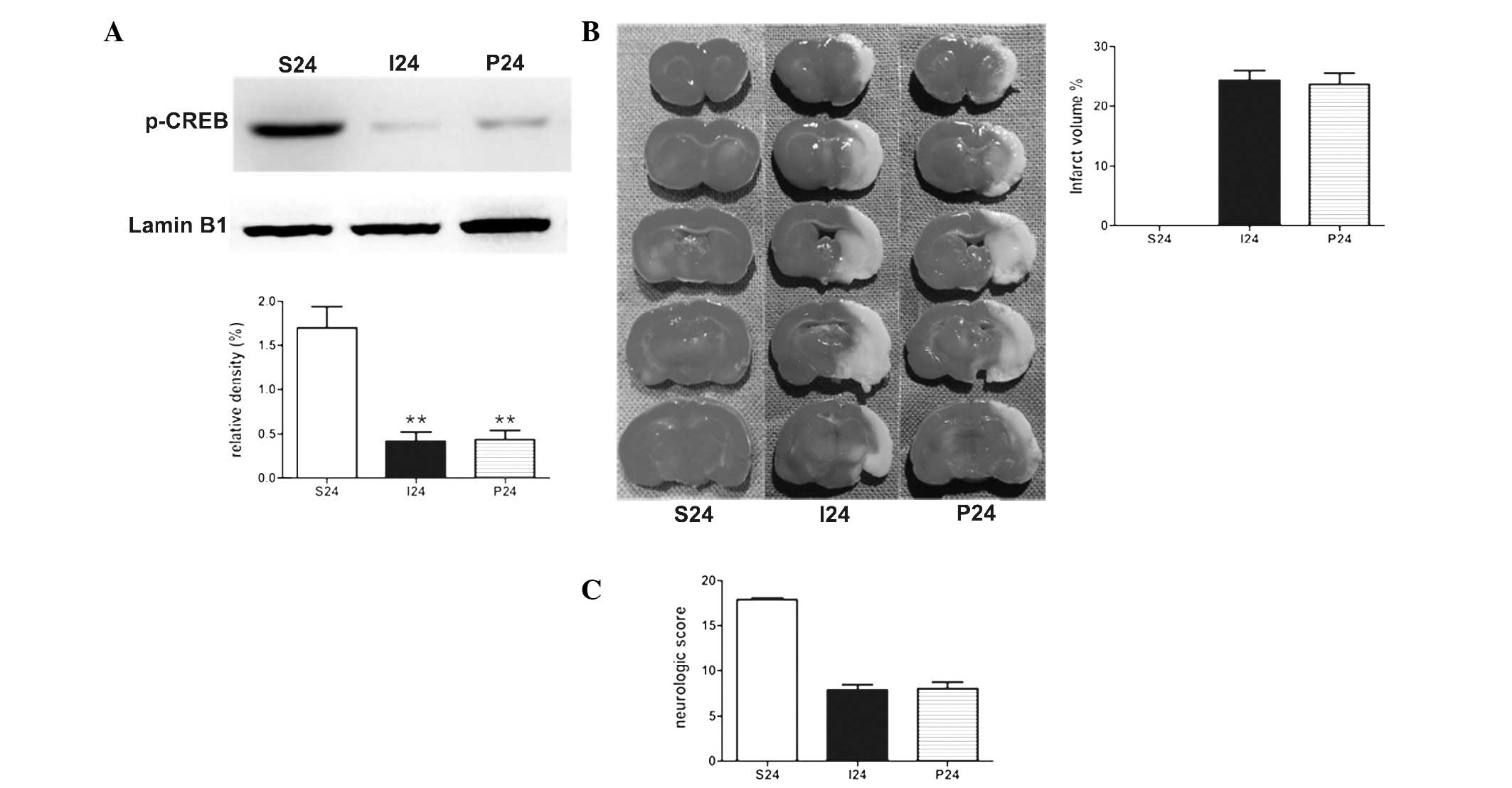
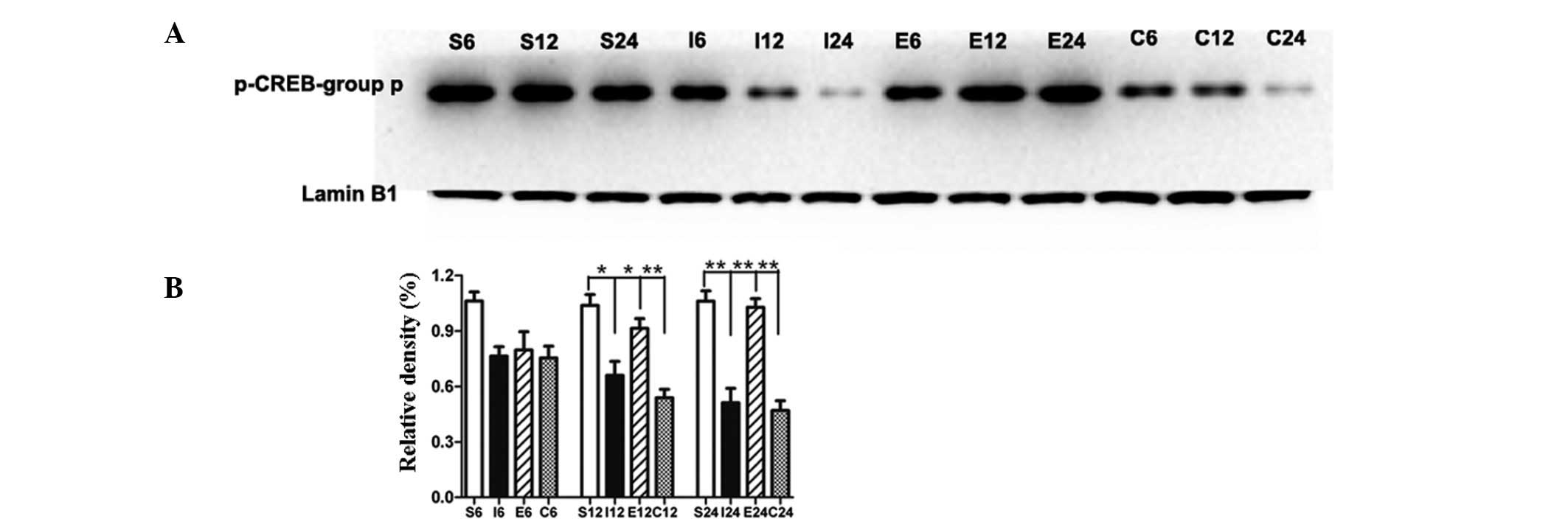
|
1
|
Kaufman RJ: Stress signaling from the
lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene
transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev.
13:1211–1233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang B, Rusciano D and Osborne NN: Orally
administered epigallocatechin gallate attenuates retinal neuronal
death in vivo and light-induced apoptosis in vitro. Brain Res.
1198:141–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vivien D, Gauberti M, Montagne A, Defer G
and Touzé E: Impact of tissue plasminogen activator on the
neurovascular unit: from clinical data to experimental evidence. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 31:2119–2134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Martinou JC, Dubois-Dauphin M, Staple JK,
et al: Overexpression of BCL-2 in transgenic mice protects neurons
from naturally occurring cell death and experimental ischemia.
Neuron. 13:1017–1030. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Montell C, Birnbaumer L and Flockerzi V:
The TRP channels, a remarkably functional family. Cell.
108:595–598. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harteneck C, Plant TD and Schultz G: From
worm to man: three subfamilies of TRP channels. Trends Neurosci.
23:159–166. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Du W, Huang J, Yao H, Zhou K, Duan B and
Wang Y: Inhibition of TRPC6 degradation suppresses ischemic brain
damage in rats. J Clin Invest. 120:3480–3492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jia Y, Zhou J, Tai Y and Wang Y: TRPC
channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nat Neurosci.
10:559–567. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Graham HN: Green tea composition,
consumption, and polyphenol chemistry. Prev Med. 21:334–350. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie W, Ramakrishna N, Wieraszko A and
Hwang YW: Promotion of neuronal plasticity by
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Neurochem Res. 33:776–783.
2008.
|
|
11
|
Haque AM, Hashimoto M, Katakura M, Tanabe
Y, Hara Y and Shido O: Long-term administration of green tea
catechins improves spatial cognition learning ability in rats. J
Nutr. 136:1043–1047. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van Praag H, Lucero MJ, Yeo GW, et al:
Plant-derived flavanol (−)epicatechin enhances angiogenesis and
retention of spatial memory in mice. J Neurosci. 27:5869–5878.
2007.
|
|
13
|
Nagai K, Jiang MH, Hada J, et al:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate protects against NO stress-induced
neuronal damage after ischemia by acting as an anti-oxidant. Brain
Res. 956:319–322. 2002.
|
|
14
|
Sutherland BA, Shaw OM, Clarkson AN,
Jackson DN, Sammut IA and Appleton I: Neuroprotective effects of
(−)-epigallocatechin gallate following hypoxia-ischemia-induced
brain damage: novel mechanisms of action. FASEB J. 19:258–260.
2005.
|
|
15
|
Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF and Hu XJ:
Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable
to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical
validation. Stroke. 26:627–635. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tsubokawa T, Jadhav V, Solaroglu I,
Shiokawa Y, Konishi Y and Zhang JH: Lecithinized superoxide
dismutase improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic
injury via antiapoptotic mechanisms in rats. Stroke. 38:1057–1062.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arab L, Liu W and Elashoff D: Green and
black tea consumption and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis. Stroke.
40:1786–1792. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang N, Komine-Kobayashi M, Tanaka R, Liu
M, Mizuno Y and Urabe T: Edaravone reduces early accumulation of
oxidative products and sequential inflammatory responses after
transient focal ischemia in mice brain. Stroke. 36:2220–2225. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W and Cong
J: The calpain system. Physiol Rev. 83:731–801. 2003.
|
|
20
|
Nath R, Raser KJ, Stafford D, et al:
Non-erythroid alpha-spectrin breakdown by calpain and interleukin 1
beta-converting-enzyme-like protease(s) in apoptotic cells:
contributory roles of both protease families in neuronal apoptosis.
Biochem J. 319:683–690. 1996.
|
|
21
|
Wang KK: Calpain and caspase: can you tell
the difference?, by kevin KW Wang Vol 23, pp 20–26. Trends
Neurosci. 23:592000.
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Jia YC, Cui K, et al: Essential role
of TRPC channels in the guidance of nerve growth cones by
brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 434:894–898. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walton MR and Dragunow I: Is CREB a key to
neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci. 23:48–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Finkbeiner S: CREB couples neurotrophin
signals to survival messages. Neuron. 25:11–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN and Korsmeyer SJ: BH1
and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis
and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 369:321–323. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He B: Viruses, endoplasmic reticulum
stress, and interferon responses. Cell Death Differ. 13:393–403.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ginsberg MD: Neuroprotection for ischemic
stroke: past, present and future. Neuropharmacology. 55:363–389.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Love S: Apoptosis and brain ischaemia.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 27:267–282. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yoshida H, Matsui T, Yamamoto A, Okada T
and Mori K: XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in
response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription
factor. Cell. 107:881–891. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Groenendyk J, Sreenivasaiah PK, Kim do H,
Agellon LB and Michalak M: Biology of endoplasmic reticulum stress
in the heart. Circ Res. 107:1185–1197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
DeGracia DJ and Montie HL: Cerebral
ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem. 91:1–8.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, et al:
Ischemia-induced neuronal cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic
reticulum stress pathway involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ.
11:403–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu DY, Lau L, Liu SH, Wei JS and Lu YM:
Activation of cAMP-response-element-binding protein (CREB) after
focal cerebral ischemia stimulates neurogenesis in the adult
dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9453–9457. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zinkstok SM, Vergouwen MD, Engelter ST, et
al: Safety and functional outcome of thrombolysis in
dissection-related ischemic stroke: a meta-analysis of individual
patient data. Stroke. 42:2515–2520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paschen W and Mengesdorf T: Cellular
abnormalities linked to endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction in
cerebrovascular disease - therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther.
108:362–375. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|