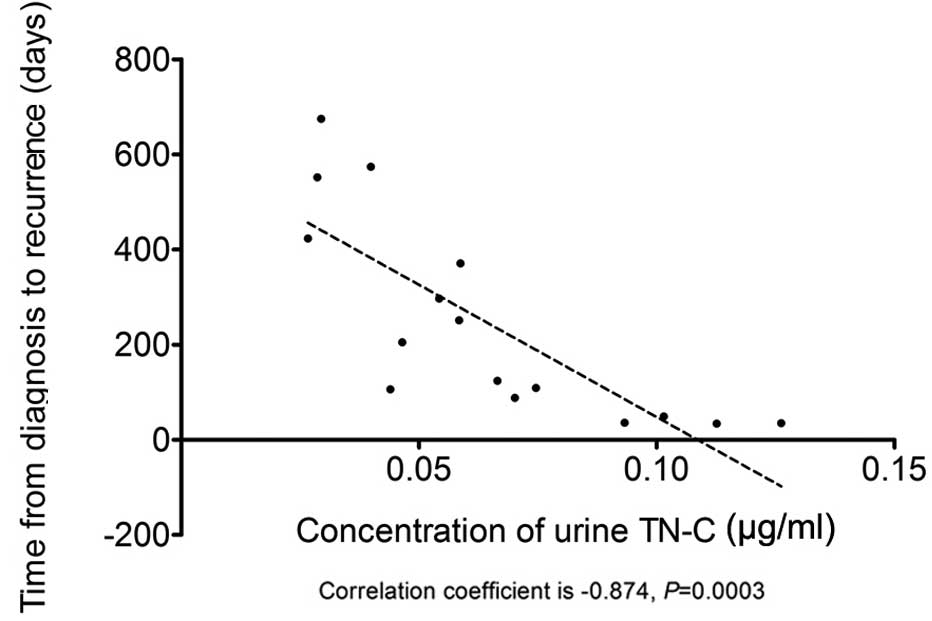
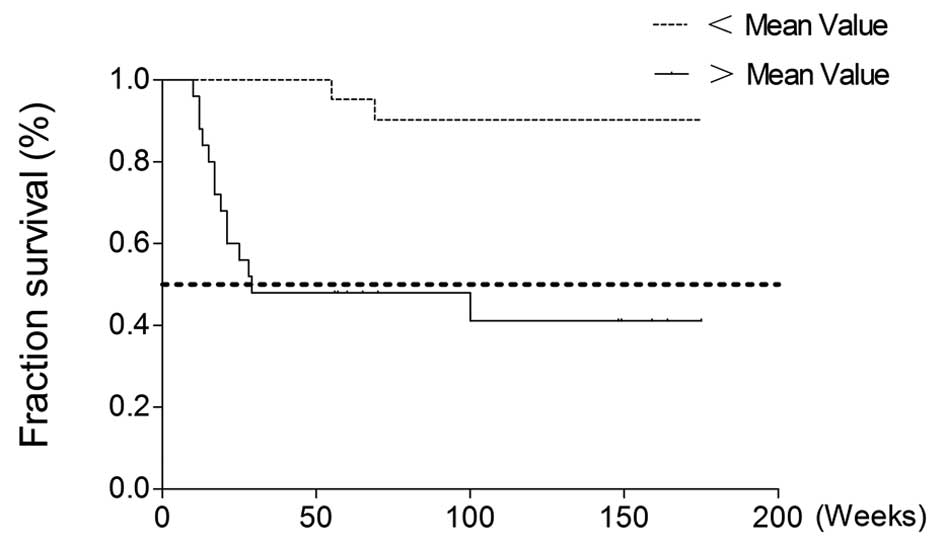
|
1
|
Griffiths TR: Action on Bladder Cancer:
Current perspectives in bladder cancer management. Int J Clin
Pract. 67:435–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al Hussain TO and Akhtar M: Molecular
basis of urinary bladder cancer. Adv Anat Pathol. 20:53–60.
2013.
|
|
4
|
Kausch I and Böhle A: Bladder cancer. II
Molecular aspects and diagnosis. Eur Urol. 39:498–506.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lokeshwar VB, Schroeder GL, Selzer MG, et
al: Bladder tumor markers for monitoring recurrence and screening
comparison of hyaluronic acid-hyaluronidase and BTA-Stat tests.
Cancer. 95:61–72. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orend G and Chiquet-Ehrismann R:
Tenascin-C induced signaling in cancer. Cancer Lett. 244:143–163.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Zhang XH, et al:
Breast cancer cells produce tenascin C as a metastatic niche
component to colonize the lungs. Nat Med. 17:867–874. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Berndt A, Köllner R, Richter P, et al: A
comparative analysis of oncofetal fibronectin and tenascin-C
incorporation in tumour vessels using human recombinant SIP format
antibodies. Histochem Cell Biol. 133:467–475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Brunner A, Mayerl C, Tzankov A, et al:
Prognostic significance of tenascin-C expression in superficial and
invasive bladder cancer. J Clin Pathol. 57:927–931. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ioachim E, Michael M, Stavropoulos NE,
Kitsiou E, Salmas M and Malamou-Mitsi V: A clinicopathological
study of the expression of extracellular matrix components in
urothelial carcinoma. BJU Int. 95:655–659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hancox RA, Allen MD, Holliday DL, et al:
Tumour-associated tenascin-C isoforms promote breast cancer cell
invasion and growth by matrix metalloproteinase-dependent and
independent mechanisms. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R242009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wunderlich H, Berndt A, Anger K, et al: A1
and D domain of tenascin C - New prognostic marker in bladder
cancer. J Urology. 179:3152008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fischer D, Brown-Lüdi M, Schulthess T and
Chiquet-Ehrismann R: Concerted action of tenascin-C domains in cell
adhesion, anti-adhesion and promotion of neurite outgrowth. J Cel
Sci. 110:1513–1522
|
|
14
|
Babjuk M, Oosterlinck W, Sylvester R, et
al: EAU guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of
the bladder. Eur Urol. 54:303–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goodison S, Rosser CJ and Urquidi V:
Bladder cancer detection and monitoring: assessment of urine- and
blood-based marker tests. Mol Diagn Ther. 17:71–84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Rhijn BW, van der Poel HG and van der
Kwast TH: Urine markers for bladder cancer surveillance: a
systematic review. Eur Urol. 47:736–748. 2005.
|
|
17
|
Jeong S, Park Y, Cho Y, Kim YR and Kim HS:
Diagnostic values of urine CYFRA21–1, NMP22, UBC, and FDP for the
detection of bladder cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 414:93–100. 2012.
|
|
18
|
Morgan R, Bryan RT, Javed S, et al:
Expression of Engrailed-2 (EN2) protein in bladder cancer and its
potential utility as a urinary diagnostic biomarker. Eur J Cancer.
Feb 21–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
19
|
Lei T, Zhao X, Jin S, Meng Q, Zhou H and
Zhang M: Discovery of potential bladder cancer biomarkers by
comparative urine proteomics and analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer.
11:56–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vrooman OP and Witjes JA: Urinary markers
in bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 53:909–916. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vargová V, Pytliak M and Mechírová V:
Matrix metalloproteinases. EXS. 103:1–33. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Paron I, Berchtold S, Vörös J, et al:
Tenascin-C enhances pancreatic cancer cell growth and motility and
affects cell adhesion through activation of the integrin pathway.
PLoS One. 6:e216842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xue Y, Li J, Latijnhouwers MA, et al:
Expression of periglandular tenascin-C and basement membrane
laminin in normal prostate, benign prostatic hyperplasia and
prostate carcinoma. Br J Urol. 81:844–851. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katenkamp K, Berndt A, Hindermann W, et
al: mRNA expression and protein distribution of the unspliced
tenascin-C isoform in prostatic adenocarcinoma. J Pathol.
203:771–779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Parekh K, Ramachandran S, Cooper J, Bigner
D, Patterson A and Mohanakumar T: Tenascin-C, over expressed in
lung cancer down regulates effector functions of tumor infiltrating
lymphocytes. Lung Cancer. 47:17–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pauli C, Stieber P, Schmitt UM,
Andratschke M, Hoffmann K and Wollenberg B: The significance of
Tenascin-C serum level as tumor marker in squamous cell carcinoma
of the head and neck. Anticancer Res. 22:3093–3097. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Booth C, Harnden P, Selby PJ and Southgate
J: Towards defining roles and relationships for tenascin-C and
TGFbeta-1 in the normal and neoplastic urinary bladder. J Pathol.
198:359–368. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Berndt A, Anger K, Richter P, et al:
Differential expression of tenascin-C splicing domains in
urothelial carcinomas of the urinary bladder. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 132:537–546. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Richter P, Tost M, Franz M, et al: B and C
domain containing tenascin-C: urinary markers for invasiveness of
urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder? J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 135:1351–1358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|