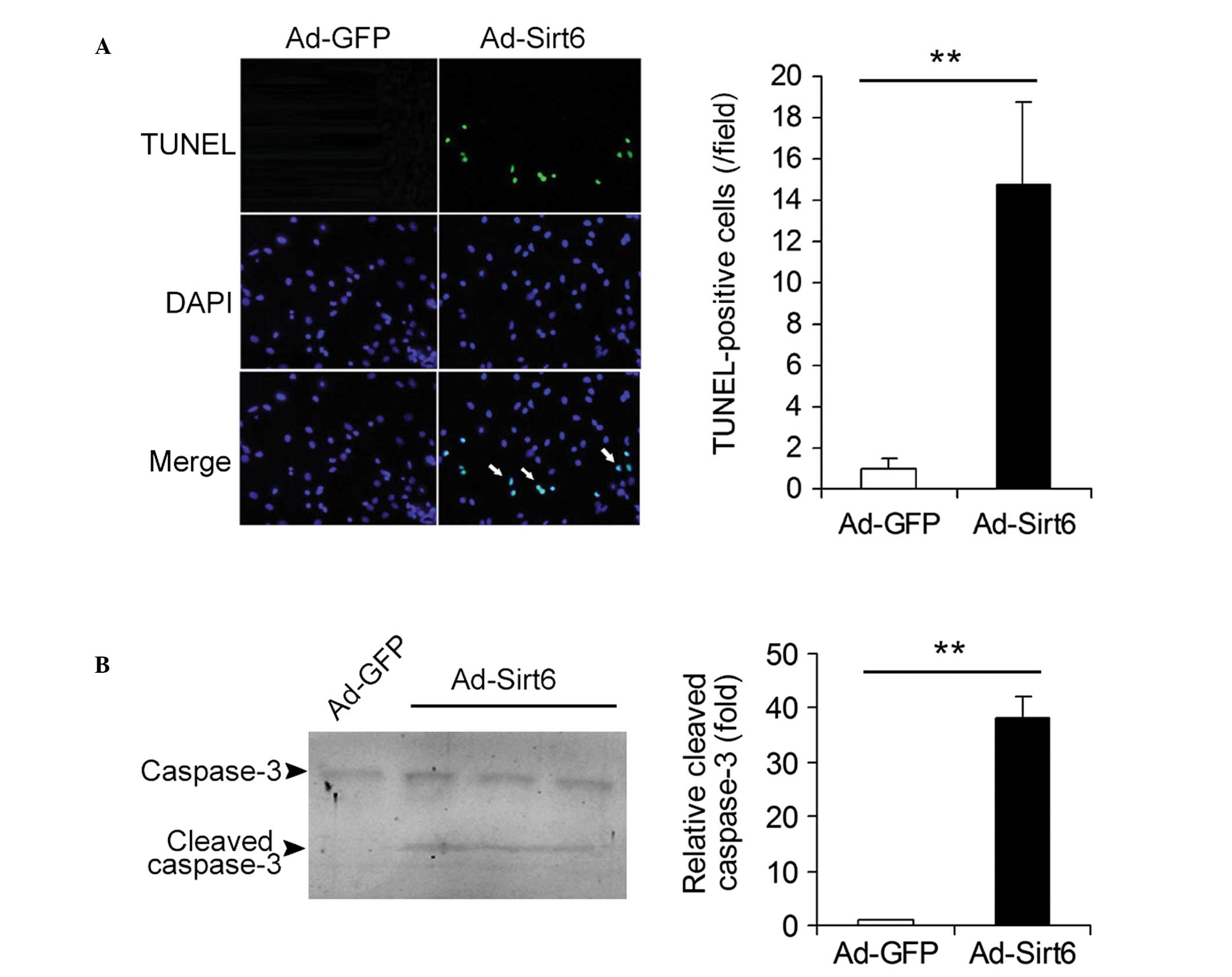
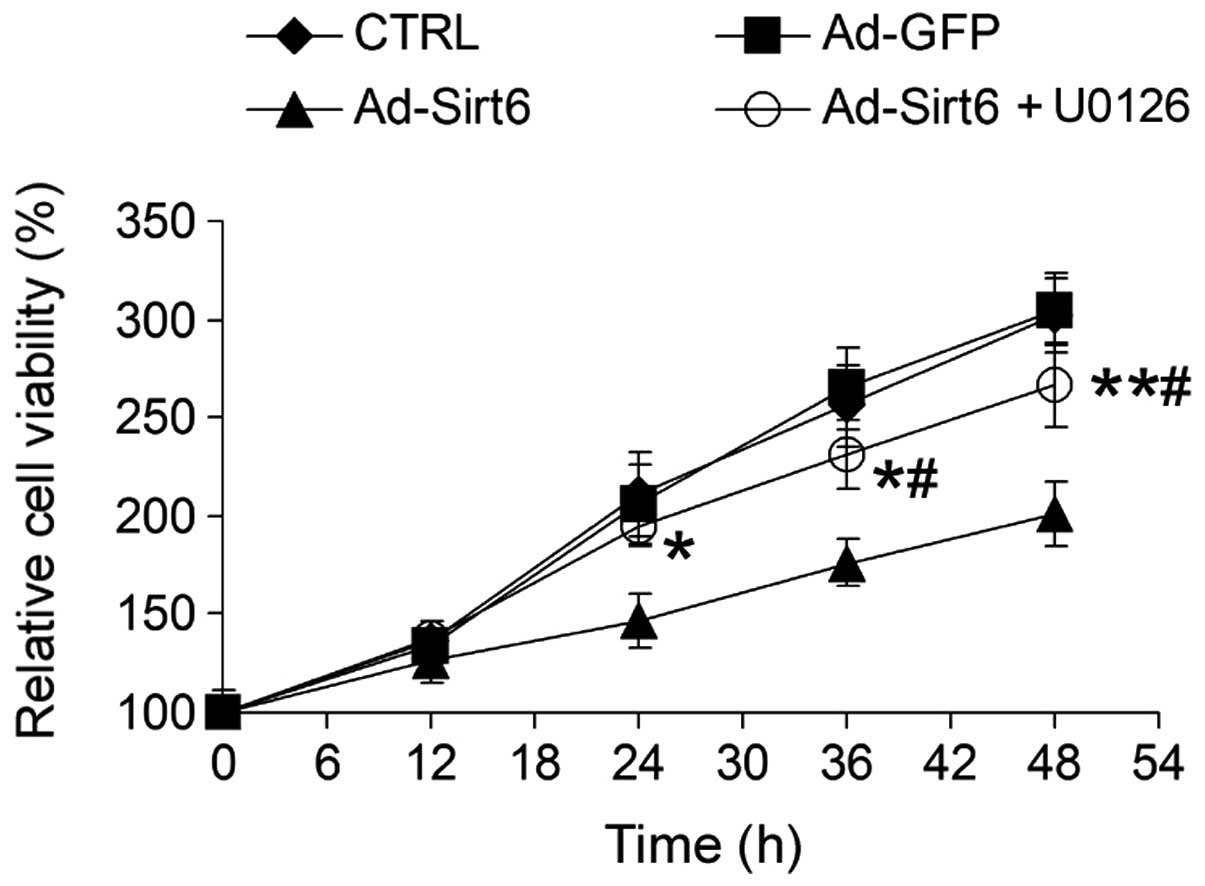
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(5 Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moradpour D, Penin F and Rice CM:
Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nat Rev Microbiol. 5:453–463.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kozyreva ON, Chi D, Clark JW, et al: A
multicenter retrospective study on clinical characteristics,
treatment patterns, and outcome in elderly patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncologist. 16:310–318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Haigis MC and Guarente LP: Mammalian
sirtuins - emerging roles in physiology, aging, and calorie
restriction. Genes Dev. 20:2913–2921. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu T, Liu PY and Marshall GM: The
critical role of the class III histone deacetylase SIRT1 in cancer.
Cancer Res. 69:1702–1705. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alhazzazi TY, Kamarajan P, Verdin E and
Kapila YL: SIRT3 and cancer: tumor promoter or suppressor? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1816:80–88. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hirschey MD, Shimazu T, Goetzman E, et al:
SIRT3 regulates mitochondrial fatty-acid oxidation by reversible
enzyme deacetylation. Nature. 464:121–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Finley LW, Carracedo A, Lee J, et al:
SIRT3 opposes reprogramming of cancer cell metabolism through HIF1α
destabilization. Cancer Cell. 19:416–428. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alhazzazi TY, Kamarajan P, Joo N, et al:
Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3), a novel potential therapeutic target for oral
cancer. Cancer. 117:1670–1678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang YY and Zhou LM: Sirt3 inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth through reducing Mdm2-mediated
p53 degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:26–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhong L, D’Urso A, Toiber D, et al: The
histone deacetylase Sirt6 regulates glucose homeostasis via
Hif1alpha. Cell. 140:280–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mao Z, Hine C, Tian X, et al: SIRT6
promotes DNA repair under stress by activating PARP1. Science.
332:1443–1446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaidi A, Weinert BT, Choudhary C and
Jackson SP: Human SIRT6 promotes DNA end resection through CtIP
deacetylation. Science. 329:1348–1353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Min L, Ji Y, Bakiri L, et al: Liver cancer
initiation is controlled by AP-1 through SIRT6-dependent inhibition
of survivin. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1203–1211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sebastián C, Zwaans BM, Silberman DM, et
al: The histone deacetylase SIRT6 is a tumor suppressor that
controls cancer metabolism. Cell. 151:1185–1199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bauer I, Grozio A, Lasigliè D, et al: The
NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT6 promotes
cytokine production and migration in pancreatic cancer cells by
regulating Ca2+ responses. J Biol Chem. 287:40924–40937.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Khongkow M, Olmos Y, Gong C, et al: SIRT6
modulates paclitaxel and epirubicin resistance and survival in
breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:1476–1486. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Guan YF, Du H, Zhai QW, Su DF and
Miao CY: Induction of autophagy contributes to the neuroprotection
of nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase in cerebral ischemia.
Autophagy. 8:77–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Filippi BM, Yang CS, Tang C and Lam TK:
Insulin activates Erk1/2 signaling in the dorsal vagal complex to
inhibit glucose production. Cell Metab. 16:500–510. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang P, Xu TY, Guan YF, Su DF, Fan GR and
Miao CY: Perivascular adipose tissue-derived visfatin is a vascular
smooth muscle cell growth factor: role of nicotinamide
mononucleotide. Cardiovasc Res. 81:370–380. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nezis IP, Shravage BV, Sagona AP, Johansen
T, Baehrecke EH and Stenmark H: Autophagy as a trigger for cell
death: autophagic degradation of inhibitor of apoptosis dBruce
controls DNA fragmentation during late oogenesis in Drosophila.
Autophagy. 6:1214–1215. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang P, Tian WW, Song J, Guan YF and Miao
CY: Deficiency of NG2+ cells contributes to the
susceptibility of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. CNS
Neurosci Ther. 17:327–332. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Wang P, Xu TY, Guan YF, et al:
Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase protects against ischemic
stroke through SIRT1-dependent adenosine monophosphate-activated
kinase pathway. Ann Neurol. 69:360–374. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang P, Yang FJ, Du H, et al: Involvement
of leptin receptor long isoform (LepRb)-STAT3 signaling pathway in
brain fat mass- and obesity-associated (FTO) downregulation during
energy restriction. Mol Med. 17:523–532. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang P, Zhang RY, Song J, et al: Loss of
AMP-activated protein kinase-α2 impairs the insulin-sensitizing
effect of calorie restriction in skeletal muscle. Diabetes.
61:1051–1061. 2012.
|
|
29
|
Devarajan A, Grijalva VR, Bourquard N, et
al: Macrophage paraoxonase 2 regulates calcium homeostasis and cell
survival under endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions and is
sufficient to prevent the development of aggravated atherosclerosis
in paraoxonase 2 deficiency/apoE−/− mice on a Western diet. Mol
Genet Metab. 107:416–427. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Colas E, Perez C, Cabrera S, et al:
Molecular markers of endometrial carcinoma detected in uterine
aspirates. Int J Cancer. 129:2435–2444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai CC, Lin PM, Lin SF, et al: Altered
expression of SIRT gene family in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:1847–1854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Van Meter M, Mao Z, Gorbunova V and
Seluanov A: SIRT6 overexpression induces massive apoptosis in
cancer cells but not in normal cells. Cell Cycle. 10:3153–3158.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nishimoto S and Nishida E: MAPK
signalling: ERK5 versus ERK1/2. EMBO Rep. 7:782–786. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wiesenauer CA, Yip-Schneider MT, Wang Y
and Schmidt CM: Multiple anticancer effects of blocking MEK-ERK
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 198:410–421.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Xu W, McBurney MW and Longo VD:
SirT1 inhibition reduces IGF-I/IRS-2/Ras/ERK1/2 signaling and
protects neurons. Cell Metab. 8:38–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Luo P, Guo Q, et al: Interactions
between SIRT1 and MAPK/ERK regulate neuronal apoptosis induced by
traumatic brain injury in vitro and in vivo. Exp Neurol.
237:489–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|