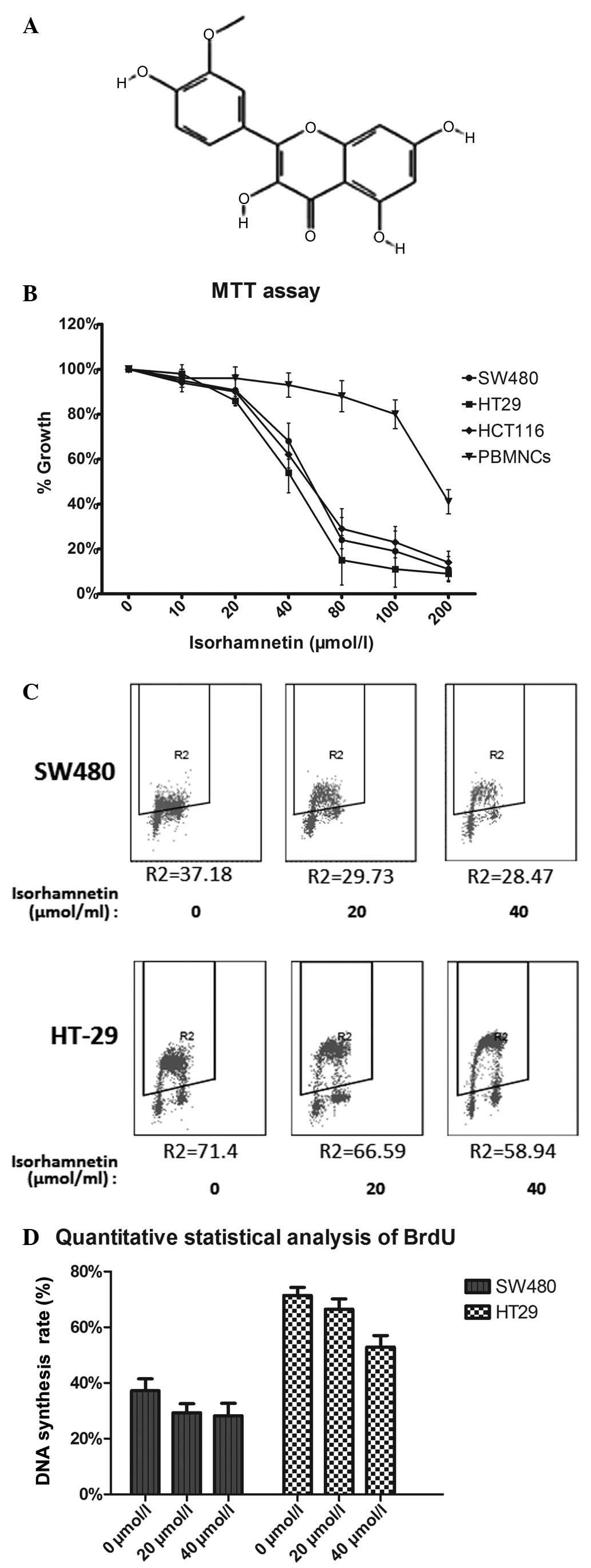
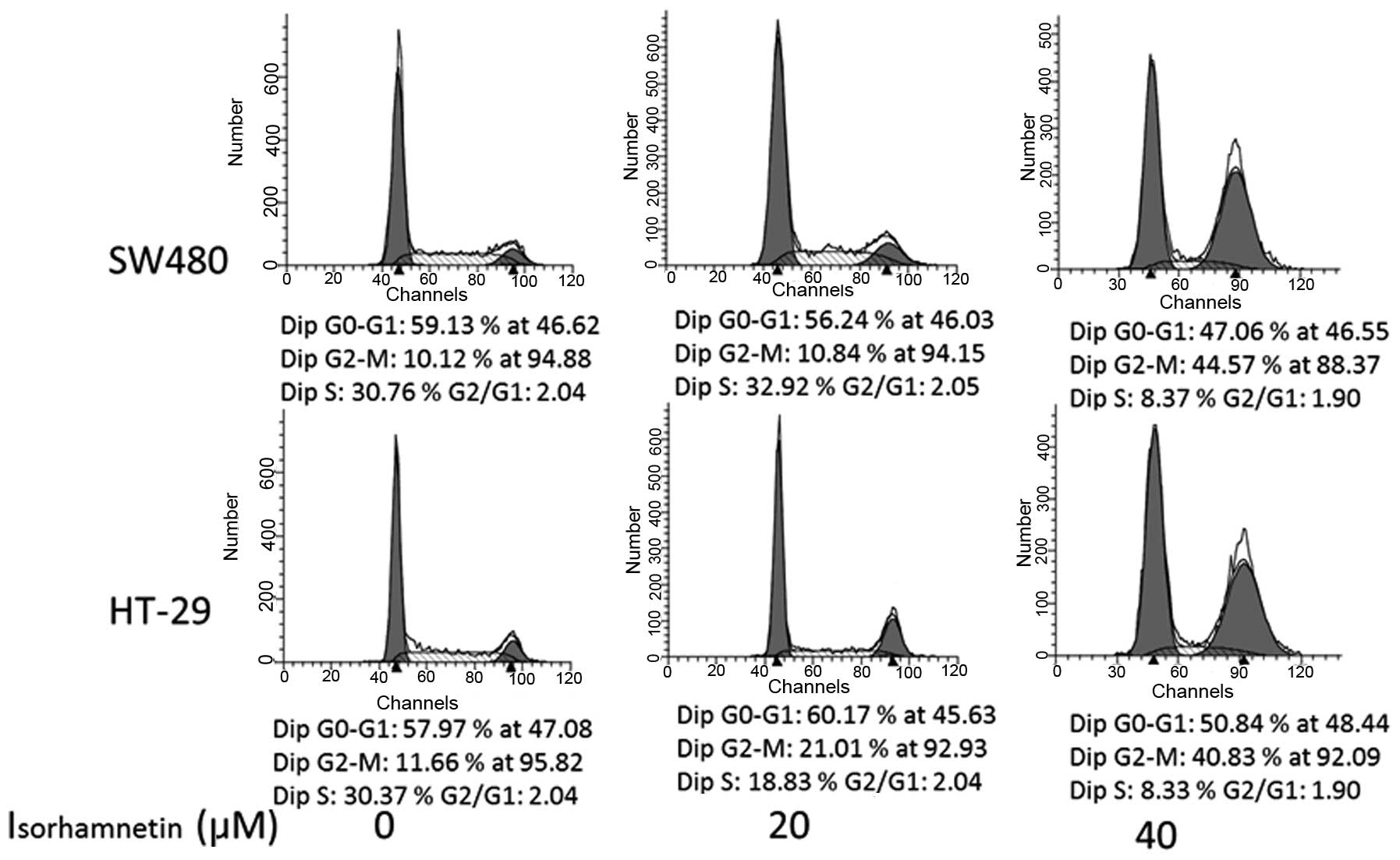
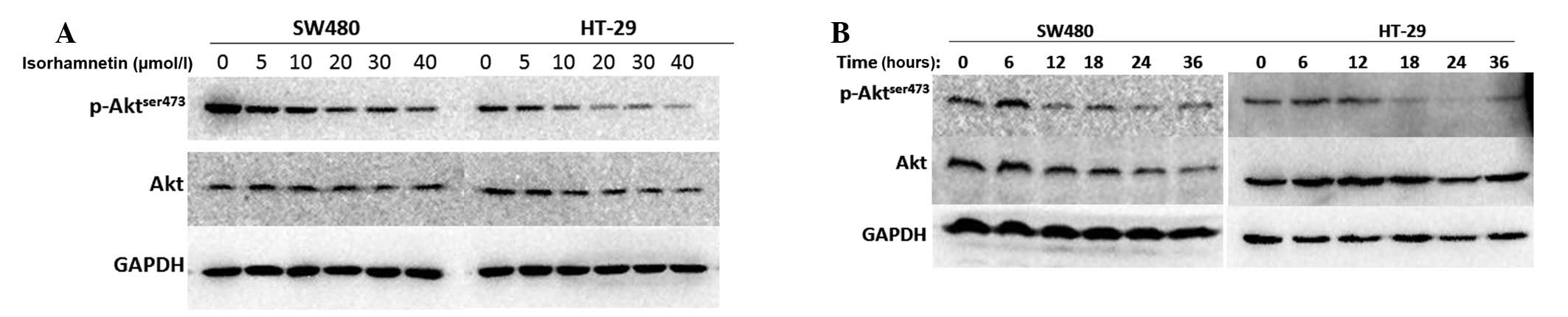
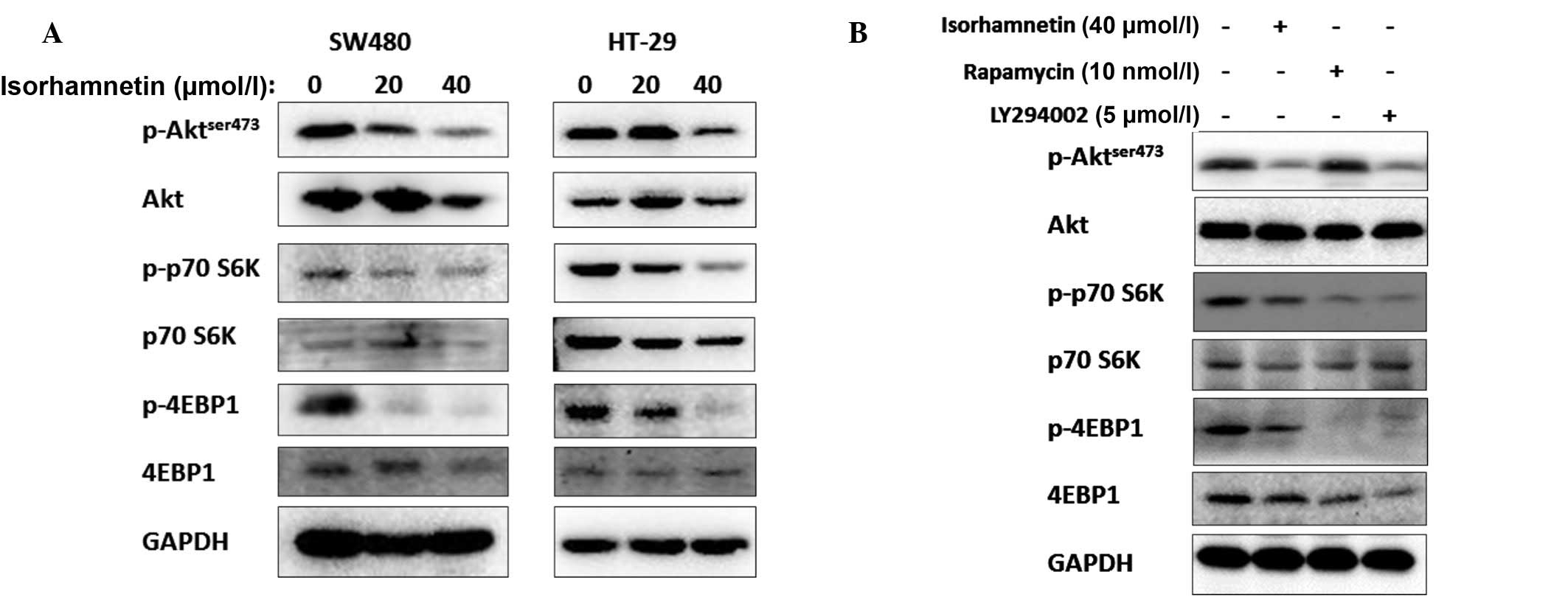
|
1
|
Murtaza I, Adhami VM, Hafeez BB, Saleem M
and Mukhtar H: Fisetin, a natural flavonoid, targets chemoresistant
human pancreatic cancer AsPC-1 cells through DR3-mediated
inhibition of NF-κB. Int J Cancer. 125:2465–2473. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X and Shen HM:
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:634–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Devi VG, Rooban BN, Sasikala V,
Sahasranamam V and Abraham A: Isorhamnetin-3-glucoside alleviates
oxidative stress and opacification in selenite cataract in vitro.
Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1662–1669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee J, Jung E, Kim S, et al: Isorhamnetin
represses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Obesity (Silver Spring).
17:226–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jaramillo S, Lopez S, Varela LM, et al:
The flavonol isorhamnetin exhibits cytotoxic effects on human colon
cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. Oct 5–2010.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
6
|
Kim JE, Lee DE, Lee KW, et al:
Isorhamnetin suppresses skin cancer through direct inhibition of
MEK1 and PI3-K. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 4:582–591. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong CS, Kim YA, Kim MM, et al: Flavonoid
glycosides isolated from Salicornia herbacea inhibit matrix
metalloproteinase in HT1080 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:1742–1748.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ma G, Yang C, Qu Y, Wei H, Zhang T and
Zhang N: The flavonoid component isorhamnetin in vitro inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in Eca-109 cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 167:153–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teng BS, Lu YH, Wang ZT, Tao XY and Wei
DZ: In vitro anti-tumor activity of isorhamnetin isolated from
Hippophae rhamnoides L. against BEL-7402 cells. Pharmacol
Res. 54:186–194. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sartore-Bianchi A, Martini M, Molinari F,
et al: PIK3CA mutations in colorectal cancer are associated with
clinical resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies. Cancer
Res. 69:1851–1857. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Samuels Y and Velculescu VE: Oncogenic
mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Cell Cycle. 3:1221–1224.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Zhou X, Xiao M, et al: Discovery
of chrysoeriol, a PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway inhibitor with potent
antitumor activity against human multiple myeloma cells in vitro. J
Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 30:734–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, et al:
Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is
rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1122–1128. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morgensztern D and McLeod HL:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer
Drugs. 16:797–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F,
de Bono JS and Workman P: Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway:
progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 8:393–412.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, et al:
Deregulation of the Akt pathway in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 8:27–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng JQ, Lindsley CW, Cheng GZ, Yang H
and Nicosia SV: The Akt/PKB pathway: molecular target for cancer
drug discovery. Oncogene. 24:7482–7492. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hidalgo M and Rowinsky EK: The
rapamycin-sensitive signal transduction pathway as a target for
cancer therapy. Oncogene. 19:6680–6686. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang WY, Cai YZ and Zhang Y: Natural
phenolic compounds from medicinal herbs and dietary plants:
potential use for cancer prevention. Nutr Cancer. 62:1–20. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeong JH, An JY, Kwon YT, Rhee JG and Lee
YJ: Effects of low dose quercetin: cancer cell-specific inhibition
of cell cycle progression. J Cell Biochem. 106:73–82. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shan BE, Wang MX and Li RQ: Quercetin
inhibit human SW480 colon cancer growth in association with
inhibition of cyclin D1 and survivin expression through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Invest. 27:604–612.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang W, VanAlstyne PC, Irons KA, Chen S,
Stewart JW and Birt DF: Individual and interactive effects of
apigenin analogs on G2/M cell-cycle arrest in human colon carcinoma
cell lines. Nutr Cancer. 48:106–114. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P and
Helman LJ: Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling
through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 26:1932–1940.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hyun J, Shin SY, So KM, Lee YH and Lim Y:
Isoflavones inhibit the clonogenicity of human colon cancer cells.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:2664–2669. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abdul-Ghani R, Serra V, Gyorffy B, et al:
The PI3K inhibitor LY294002 blocks drug export from resistant colon
carcinoma cells overexpressing MRP1. Oncogene. 25:1743–1752. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hoeffer CA and Klann E: mTOR signaling: at
the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci.
33:67–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bjornsti MA and Houghton PJ: The TOR
pathway: a target for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:335–348.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nasmyth K: Viewpoint: putting the cell
cycle in order. Science. 274:1643–1645. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cappelletti V, Fioravanti L, Miodini P and
Di Fronzo G: Genistein blocks breast cancer cells in the G(2)M
phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biochem. 79:594–600. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|