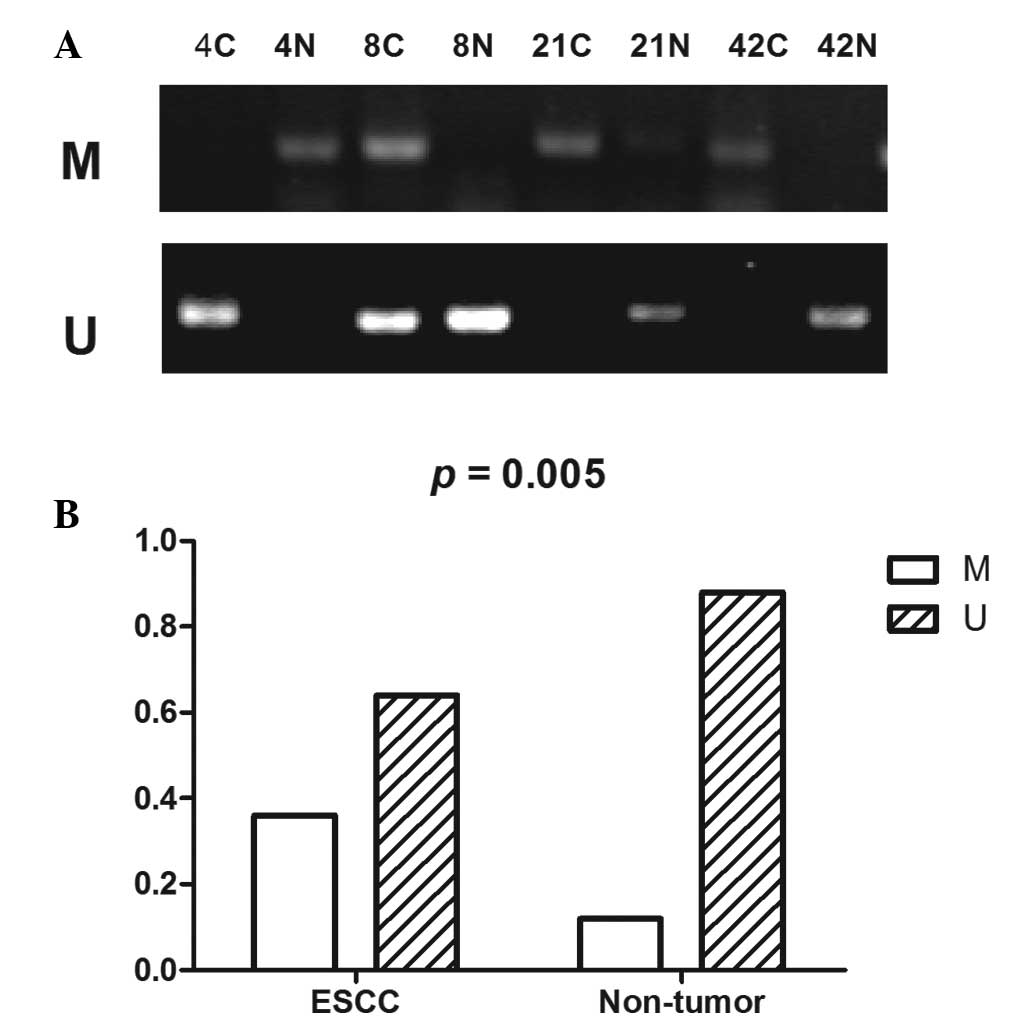
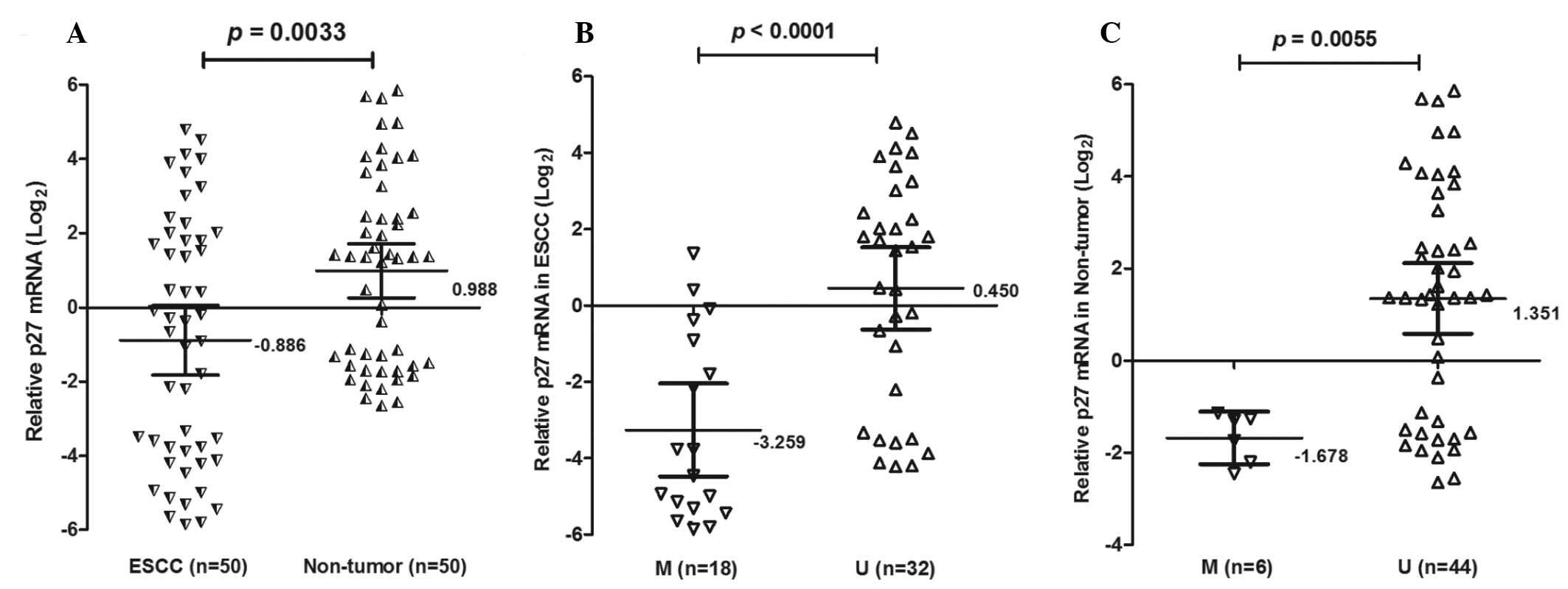
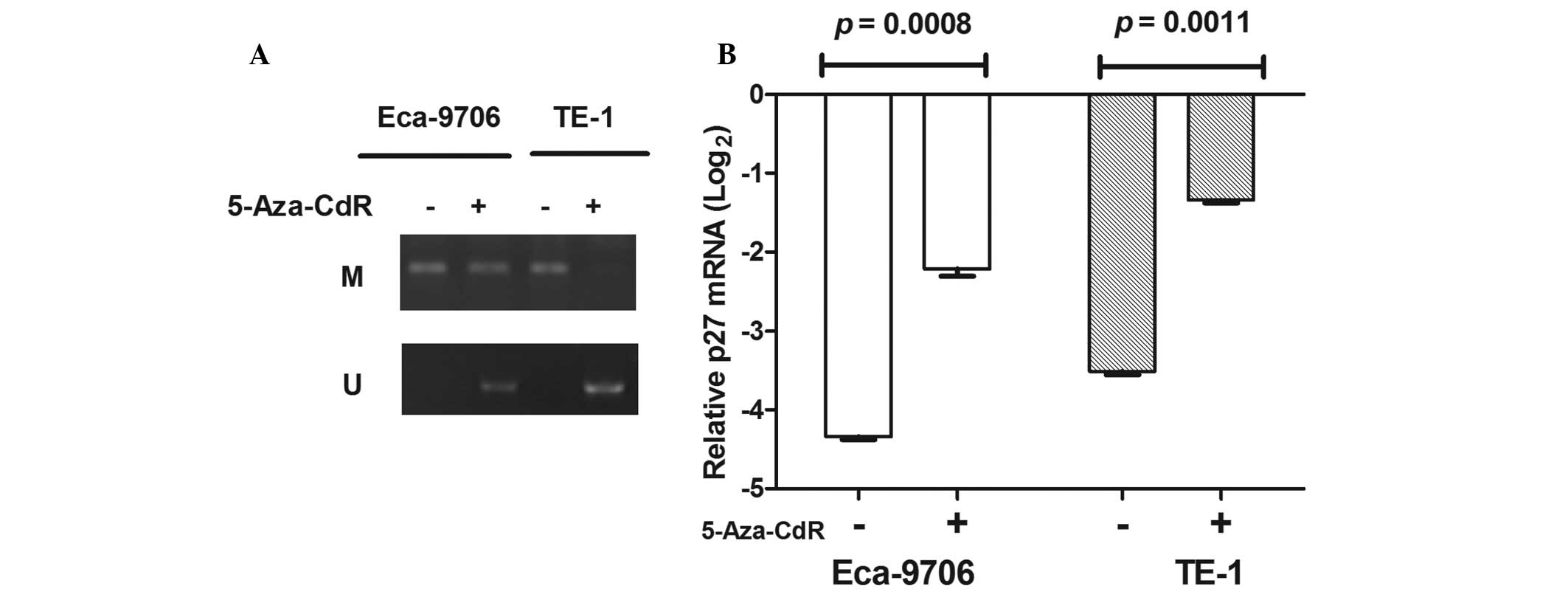
|
1
|
Hongo M, Nagasaki Y and Shoji T:
Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Orient to Occident. Effects of
chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:729–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bagui TK, Cui D, Roy S, et al: Inhibition
of p27Kip1 gene transcription by mitogens. Cell Cycle. 8:115–124.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li H, Collado M, Villasante A, et al:
p27(Kip1) directly represses Sox2 during embryonic stem cell
differentiation. Cell Stem Cell. 11:845–852. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garcia-Fernández RA, García-Palencia P,
Sánchez MA, et al: Combined loss of p21(waf1/cip1) and p27(kip1)
enhances tumorigenesis in mice. Lab Invest. 91:1634–1642.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clurman BE and Porter P: New insights into
the tumor suppression function of P27(kip1). Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:15158–15160. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Viglietto G, Motti ML and Fusco A:
Understanding p27(kip1) deregulation in cancer: down-regulation or
mislocalization. Cell Cycle. 1:394–400. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh SP, Lipman J, Goldman H, et al: Loss
or altered subcellular localization of p27 in Barrett’s associated
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:1730–1735. 1998.
|
|
10
|
Nitti D, Belluco C, Mammano E, et al: Low
level of p27(Kip1) protein expression in gastric adenocarcinoma is
associated with disease progression and poor outcome. J Surg Oncol.
81:167–176. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng JY, Wang WZ, Li KZ, Guan WX and Yan
W: Effect of p27(KIP1) on cell cycle and apoptosis in gastric
cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 11:7072–7077. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heyn H and Esteller M: DNA methylation
profiling in the clinic: applications and challenges. Nat Rev
Genet. 13:679–692. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei PP, Zhang ZJ, Shen LJ, Li JY, Zou Q
and Zhang HX: Expression and hypermethylation of p27 kip1 in
hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:4587–4591.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qian X, Jin L, Kulig E and Lloyd RV: DNA
methylation regulates p27kip1 expression in rodent pituitary cell
lines. Am J Pathol. 153:1475–1482. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Serres MP, Kossatz U, Chi Y, Roberts JM,
Malek NP and Besson A: p27(Kip1) controls cytokinesis via the
regulation of citron kinase activation. J Clin Invest. 122:844–858.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jäkel H, Peschel I, Kunze C, Weinl C and
Hengst L: Regulation of p27 (Kip1) by mitogen-induced tyrosine
phosphorylation. Cell Cycle. 11:1910–1917. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang C, Ling Y, Xu Y, et al: The
silencing of RECK gene is associated with promoter hypermethylation
and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci.
8:451–458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ling Y, Huang G, Fan L, et al: CpG island
methylator phenotype of cell-cycle regulators associated with TNM
stage and poor prognosis in patients with oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 64:246–251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, et al: Functional
links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle
inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids
Res. 37:1672–1681. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hitomi M, Yang K, Guo Y, Fretthold J,
Harwalkar J and Stacey DW: p27Kip1 and cyclin dependent kinase 2
regulate passage through the restriction point. Cell Cycle.
5:2281–2289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vervoorts J and Lüscher B:
Post-translational regulation of the tumor suppressor p27(KIP1).
Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3255–3264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hengst L and Reed SI: Inhibitors of the
Cip/Kip family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 227:25–41.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blain SW and Massagué J: Breast cancer
banishes p27 from nucleus. Nat Med. 8:1076–1078. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: Inhibitors of
mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 9:1149–1163.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Slingerland J and Pagano M: Regulation of
the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 183:10–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tong Q, Zhang W, Jin S, Li S and Chen Z:
The relationship between p27(kip1) expression and the change of
radiosensitivity of esophageal carcinoma cells. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 46:173–176. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sgambato A, Cittadini A, Faraglia B and
Weinstein IB: Multiple functions of p27(Kip1) and its alterations
in tumor cells: a review. J Cell Physiol. 183:18–27. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chu IM, Hengst L and Slingerland JM: The
Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: prognostic potential and
relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:253–267. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee J and Kim SS: The function of p27 KIP1
during tumor development. Exp Mol Med. 41:765–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|