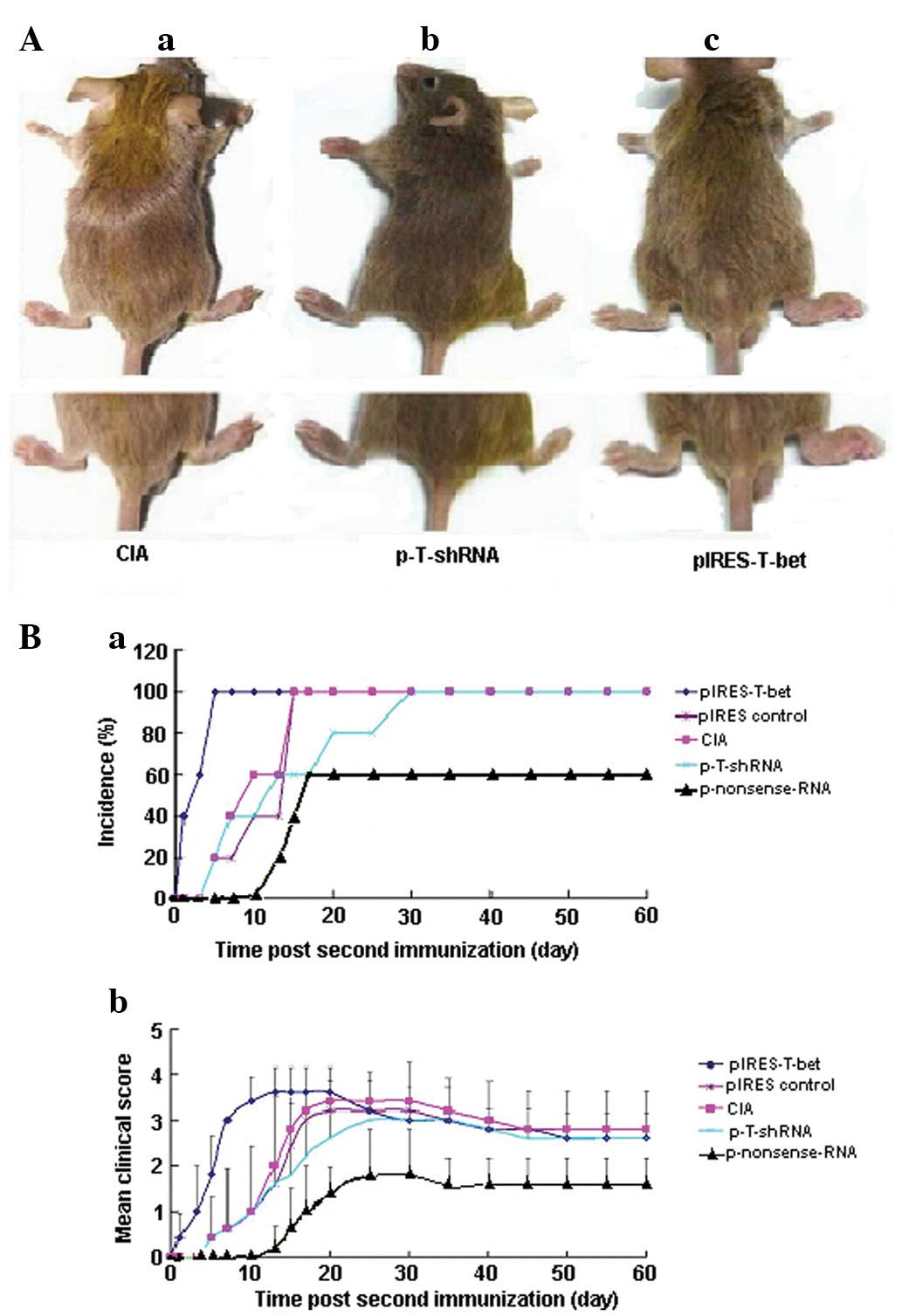
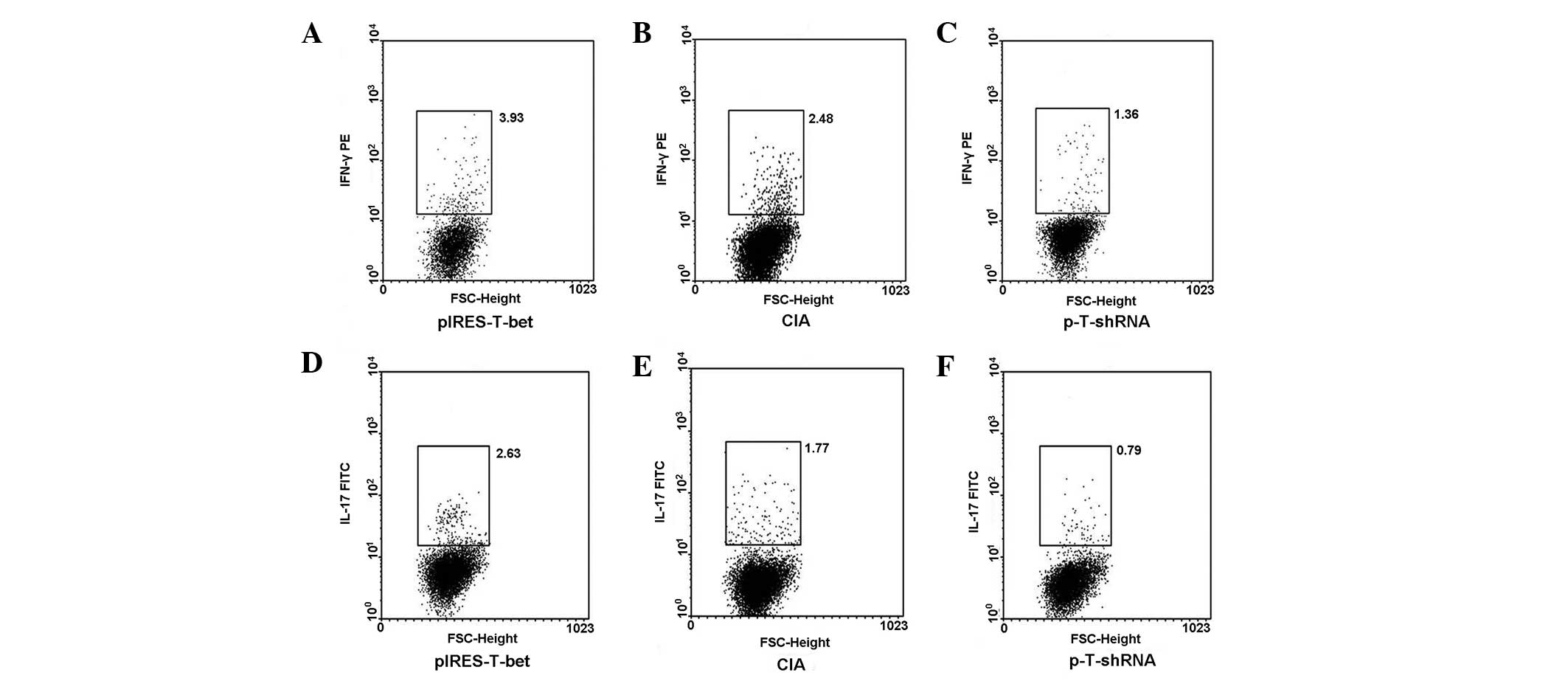
|
1
|
Rodeghero R, Cao Y, Olalekan SA, Iwakua Y,
Glant TT and Finnegan A: Location of CD4+ T cell priming
regulates the differentiation of Th1 and Th17 cells and their
contribution to arthritis. J Immunol. 190:5423–5435.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin GJ, Huang SH, Chen SJ, Wang CH, Chang
DM and Sytwu HK: Modulation by melatonin of the pathogenesis of
inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 14:11742–11766.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Su Z, Shotorbani SS, Jiang X, Ma R, Shen
H, Kong F and Xu H: A method of experimental rheumatoid arthritis
induction using collagen type II isolated from chicken sternal
cartilage. Mol Med Rep. 8:113–117. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fox DA, Gizinski A, Morgan R and Lundy SK:
Cell-cell interactions in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Rheum Dis
Clin North Am. 36:311–323. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chabas D, Baranzini SE, Mitchell D, et al:
The influence of the proinflammatory cytokine, osteopontin, on
autoimmune demyelinating disease. Science. 294:1731–1735. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X,
Fathman CG and Glimcher LH: A novel transcription factor, T-bet,
directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 100:655–669. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shier P, Hofstra CL, Ma XJ, Wu Y, Ngo K
and Fung-Leung WP: Tbt-1, a new T-box transcription factor induced
in activated Th1 and CD8+ T cells. Immunogenetics.
51:771–778. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hwang ES: Transcriptional regulation of T
helper 17 cell differentiation. Yonsei Med J. 51:484–491. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tesmer LA, Lundy SK, Sarkar S and Fox DA:
Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol Rev. 223:87–113. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shahrara S, Huang Q, Mandelin AM 2nd and
Pope RM: TH-17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
10:R932008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stamp LK, James MJ and Cleland LG:
Interleukin-17: the missing link between T-cell accumulation and
effector cell actions in rheumatoid arthritis? Immunol Cell Biol.
82:1–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mathur AN, Chang HC, Zisoulis DG, Kapur R,
Belladonna ML, Kansas GS and Kaplan MH: T-bet is a critical
determinant in the instability of the IL-17-secreting T-helper
phenotype. Blood. 108:1595–1601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Weiner J, Liu Y, Smith AJ, Huss
DJ, Winger R, Peng H, Cravens PD, Racke MK and Lovett-Racke AE:
T-bet is essential for encephalitogenicity of both Th1 and Th17
cells. J Exp Med. 206:1549–1564. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gocke AR, Cravens PD, Ben LH, Hussain RZ,
Northrop SC, Racke MK and Lovett-Racke AE: T-bet regulates the fate
of Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes in autoimmunity. J Immunol.
178:1341–1348. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ortmann RA and Shevach EM: Susceptibility
to collagen-induced arthritis: cytokine-mediated regulation. Clin
Immunol. 98:109–118. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scrivo R, Di Franco M, Spadaro A and
Valesini G: The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1108:312–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sarkar S and Fox DA: Dendritic cells in
rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci. 10:656–665. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Modi S, Soejima M and Levesque MC: The
effect of targeted rheumatoid arthritis therapies on
anti-citrullinated protein autoantibody levels and B cell
responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 173:8–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Fathman JW, Lugo-Villarino G,
Scimone L, von Andrian U, Dorfman DM and Glimcher LH: Transcription
factor T-bet regulates inflammatory arthritis through its function
in dendritic cells. J Clin Invest. 116:414–421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lametschwandtner G, Biedermann T,
Schwärzler C, Günther C, Kund J, Fassl S, Hinteregger S,
Carballido-Perrig N, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH and Carballido JM:
Sustained T-bet expression confers polarized human Th2 cells with
Th1-like cytokine production and migratory capacities. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 113:987–994. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lovett-Racke AE, Rocchini AE, Choy J,
Northrop SC, Hussain RZ, Ratts RB, Sikder D and Racke MK: Silencing
T-bet defines a critical role in the differentiation of
autoreactive T lymphocytes. Immunity. 21:719–731. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lai Kwan Lam Q, King Hung Ko O, Zheng BJ
and Lu L: Local BAFF gene silencing suppresses Th17-cell generation
and ameliorates autoimmune arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:14993–14998. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bettelli E, Sullivan B, Szabo SJ, Sobel
RA, Glimcher LH and Kuchroo VK: Loss of T-bet, but not STAT1,
prevents the development of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Exp Med. 200:79–87. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hannon GJ: RNA interference. Nature.
418:244–251. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Denli AM and Hannon GJ: RNAi: an
ever-growing puzzle. Trends Biochem Sci. 28:196–201. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Escobar T, Yu CR, Muljo SA and Egwuagu CE:
STAT3 activates miR-155 in Th17 cells and acts in concert to
promote experimental autoimmune uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
54:4017–4025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|