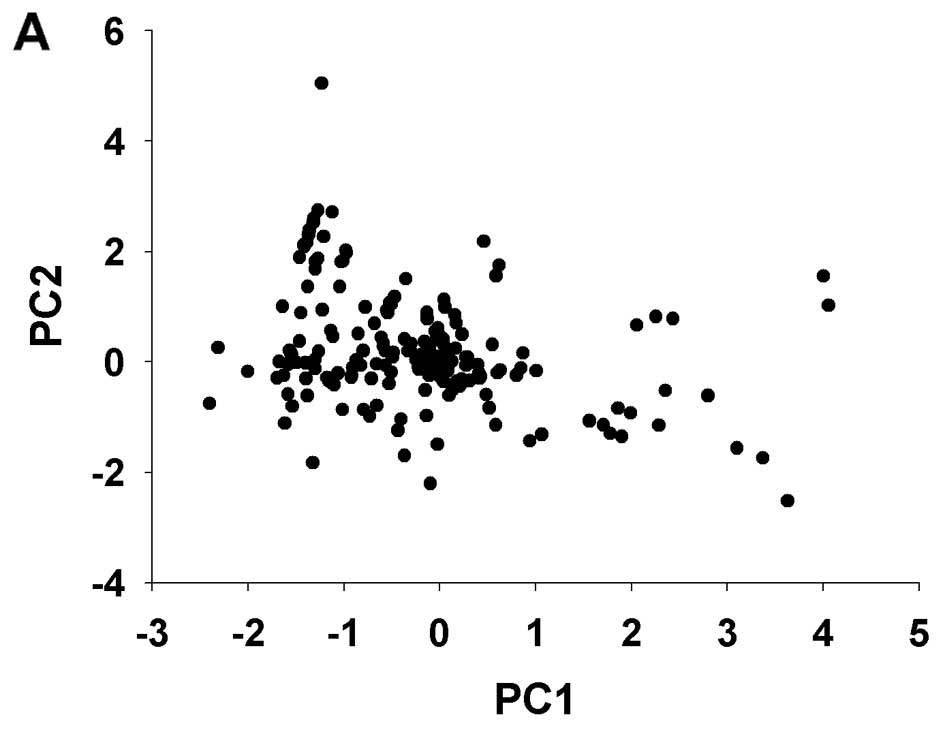
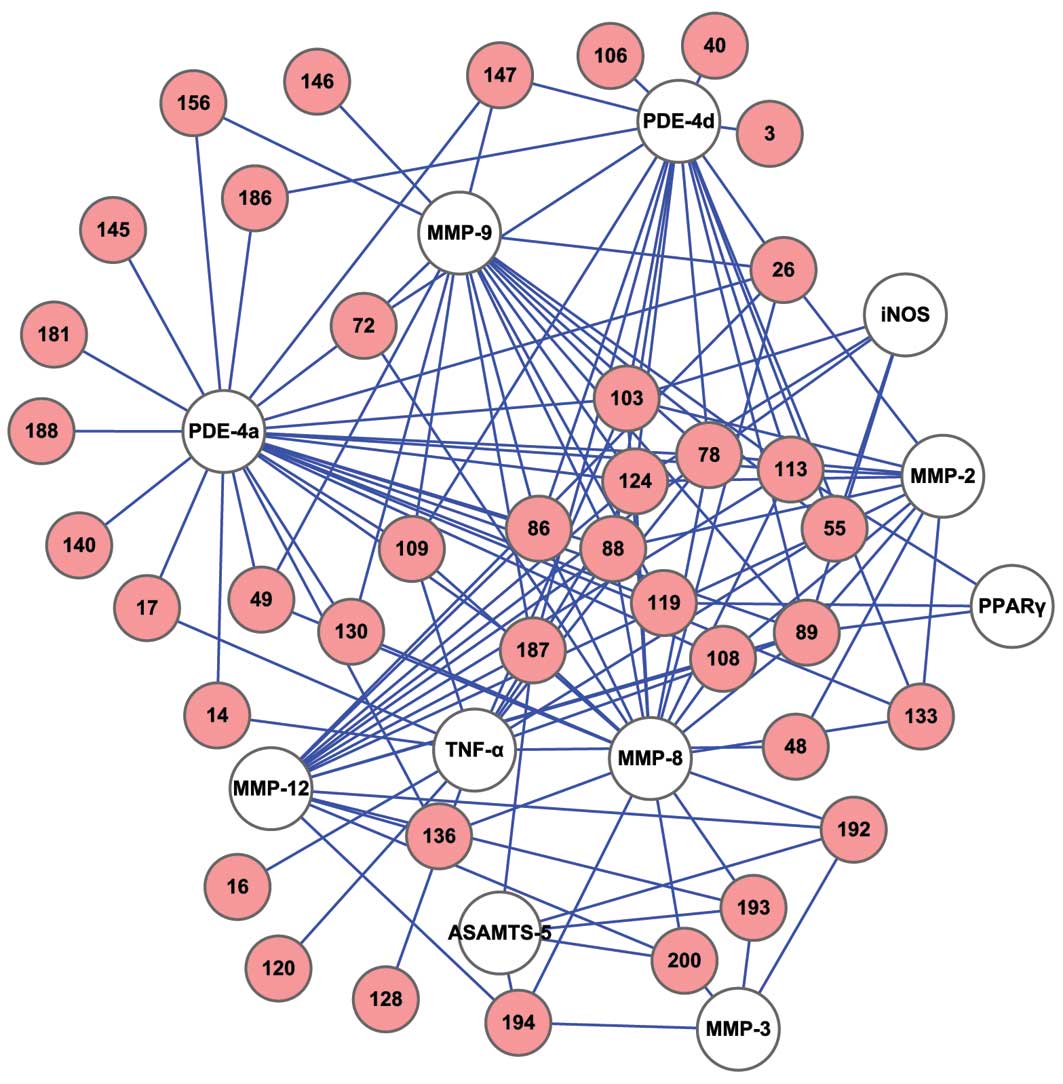
|
1
|
Swoboda B: Epidemiological arthrosis
research. Orthopade. 30:834–840. 2001.(In German).
|
|
2
|
Rubio-Terres C; Grupo del estudio VECTRA.
An economic evaluation of chondroitin sulfate and non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Data
from the VECTRA study. Reumatol Clin. 6:187–195. 2010.(In
Spanish).
|
|
3
|
Bitton R: The economic burden of
osteoarthritis. Am J Manag Care. 15(Suppl 8): S230–S235.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo ZR: Drug promiscuity. Yao Xue Xue Bao.
46:361–369. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Frantz S: Drug discovery: playing dirty.
Nature. 437:942–943. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ernst E: Complementary or alternative
therapies for osteoarthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2:74–80.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rezende MU, Gurgel HM, Vilaca PR Jr,
Kuroba RK, Lopes AS, Phillipi RZ and Hernandez AJ: Diacerhein
versus glucosamine in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 61:461–466. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi JH, Choi JH, Kim DY, Yoon JH, Youn
HY, Yi JB, Rhee HI, Ryu KH, Jung K, Han CK, et al: Effects of SKI
306X, a new herbal agent, on proteoglycan degradation in cartilage
explant culture and collagenase-induced rabbit osteoarthritis
model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 10:471–478. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang P, Gu EP and Cao HY: Effect of Huoxue
Huayu plaster on NO and MMP-13 in joint fluid of osseous arthritis
of knee in the early and middle stage. Tianjin Zhong Yi Yao.
27:192–193. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Wang P, Gu EP and Cao HY: Clinical
efficacy observation for osseous arthritis of knee in the early and
middle stage treated with Huoxue Huayu plaster. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao.
30:491–492. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Liu XX, Li XH and Zhou JT: Research on
mechanism of Tougu Xiaotong Granule in preventing and treating knee
osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 27:50–54.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Yu F, Li X, Cai L, Li H, Chen J, Wong X,
Xu H, Zheng C, Liu X and Ye H: Achyranthes bidentata
polysaccharides induce chondrocyte proliferation via the promotion
of the G1/S cell cycle transition. Mol Med Rep.
7:935–940. 2013.
|
|
13
|
Zhu HF, Wang WJ and Wang ZM: Recent
advances of Drynaria fortunei. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 1:66–68.
2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Qiao X, Hou T, Zhang W, Guo S and Xu X: A
3D structure database of components from Chinese traditional
medicinal herbs. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 42:481–489. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D,
Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B and Hassanali M: DrugBank: a
knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic
Acids Res. 36:D901–D906. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dobson CM: Chemical space and biology.
Nature. 432:824–828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang Q, Qiao X and Xu X: Potential
synergism and inhibitors to multiple target enzymes of Xuefu Zhuyu
Decoction in cardiac disease therapeutics: a computational
approach. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 17:1779–1783. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW and
Feeney PJ: Experimental and computational approaches to estimate
solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development
settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 46:3–26. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bonnet CS and Walsh DA: Osteoarthritis,
angiogenesis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford). 44:7–16.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Loeser RF: Articular cartilage nuclear
receptors: an emerging target for treatment of osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 17:829–831. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tenor H, Hedbom E, Hauselmann HJ, Schudt C
and Hatzelmann A: Phosphodiesterase isoenzyme families in human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes - functional importance of
phosphodiesterase 4. Br J Pharmacol. 135:609–618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Montes M, Braud E, Miteva MA, Goddard ML,
Mondesert O, Kolb S, Brun MP, Ducommun B, Garbay C and Villoutreix
BO: Receptor-based virtual ligand screening for the identification
of novel CDC25 phosphatase inhibitors. J Chem Inf Model.
48:157–165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu F, Shi Z, Qin C, Tao L, Liu X, Xu F,
Zhang L, Song Y, Liu XH, Zhang J, et al: Therapeutic target
database update 2012: a resource for facilitating target-oriented
drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:D1128–D1136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Assenov Y, Ramirez F, Schelhorn SE,
Lengauer T and Albrecht M: Computing topological parameters of
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 24:282–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haringman JJ, Ludikhuize J and Tak PP:
Chemokines in joint disease: the key to inflammation? Ann Rheum
Dis. 63:1186–1194. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wagner H: Multitarget therapy - the future
of treatment for more than just functional dyspepsia.
Phytomedicine. 13(Suppl 5): 122–129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Espinoza-Fonseca LM: The benefits of the
multi-target approach in drug design and discovery. Bioorg Med
Chem. 14:896–897. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabasi AL and Oltvai
ZN: Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature.
411:41–42. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Zang B, Wu W, Tong J and Jin M:
Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on endothelial cell
injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
36:1650–1653. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Rosenbaum CC, O’Mathuna DP, Chavez M and
Shields K: Antioxidants and antiinflammatory dietary supplements
for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Altern Ther Health
Med. 16:32–40. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo P, Tan Z, Zhang Z, Li H and Mo Z:
Inhibitory effects of salvianolic acid B on the high
glucose-induced mesangial proliferation via NF-κB-dependent
pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:1381–1386. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li AZ: The therapeutic effect of retinal
vein occlusion with Huoxue Huayu method in traditional Chinese
medicine. Guiding J Trad Chin Med Pharm. 19:63–65. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Zhang P, Wang H and Ou YL: The therapeutic
experience of Huoxue Huayu method in diabetic nephropathy. J Pract
Tradit Chin Med. 2:1302013.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Gao CX: Clinical practice of Huoxue Huayu
method in eye diseases treatment. Seek medical and ask the
medicine. 10:622012.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Liu H, Wang J, Zhou W, Wang Y and Yang L:
Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from
herbal medicines: an example using licorice. J Ethnopharmacol.
146:773–793. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tanabe H, Suzuki H, Nagatsu A, Mizukami H,
Ogihara Y and Inoue M: Selective inhibition of vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation by coptisine isolated from Coptis
rhizoma, one of the crude drugs composing Kampo medicines Unsei-in.
Phytomedicine. 13:334–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gong LL, Fang LH, Wang SB, Sun JL, Qin HL,
Li XX, Wang SB and Du GH: Coptisine exert cardioprotective effect
through anti-oxidative and inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase pathway on
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats.
Atherosclerosis. 222:50–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|