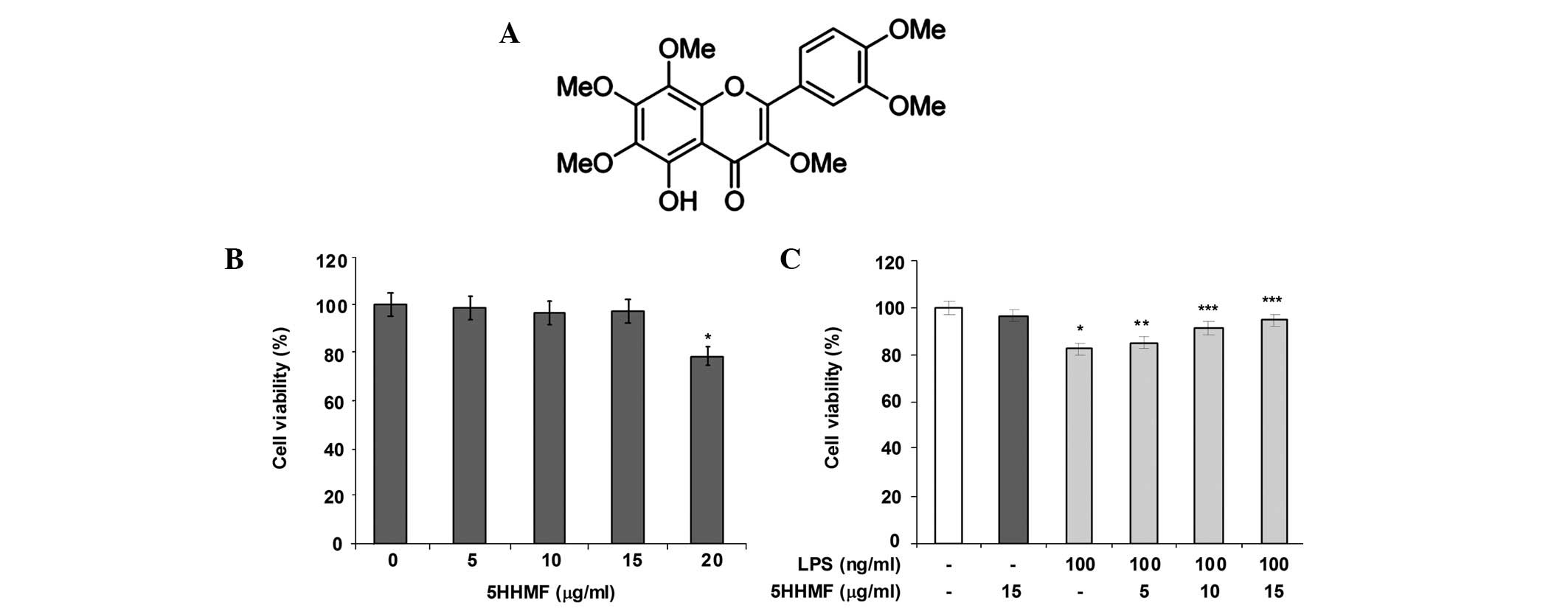
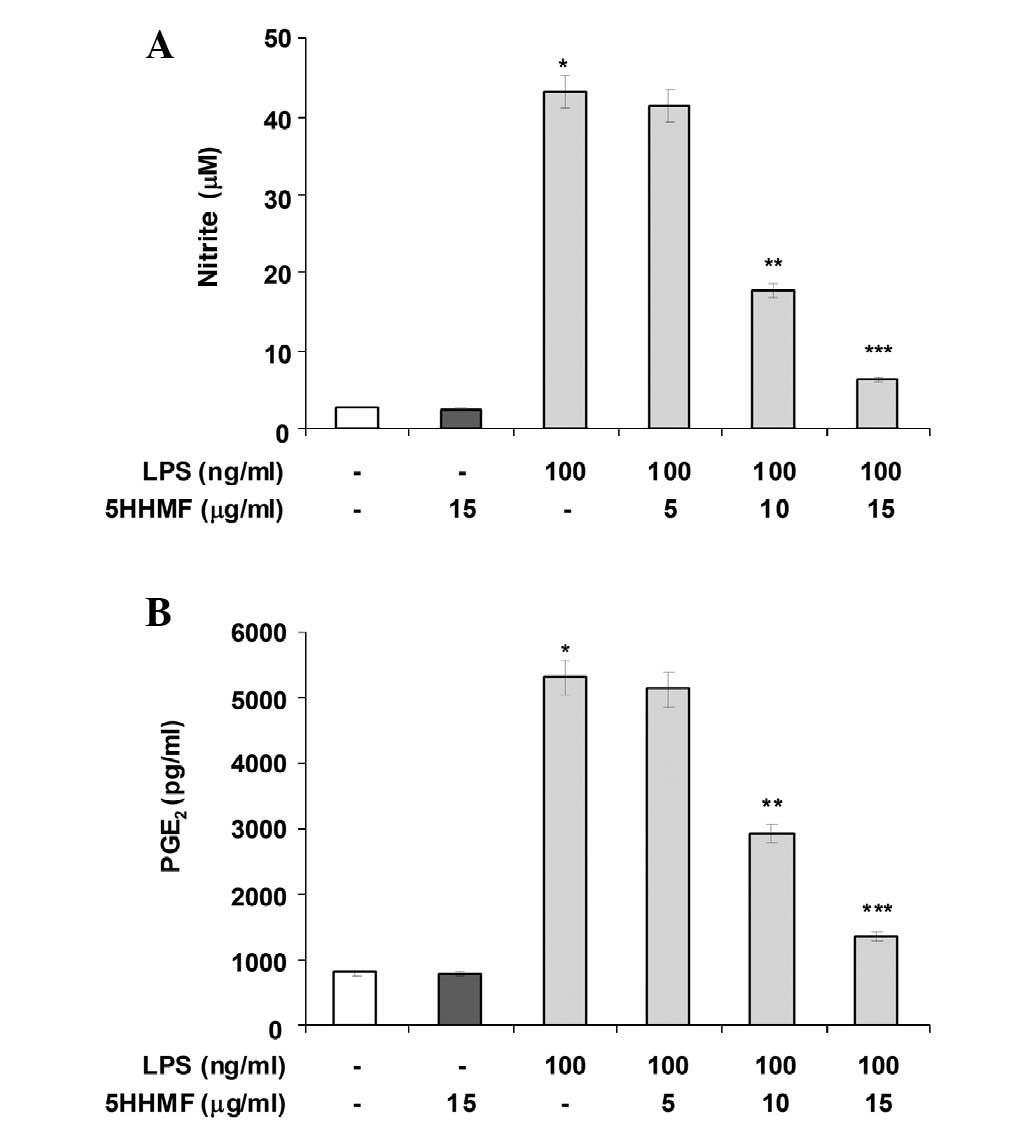
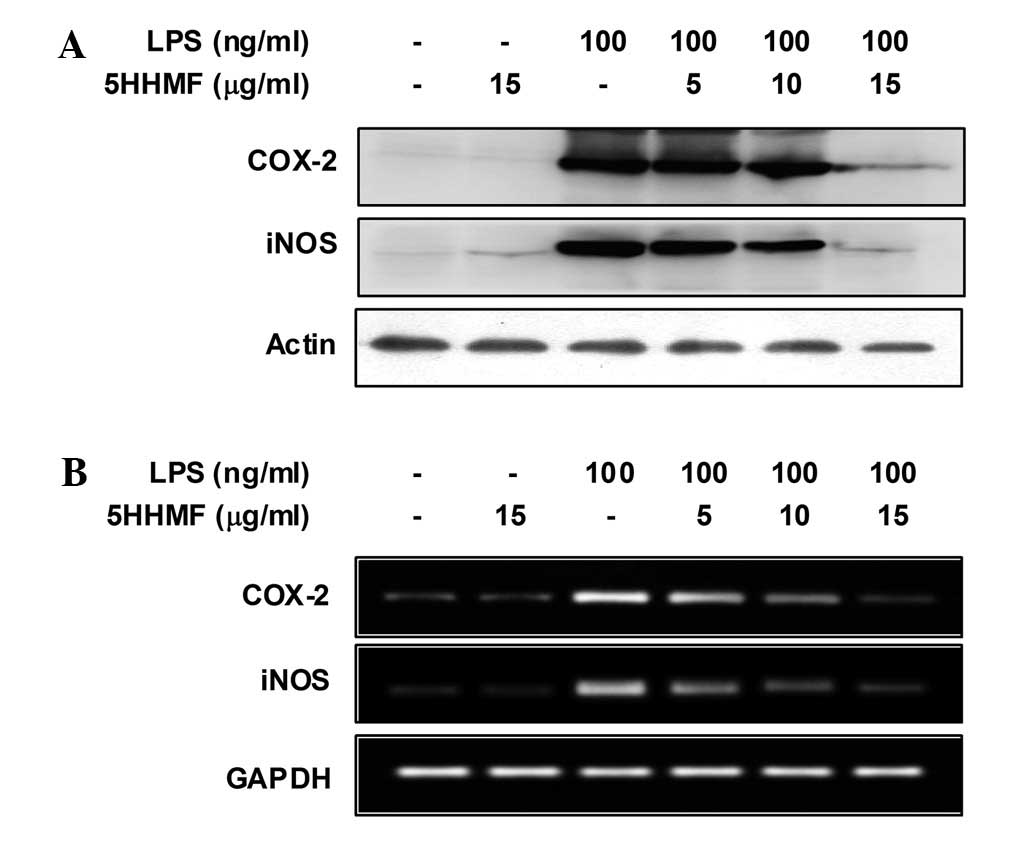
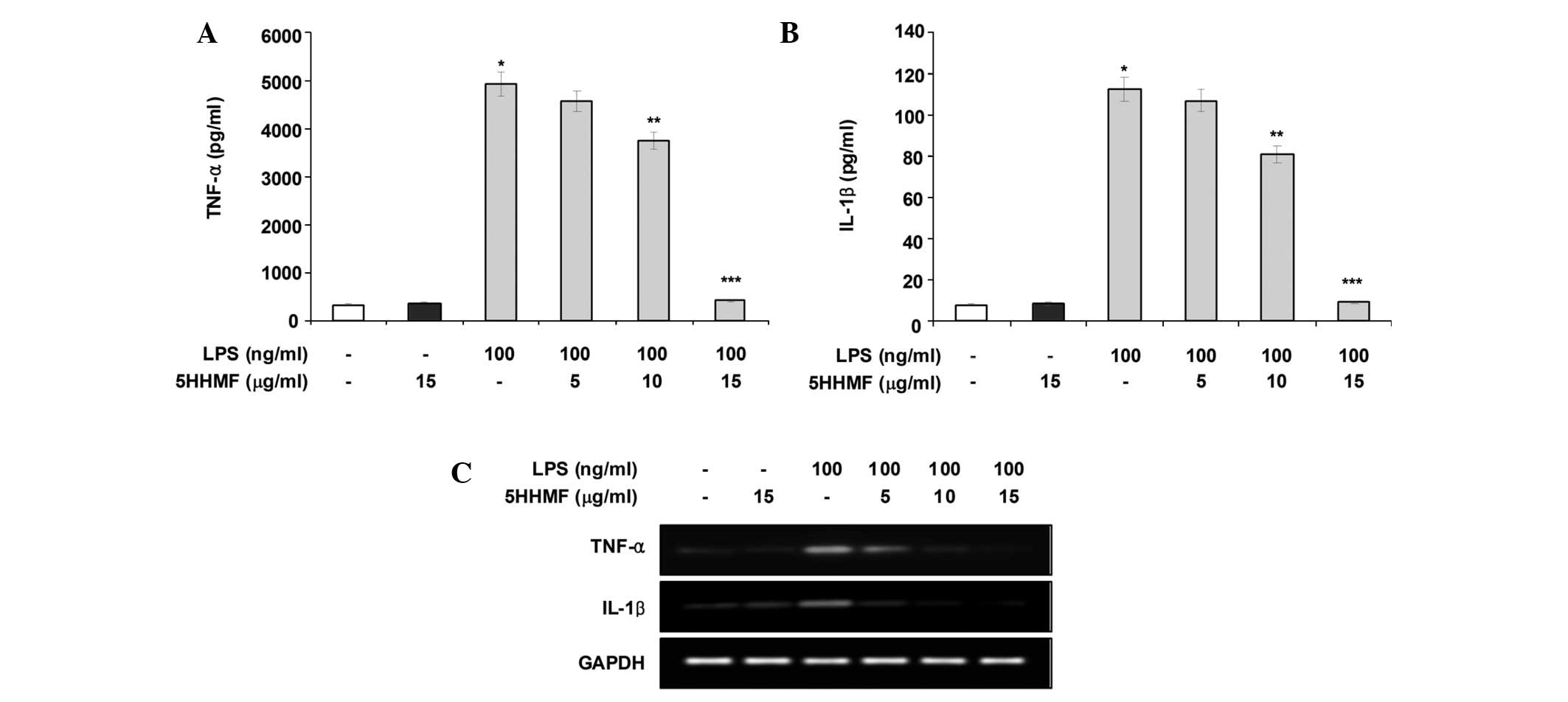
|
1
|
Andreasen AS, Krabbe KS, Krogh-Madsen R,
Taudorf S, Pedersen BK and Møller K: Human endotoxemia as a model
of systemic inflammation. Curr Med Chem. 15:1697–1705. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aderem A: Role of Toll-like receptors in
inflammatory response in macrophages. Crit Care Med. 29(Suppl 7):
S16–S18. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ritchlin CT, Haas-Smith SA, Li P, Hicks DG
and Schwarz EM: Mechanisms of TNF-alpha- and RANKL-mediated
osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in psoriatic arthritis. J
Clin Invest. 111:821–831. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown MD and Sacks DB: Compartmentalised
MAPK pathways. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 186:205–235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ci X, Song Y, Zeng F, Zhang X, Li H, Wang
X, Cui J and Deng X: Ceftiofur impairs pro-inflammatory cytokine
secretion through the inhibition of the activation of NF-κB and
MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 372:73–77. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu RH and Hotchkiss JH: Potential
genotoxicity of chronically elevated nitric oxide: a review. Mutat
Res. 339:73–89. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G and Brown K:
Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu Rev Cell
Biol. 10:405–455. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Li H, Feng H, Xiong H, Zhang L,
Song Y, Yu L and Deng X: Valnemulin downregulates nitric oxide,
prostaglandin E2, and cytokine production via inhibition of
NF-kappaB and MAPK activity. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:810–816. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Edwards MR, Bartlett NW, Clarke D, Birrell
M, Belvisi M and Johnston SL: Targeting the NF-kappaB pathway in
asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol Ther.
121:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ghosh S and Hayden MS: New regulators of
NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:837–848. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wong ET and Tergaonkar V: Roles of
NF-kappaB in health and disease: mechanisms and therapeutic
potential. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:451–465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barak V, Kalickman I, Halperin T,
Birkenfeld S and Ginsburg I: PADMA-28, a Tibetan herbal preparation
is an inhibitor of inflammatory cytokine production. Eur Cytokine
Netw. 15:203–209. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chi YS, Lim H, Park H and Kim HP: Effects
of wogonin, a plant flavone from Scutellaria radix, on skin
inflammation: in vivo regulation of inflammation-associated gene
expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1271–1278. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Genovese MC: Biologic therapies in
clinical development for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J
Clin Rheumatol. 11:S45–S54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim KI, Seo HD, Lee HS, Jo HY and Yang HC:
Studies on the blood anticoagulant polysaccharide isolated from hot
water extracts of Hizikia fusiforme. Korean J Food Sci Nutr.
27:1204–1210. 1998.
|
|
16
|
Nagai T and Yukimoto T: Preparation and
functional properties of beverages made from sea algae. Food Chem.
81:327–332. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Okai Y, Okai KH, Ishizaka S, Ohtani K,
Yuasa IS and Yamashita U: Possible immunodulating activities in
extract of edible brown alga Hizikia fusiforme (Hiziki). J
Food Agricul. 76:56–62. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yan X, Chuda Y, Suzuki M and Nagata T:
Fucoxanthin as the major antioxidant in Hijikia fusiformis, a
common edible seaweed. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 63:605–607. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim MJ, Lee HH, Seo MJ, Kang BW, Park JU,
Kim KS, Kim KY, Joo WH, Choi YH, Cho YS and Jeong YK:
Identification of 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone from
Hizikia fusiforme involved in the induction of the apoptosis
mediators in human AGS carcinoma cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol.
22:1665–1672. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Pan MH, Lai YS, Lai CS, Wang YJ, Li S, Lo
CY, Dushenkov S and Ho CT:
5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone induces apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species production, growth arrest and DNA
damage-inducible gene 153 expression, and caspase activation in
human leukemia cells. J Agric Food Chem. 55:5081–5091. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Sergeev IN, Li S, Colby J, Ho CT and
Dushenkov S: Polymethoxylated flavones induce
Ca2+-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Life
Sci. 80:245–253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bae DS, Kim YH, Pan CH, Nho CW, Samdan J,
Yansan J and Lee JK: Protopine reduces the inflammatory activity of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages. BMB Rep.
5:108–113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YH, Jeon SH, Kim SH, Kim C, Lee SJ,
Koh D, Lim Y, Ha K and Shin SY: A new synthetic chalcone
derivative, 2-hydroxy-3′,5,5′-trimethoxychalcone (DK-139),
suppresses the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response
through inhibition of the Akt/NF-κB pathway in BV2 microglial
cells. Exp Mol Med. 44:369–377. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo LY, Hung TM, Bae KH, Shin EM, Zhou HY,
Hong YN, Kang SS, Kim HP and Kim YS: Anti-inflammatory effects of
schisandrin isolated from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis
Baill. Eur J Pharmacol. 591:293–299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Southan GJ and Szabó C: Selective
pharmacological inhibition of distinct nitric oxide synthase
isoforms. Biochem Pharmacol. 51:383–394. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Plummer SM, Holloway KA, Manson MM, Munks
RJ, Kaptein A, Farrow S and Howells L: Inhibition of
cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive
agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the
NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene. 18:6013–6020. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sarkar D, Saha P, Gamre S, Bhattacharjee
S, Hariharan C, Ganguly S, Sen R, Mandal G, Chattopadhyay S,
Majumdar S and Chatterjee M: Anti-inflammatory effect of
allylpyrocatechol in LPS-induced macrophages is mediated by
suppression of iNOS and COX-2 via the NF-kappaB pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 8:1264–1271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tao JY, Zheng GH, Zhao L, Wu JG, Zhang XY,
Zhang SL, Huang ZJ, Xiong FL and Li CM: Anti-inflammatory effects
of ethyl acetate fraction from Melilotus suaveolens Ledeb on
LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 123:97–105. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Q, Nayak BN, Reimer M, Jones PJ,
Fulcher RG and Rempel CB: Anti-inflammatory effect of Inonotus
obliquus, Polygala senega L, and Viburnum
trilobum in a cell screening assay. J Ethnopharmacol.
125:487–493. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Yun KJ, Kim JY, Kim JB, Lee KW, Jeong SY,
Park HJ, Jung HJ, Cho YW, Yun K and Lee KT: Inhibition of
LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-kappa B
inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: possible involvement of the
IKK and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:431–441. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Aggarwal BB and Natarajan K: Tumor
necrosis factors: developments during the last decade. Eur Cytokine
Netw. 7:93–124. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee HS, Ryu DS, Lee GS and Lee DS:
Anti-inflammatory effects of dichloromethane fraction from
Orostachys japonicus in RAW 264.7 cells: suppression of
NF-kappaB activation and MAPK signaling. J Ethnopharmacol.
140:271–276. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim YG, Ohta T, Takahashi T, Kushiro A,
Nomoto K, Yokokura T, Okada N and Danbara H: Probiotic
Lactobacillus casei activates innate immunity via NF-kappaB
and p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways. Microbes Infect. 8:994–1005.
2006.
|
|
34
|
Rajapakse N, Kim MM, Mendis E and Kim SK:
Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2
in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by
carboxybutyrylated glucosamine takes place via down-regulation of
mitogen-activated protein kinase-mediated nuclear factor-kappaB
signaling. Immunology. 123:348–357. 2008.
|
|
35
|
Lee SJ, Bai SK, Lee KS, Namkoong S, Na HJ,
Ha KS, Han JA, Yim SV, Chang K, Kwon YG, et al: Astaxanthin
inhibits nitric oxide production and inflammatory gene expression
by suppressing IκB kinase-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Mol
Cells. 16:97–105. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Abraham E: Nuclear factor-kappaB and its
role in sepsis-associated organ failure. J Infect Dis. 187(Suppl
2): S364–S369. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|