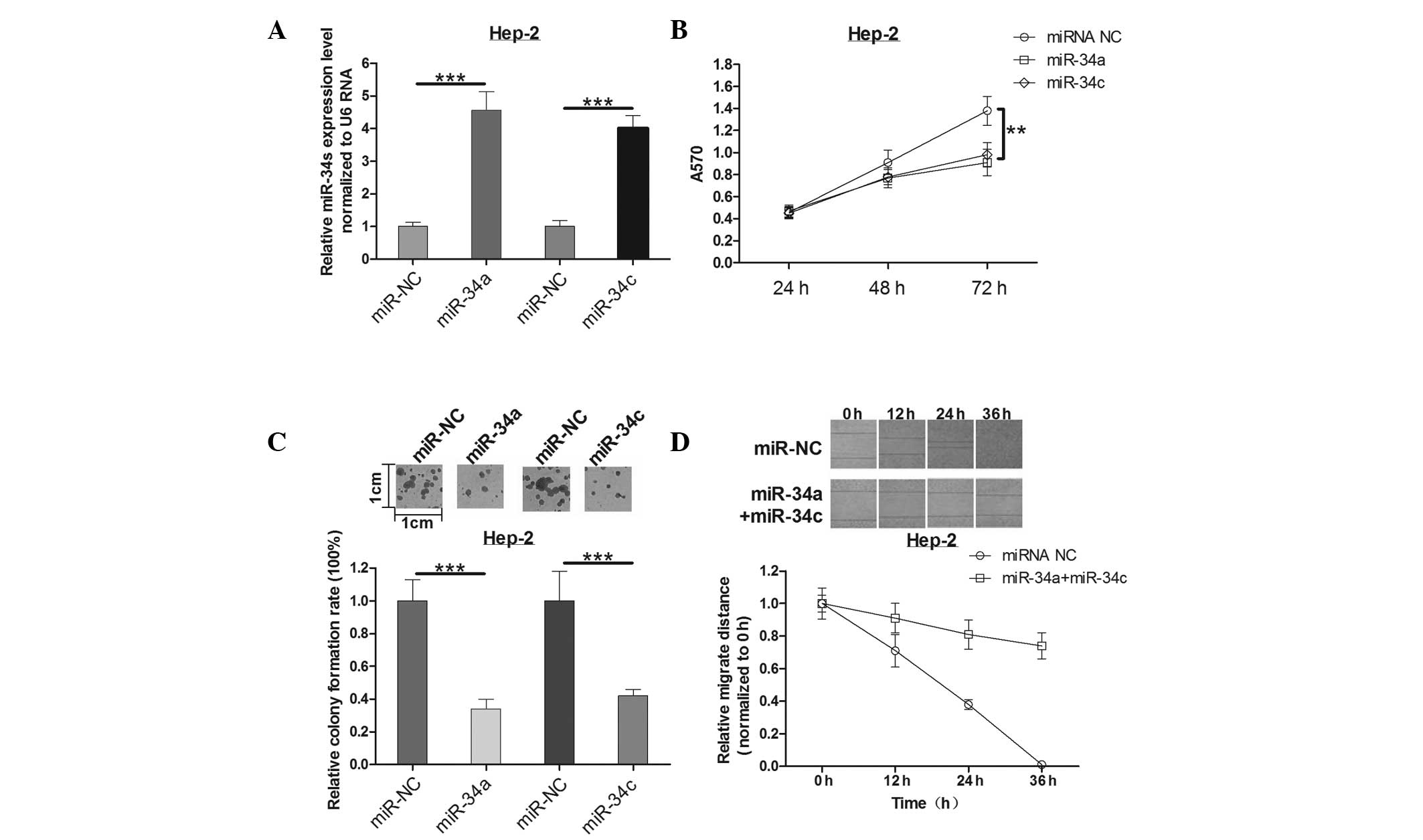
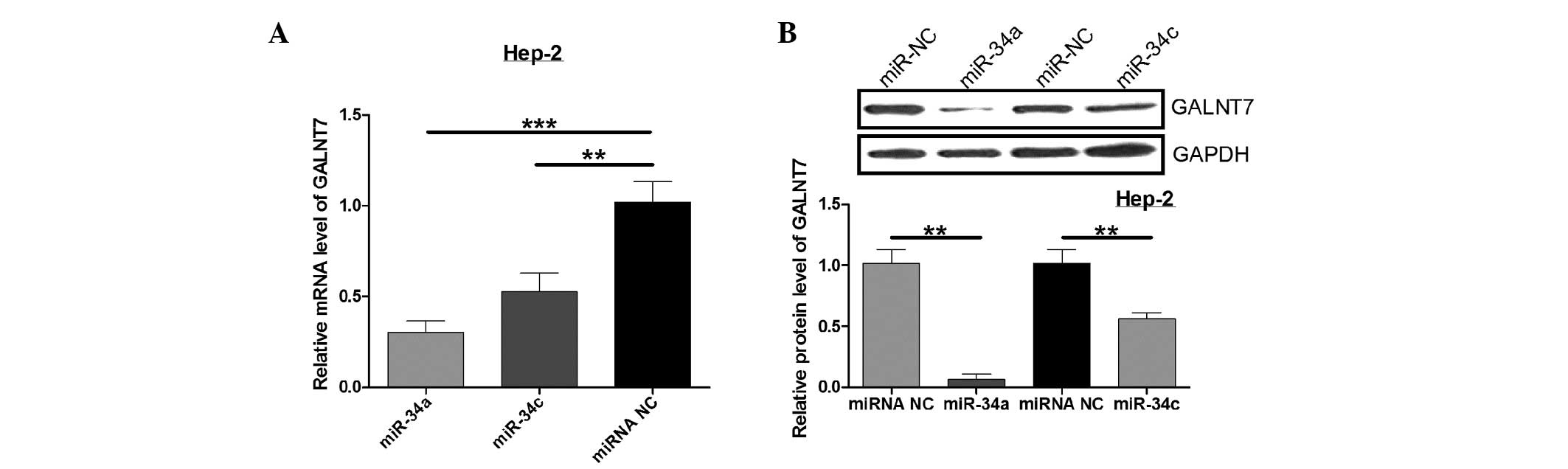
|
1
|
Breving K and Esquela-Kerscher A: The
complexities of microRNA regulation: mirandering around the rules.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1316–1329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim VN: Small RNAs: classification,
biogenesis, and function. Mol Cells. 19:1–15. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mao L, Hong WK and Papadimitrakopoulou VA:
Focus on head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell. 5:311–316. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Licitra L, Bernier J, Grandi C, et al:
Cancer of the larynx. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 47:65–80. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Vokes EE, Weichselbaum RR, Lippman SM and
Hong WK: Head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 328:184–194. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tivnan A, Tracey L, Buckley PG, Alcock LC,
Davidoff AM and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-34a is a potent tumor
suppressor molecule in vivo in neuroblastoma. BMC Cancer.
11:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai KM, Bao XL, Kong XH, et al:
Hsa-miR-34c suppresses growth and invasion of human laryngeal
carcinoma cells via targeting c-Met. Int J Mol Med. 25:565–571.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng RQ, Wan HY, Li HF, Liu M, Li X and
Tang H: MicroRNA-214 suppresses growth and invasiveness of cervical
cancer cells by targeting
UDP-N-acetyl-α-D-galactosamine:polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 7. J Biol Chem. 287:14301–14309.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu M, Wu H, Liu T, et al: Regulation of
the cell cycle gene, BTG2, by miR-21 in human laryngeal carcinoma.
Cell Res. 19:828–837. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peter ME: Targeting of mRNAs by multiple
miRNAs: the next step. Oncogene. 29:2161–2164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hobert O: miRNAs play a tune. Cell.
131:22–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gaziel-Sovran A, Segura MF, Di Micco R, et
al: miR-30b/30d regulation of GalNAc transferases enhances invasion
and immunosuppression during metastasis. Cancer Cell. 20:104–118.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et
al: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, et al:
A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in
human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res.
65:9628–9632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tazawa H, Tsuchiya N, Izumiya M and
Nakagama H: Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like
growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon
cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:15472–15477. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, et al: MicroRNA
miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells.
PLoS One. 4:e68162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pang RT, Leung CO, Ye TM, et al:
MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion through downregulation of Notch1
and Jagged1 in cervical carcinoma and choriocarcinoma cells.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1037–1044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, et al: miR-34a inhibits
migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 275:44–53. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M and Lowenstein CJ:
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:13421–13426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Welch C, Chen Y and Stallings RL:
MicroRNA-34a functions as a potential tumor suppressor by inducing
apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene. 26:5017–5022. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei JS, Song YK, Durinck S, et al: The
MYCN oncogene is a direct target of miR-34a. Oncogene.
27:5204–5213. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun F, Fu H, Liu Q, et al: Downregulation
of CCND1 and CDK6 by miR-34a induces cell cycle arrest. FEBS Lett.
582:1564–1568. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bommer GT, Gerin I, Feng Y, et al:
p53-mediated activation of miRNA34 candidate tumor-suppressor
genes. Curr Biol. 17:1298–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Brannon AR, Reddy AR, et al:
Identifying mRNA targets of microRNA dysregulated in cancer: with
application to clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Syst Biol.
4:512010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luan S, Sun L and Huang F: MicroRNA-34a: a
novel tumor suppressor in p53-mutant glioma cell line U251. Arch
Med Res. 41:67–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ten Hagen KG, Fritz TA and Tabak LA: All
in the family: the UDP-GalNAc:polypeptide
N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases. Glycobiology. 13:1R–16R.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Casey RC, Oegema TR Jr, Skubitz KM,
Pambuccian SE, Grindle SM and Skubitz AP: Cell membrane
glycosylation mediates the adhesion, migration, and invasion of
ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Metastasis. 20:143–152. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kahai S, Lee SC, Lee DY, et al: MicroRNA
miR-378 regulates nephronectin expression modulating osteoblast
differentiation by targeting GalNT-7. PLoS One. 4:e75352009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|