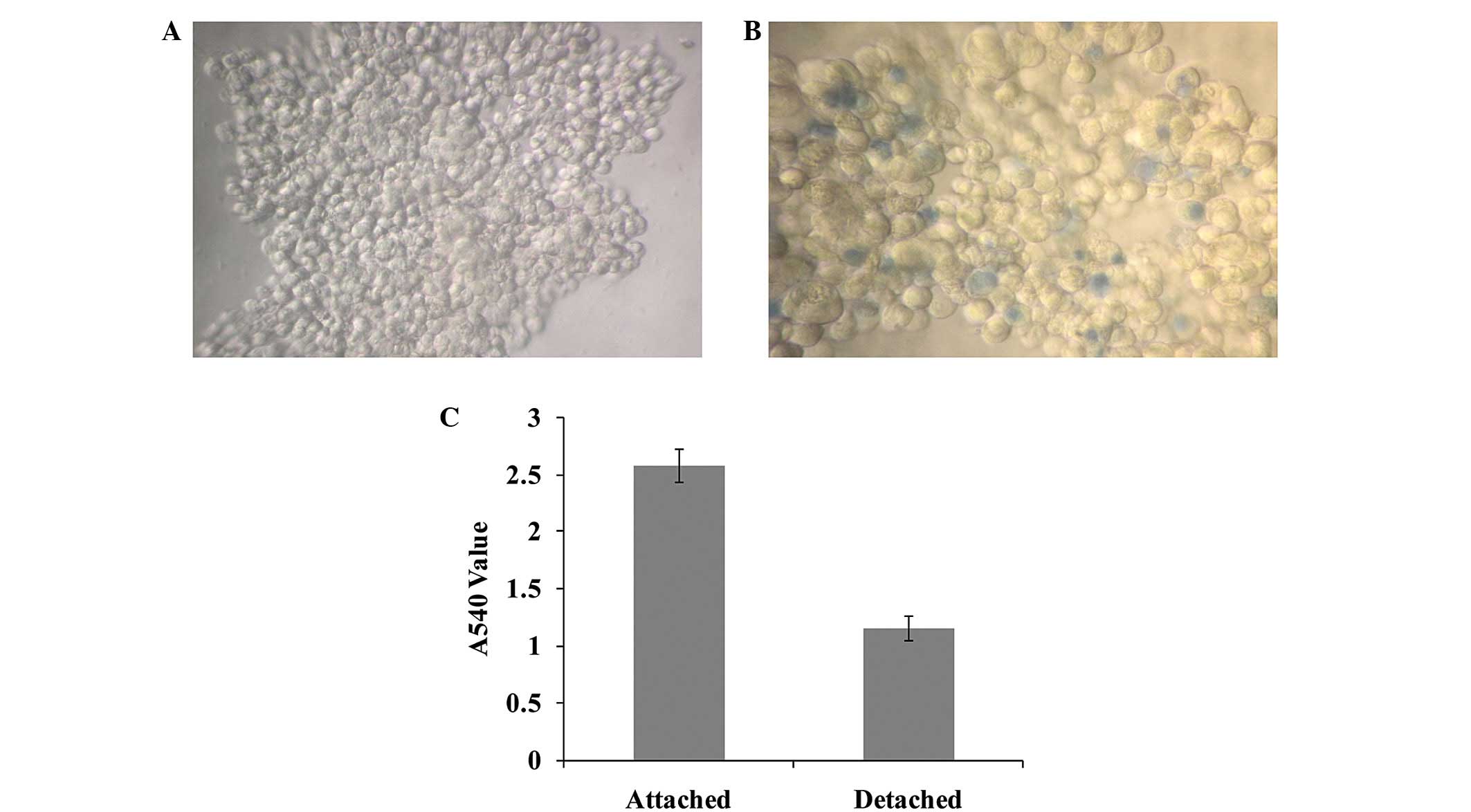
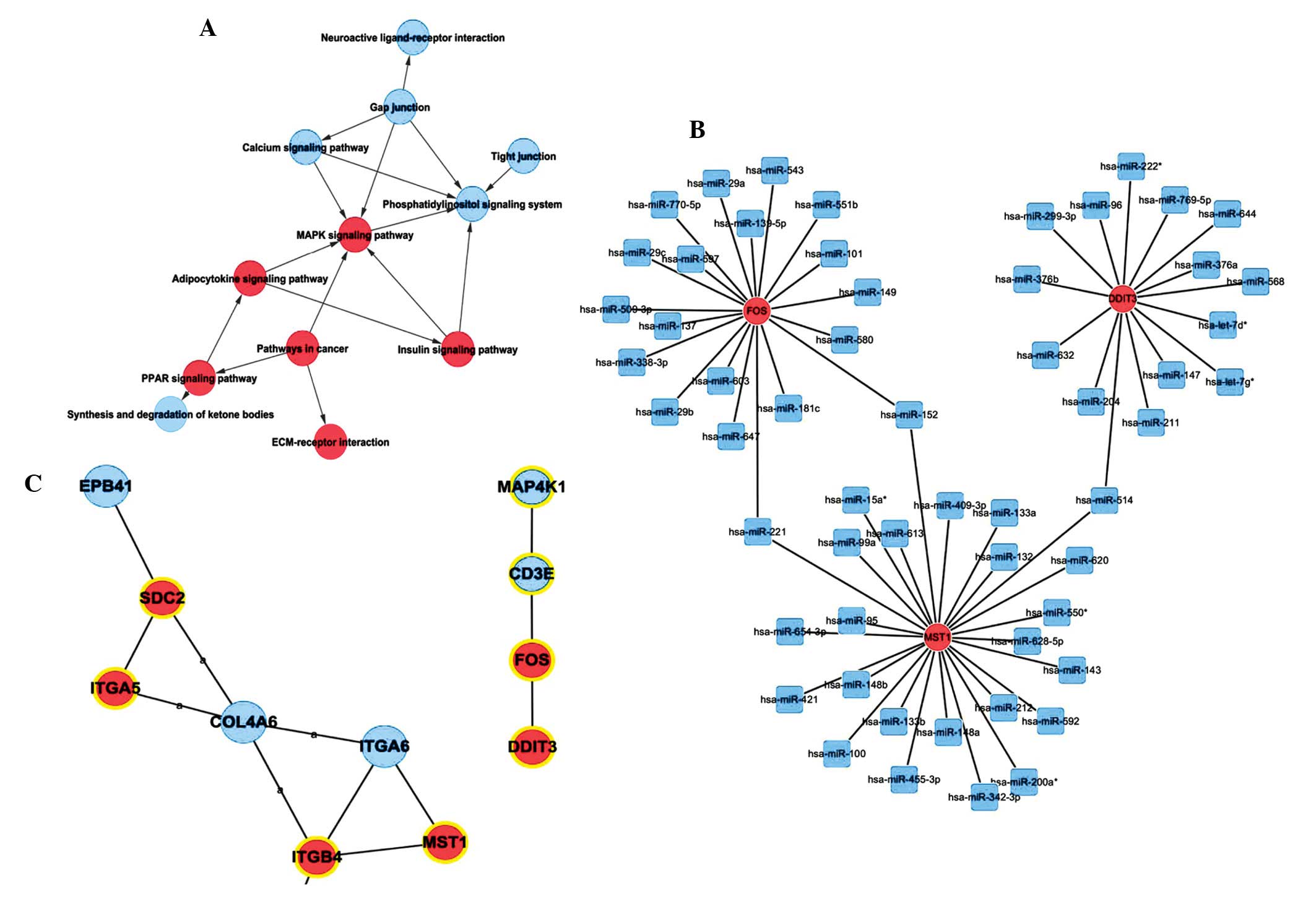
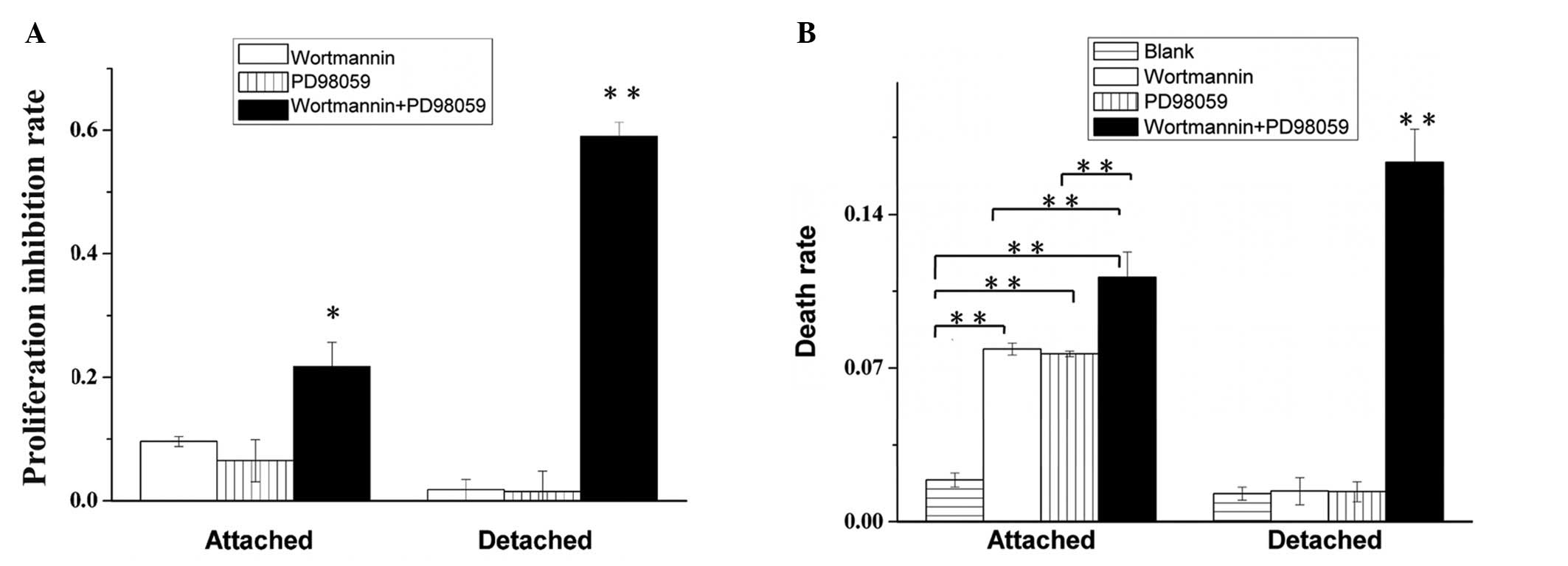
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mazzocca A and Carloni V: The metastatic
process: methodological advances and pharmacological challenges.
Curr Med Chem. 16:1704–1717. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sleeman J and Steeg PS: Cancer metastasis
as a therapeutic target. Eur J Cancer. 46:1177–1180. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loberg RD, Fridman Y, Pienta BA, Keller
ET, McCauley LK, Taichman RS and Pienta KJ: Detection and isolation
of circulating tumor cells in urologic cancers: a review.
Neoplasia. 6:302–309. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Simpson CD, Anyiwe K and Schimmer AD:
Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 272:177–185.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Frisch SM: Evidence for a function of
death-receptor-related, death-domain-containing proteins in
anoikis. Curr Biol. 9:1047–1049. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Derouet M, Wu X, May L, Hoon Yoo B,
Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, et al: Acquisition of anoikis resistance
promotes the emergence of oncogenic K-ras mutations in colorectal
cancer cells and stimulates their tumorigenicity in vivo.
Neoplasia. 9:536–545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Z, Cao L, Li J, Liang X, Liu Y, Liu
H, et al: Acquisition of anoikis resistance reveals a synoikis-like
survival style in BEL7402 hepatoma cells. Cancer Lett. 267:106–115.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geiger TR and Peeper DS: Critical role for
TrkB kinase function in anoikis suppression, tumorigenesis, and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 67:6221–6229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Lu H, Dazin P and Kapila Y:
Squamous cell carcinoma cell aggregates escape suspension-induced,
p53-mediated anoikis: fibronectin and integrin alphav mediate
survival signals through focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem.
279:48342–48349. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol.
124:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frisch SM and Screaton RA: Anoikis
mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 13:555–562. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christofori G: Changing neighbours,
changing behaviour: cell adhesion molecule-mediated signalling
during tumour progression. EMBO J. 22:2318–2323. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cao L, Han L, Zhang Z, Li J, Qu Z, Du J,
et al: Involvement of anoikis-resistance in the metastasis of
hepatoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 315:1148–1156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aplin AE, Howe A, Alahari SK and Juliano
RL: Signal transduction and signal modulation by cell adhesion
receptors: the role of integrins, cadherins, immunoglobulin-cell
adhesion molecules, and selectins. Pharmacol Rev. 50:197–263.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giancotti FG and Ruoslahti E: Integrin
signaling. Science. 285:1028–1032. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J,
Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E and Peeper DS: Suppression of anoikis
and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB.
Nature. 430:1034–1039. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhan M, Zhao H and Han ZC: Signalling
mechanisms of anoikis. Histol Histopathol. 19:973–983. 2004.
|
|
20
|
Saxena NK, Sharma D, Ding X, Lin S, Marra
F, Merlin D and Anania FA: Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT,
PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated
promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 67:2497–2507. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Díaz-Montero CM, Wygant JN and McIntyre
BW: PI3-K/Akt-mediated anoikis resistance of human osteosarcoma
cells requires Src activation. Eur J Cancer. 42:1491–1500.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Horowitz JC, Rogers DS, Sharma V, Vittal
R, White ES, Cui Z and Thannickal VJ: Combinatorial activation of
FAK and AKT by transforming growth factor-beta1 confers an
anoikis-resistant phenotype to myofibroblasts. Cell Signal.
19:761–771. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Collins NL, Reginato MJ, Paulus JK, Sgroi
DC, Labaer J and Brugge JS: G1/S cell cycle arrest provides anoikis
resistance through Erk-mediated Bim suppression. Mol Cell Biol.
25:5282–5291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fukazawa H, Noguchi K, Murakami Y and
Uehara Y: Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors restore anoikis sensitivity in human
breast cancer cell lines with a constitutively activated
extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Mol Cancer Ther.
1:303–309. 2002.
|
|
25
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y
and Hattori M: The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome.
Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D277–D280. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yi M, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH and
Stephens RM: WholePathwayScope: a comprehensive pathway-based
analysis tool for high-throughput data. BMC Bioinformatics.
7:302006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Draghici S, Khatri P, Tarca AL, Amin K,
Done A, Voichita C, et al: A systems biology approach for pathway
level analysis. Genome Res. 17:1537–1545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jansen R, Greenbaum D and Gerstein M:
Relating whole-genome expression data with protein-protein
interactions. Genome Res. 12:37–46. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C and Li H: Network-constrained
regularization and variable selection for analysis of genomic data.
Bioinformatics. 24:1175–1182. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wei Z and Li H: A Markov random field
model for network-based analysis of genomic data. Bioinformatics.
23:1537–1544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang JD and Wiemann S: KEGGgraph: a graph
approach to KEGG PATHWAY in R and bioconductor. Bioinformatics.
25:1470–1471. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spirin V and Mirny LA: Protein complexes
and functional modules in molecular networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:12123–12128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee ER, Kim JY, Kang YJ, Ahn JY, Kim JH,
Kim BW, et al: Interplay between PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling
pathways in DNA-damaging drug-induced apoptosis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1763:958–968. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rul W, Zugasti O, Roux P, Peyssonnaux C,
Eychene A, Franke TF, et al: Activation of ERK, controlled by Rac1
and Cdc42 via Akt, is required for anoikis. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
973:145–148. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ishida K, Nagahara H, Kogiso T, Aso T,
Hayashi N and Akaike T: Cell adhesion aside from integrin system
can abrogate anoikis in rat liver cells by down-regulation of FasL
expression, not by activation of PI-3K/Akt and ERK signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 300:201–208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choi EM, Kwak SJ, Kim YM, Ha KS, Kim JI,
Lee SW and Han SJ: COX-2 inhibits anoikis by activation of the
PI-3K/Akt pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Exp Mol Med.
37:199–203. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zugasti O, Rul W, Roux P, Peyssonnaux C,
Eychene A, Franke TF, et al: Raf-MEK-Erk cascade in anoikis is
controlled by Rac1 and Cdc42 via Akt. Mol Cell Biol. 21:6706–6717.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang W and Liu HT: MAPK signal pathways
in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell
Res. 12:9–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|