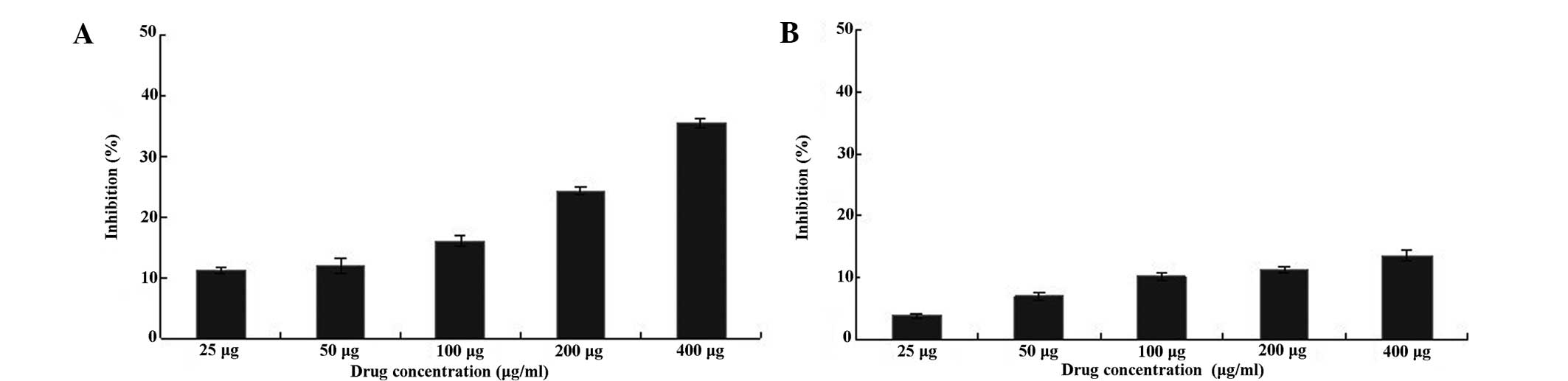
|
1
|
Hibbett DS, Binder M, Bischoff JF,
Blackwell M, Cannon PF, Eriksson OE, et al: A higher level
phylogenetic classification of the Fungi. Mycol Res. 111:509–547.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bertozzi CR and Kiessling LL: Chemical
glycobiology. Science. 291:2357–2364. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wasser SP: Medicinal mushrooms as a source
of antitumor and immunomodulating polysaccharides. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 60:258–274. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Borchers AT, Stern JS, Hackman RM, Keen CL
and Gershwin ME: Mushrooms, tumors, and immunity. Proc Soc Exp Biol
Med. 221:281–293. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rudd PM, Elliott T, Cresswell P, Wilson IA
and Dwek RA: Glycosylation and the immune system. Science.
291:2370–2376. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen Y, Xie MY, Nie SP, Li C and Wang YX:
Purification, composition analysis and antioxidant activity of a
polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma atrum.
Food Chem. 107:231–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Angeli JP, Ribeiro LR, Gonzaga ML, de
Soares SA, Ricardo MP, Tsuboy MS, Stidl R, Knasmueller S, Linhares
RE and Mantovani MS: Protective effects of beta-glucan extracted
from Agaricus brasiliensis against chemically induced DNA
damage in human lymphocytes. Cell Biol Toxicol. 22:285–291.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li SP, Zhao KJ, Ji ZN, Song ZH, Dong TT,
Lo CK, Cheung JK, Zhu SQ and Tsim KW: A polysaccharide isolated
from Cordyceps sinensis, a traditional Chinese medicine,
protects PC12 cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury. Life
Sci. 73:2503–2513. 2003.
|
|
9
|
Hetland G, Johnson E, Lyberg T,
Bernardshaw S, Tryggestad AM and Grinde B: Effects of the medicinal
mushroom Agaricus blazei Murill on immunity, infection and
cancer. Scand J Immunol. 68:363–370. 2008.
|
|
10
|
Firenzuoli F, Gori L and Lombardo G: The
medicinal mushroom Agaricus blazei Murrill: Review of literature
and pharmaco-toxicological problems. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 5:3–15. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paterson RR: Ganoderma - a therapeutic
fungal biofactory. Phytochemistry. 67:1985–2001. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Paterson RR: Cordyceps: a traditional
Chinese medicine and another fungal therapeutic biofactory?
Phytochemistry. 69:1469–1495. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sullivan R, Smith JE and Rowan NJ:
Medicinal mushrooms and cancer therapy: translating a traditional
practice into Western medicine. Perspect Biol Med. 49:159–170.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang P, Liang M, Zhang Y and Shen B:
Clinical application of a combination therapy of lentinan,
multi-electrode RFA and TACE in HCC. Adv Ther. 25:787–794. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fisher M and Yang LX: Anticancer effects
and mechanisms of polysaccharide-K (PSK): implications of cancer
immunotherapy. Anticancer Res. 22:1737–1754. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding X, Hou YL and Hou WR: Structure
elucidation and antioxidant activity of a novel polysaccharide
isolated from Boletus speciosus Frost. Int J Biol Macromol.
50:613–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Staub AM: Removal of proteins - Sevag
method. Methods Carbohydr Chem. 5:5–6. 1965.
|
|
18
|
Dubois M, Gillis KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers
PA and Smith F: Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and
related substances. Anal Chem. 28:350–356. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shantha LK, Lynette D and Andrew L:
Preparation and characterisation of chitosan microspheres for
antioxidant delivery. Carbohydr Poly. 64:163–167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yin Z, Jia R, Gao P, Gao R, Jiang D, Liu K
and Liu S: Preparation of contraceptive pill microcapsule and its
anti-fertility effect. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.
21:979–982. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Cho JS, Kwon A and Cho CG:
Microencapsulation of octadecane as a phase-change material by
interfacial polymerization in an emulsion system. Colloid Polym
Sci. 280:260–266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Keller R, Geiges M and Keist R:
L-arginine-dependent reactive nitrogen intermediates as mediators
of tumor cell killing by activated macrophages. Cancer Res.
50:1421–1425. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Anna S, Harald DH and Stöver X: Polymer
microcapsules by interfacial polyaddition between styrene-maleic
anhydride copolymers and amines. J Membr Sci. 209:421–432. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rasenack N, Hartenhauer H and Müller BW:
Microcrystals for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly
water-soluble drugs. Int J Pharm. 254:137–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ooi VE and Liu F: Immunomodulation and
anti-cancer activity of polysaccharide-protein complexes. Curr Med
Chem. 7:715–729. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fidler IJ and Kleinerman ES: Therapy of
cancer metastasis by systemic activation of macrophages; from bench
to the clinic. Res Immunol. 144:284–287; discussion 294–298. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Flick DA and Gifford GE: Comparison of in
vitro cell cytotoxicity assays for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol
Methods. 68:167–175. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Klostergaard J: Macrophage tumoricidal
mechanisms. Res Immunol. 144:274–276. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Klimp AH, deVries EG, Scherphof GL and
Daemen T: A potential role of macrophage activation in the
treatment of cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 44:143–161. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Goossens V, Grooten J, De Vos K and Fiers
W: Direct evidence for tumor necrosis factor-induced mitochondrial
reactive oxygen intermediates and their involvement in
cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:8115–8119. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kröncke KD, Fehsel K and Kolb-Bachofen V:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase and its product nitric oxide, a
small molecule with complex biological activities. Biol Chem Hoppe
Seyler. 376:327–343. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yu L, Li HZ, Lu SM, Liu WW, Li JF, Wang HB
and Xu W: Alteration in TWIST expression: possible role in
paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2
cell line. Croat Med J. 50:536–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nutting CM, Robinson M and Birchall M:
Survival from laryngeal cancer in England and Wales up to 2001. Br
J Cancer. 99(Suppl 1): S38–S39. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen CC and Chan WH: Inhibition of
citrinin-induced apoptotic biochemical signaling in human hepatoma
G2 cells by resveratrol. Int J Mol Sci. 10:3338–3357. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|