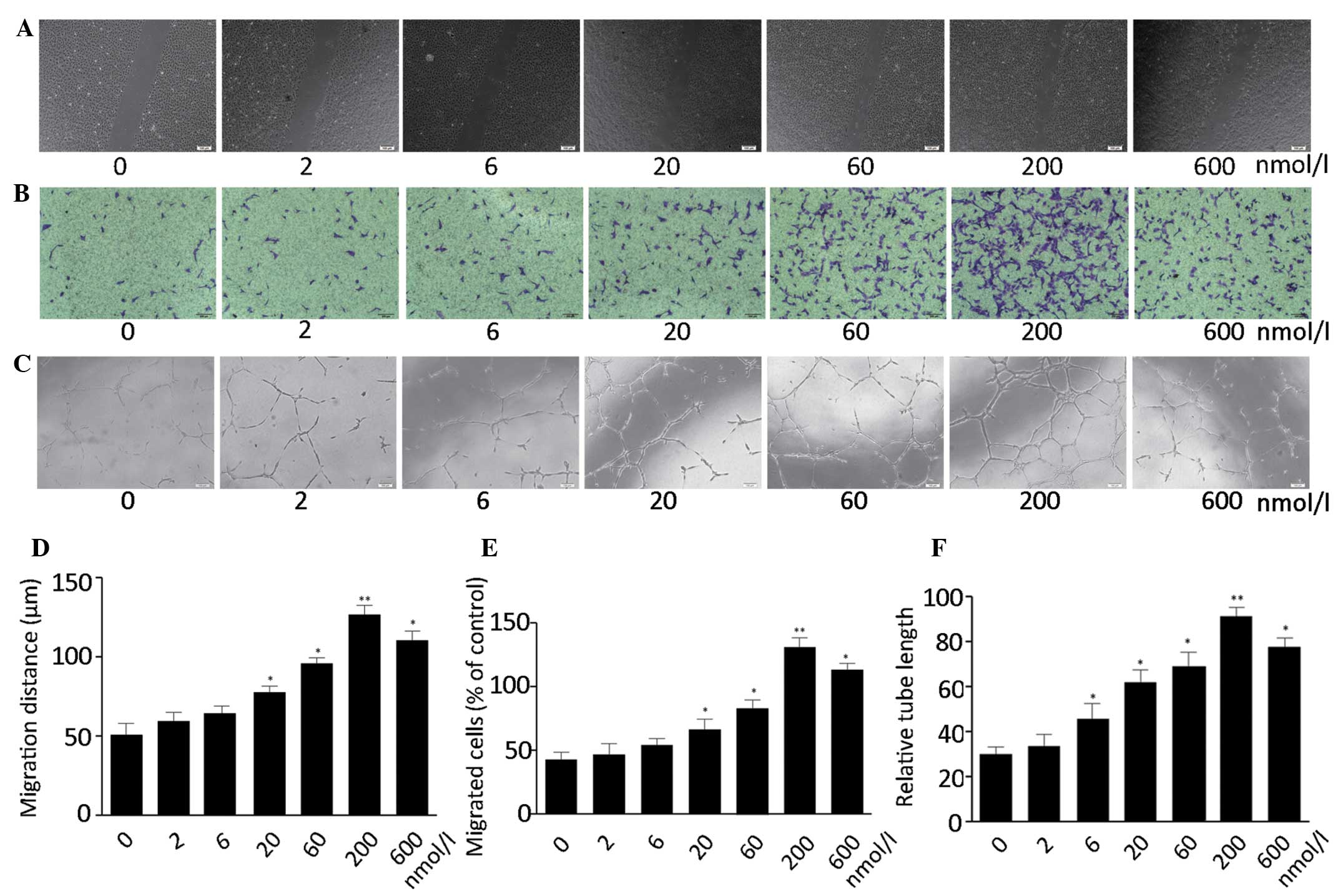
|
1
|
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, et al:
Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand
for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:471–476. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kawamata Y, Habata Y, Fukusumi S, et al:
Molecular properties of apelin: tissue distribution and receptor
binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1538:162–171. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kälin RE, Kretz MP, Meyer AM, et al:
Paracrine and autocrine mechanisms of apelin signaling govern
embryonic and tumor angiogenesis. Dev Biol. 305:599–614.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hosoya M, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, et al:
Molecular and functional characteristics of APJ. Tissue
distribution of mRNA and interaction with the endogenous ligand
apelin. J Biol Chem. 275:21061–21067. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
O’Carroll AM, Selby TL, Palkovits M and
Lolait SJ: Distribution of mRNA encoding B78/apj, the rat homologue
of the human APJ receptor, and its endogenous ligand apelin in
brain and peripheral tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1492:72–80.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng X, Cheng XS and Pang CC: Venous
dilator effect of apelin, an endogenous peptide ligand for the
orphan APJ receptor, in conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol.
470:171–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Szokodi I, Tavi P, Földes G, et al:
Apelin, the novel endogenous ligand of the orphan receptor APJ,
regulates cardiac contractility. Circ Res. 91:434–440. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farkasfalvi K, Stagg MA, Coppen SR, et al:
Direct effects of apelin on cardiomyocyte contractility and
electrophysiology. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 357:889–895. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ribatti D, Vacca A, Roncali L and Dammacco
F: The chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane as a model for in vivo
research on angiogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 40:1189–1197.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mu J, Brozinick JT Jr, Valladares O, Bucan
M and Birnbaum MJ: A role for AMP-activated protein kinase in
contraction- and hypoxia-regulated glucose transport in skeletal
muscle. Mol Cell. 7:1085–1094. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nagata D, Mogi M and Walsh K:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells
is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress. J Biol
Chem. 278:31000–31006. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu S, Sun F, Li W, et al: Apelin
stimulates glucose uptake through the PI3K/Akt pathway and improves
insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Cell Biochem.
353:305–313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yue P, Jin H, Xu S, et al: Apelin
decreases lipolysis via G(q), G(i), and AMPK-Dependent Mechanisms.
Endocrinology. 152:59–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chandra SM, Razavi H, Kim J, et al:
Disruption of the apelin-APJ system worsens hypoxia-induced
pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:814–820.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shiojima I and Walsh K: Role of Akt
signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res.
90:1243–1250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morales-Ruiz M, Fulton D, Sowa G, Languino
LR, Fujio Y, Walsh K and Sessa WC: Vascular endothelial growth
factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial
cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ Res.
86:892–896. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Luo Z, Fujio Y, Kureishi Y, et al: Acute
modulation of endothelial Akt/PKB activity alters nitric
oxide-dependent vasomotor activity in vivo. J Clin Invest.
106:493–499. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Witzenbichler B, Kureishi Y, Luo Z, Le
Roux A, Branellec D and Walsh K: Regulation of smooth muscle cell
migration and integrin expression by the Gax transcription factor.
J Clin Invest. 104:1469–1480. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kureishi Y, Luo Z, Shiojima I, et al: The
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor simvastatin activates the protein
kinase Akt and promotes angiogenesis in normocholesterolemic
animals. Nat Med. 6:1004–1010. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagata D, Suzuki E, Nishimatsu H, et al:
Cyclin A downregulation and p21(cip1) upregulation correlate with
GATA-6-induced growth arrest in glomerular mesangial cells. Circ
Res. 87:699–704. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kovacic S, Soltys CL, Barr AJ, Shiojima I,
Walsh K and Dyck JR: Akt activity negatively regulates
phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart. J
Biol Chem. 278:39422–39427. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kleinz MJ and Davenport AP:
Immunocytochemical localization of the endogenous vasoactive
peptide apelin to human vascular and endocardial endothelial cells.
Regul Pept. 118:119–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Eyries M, Siegfried G, Ciumas M, Montagne
K, Agrapart M, Lebrin F and Soubrier F: Hypoxia-induced apelin
expression regulates endothelial cell proliferation and
regenerative angiogenesis. Circ Res. 103:432–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Masri B, Morin N, Cornu M, Knibiehler B
and Audigier Y: Apelin (65–77) activates p70 S6 kinase and is
mitogenic for umbilical endothelial cells. FASEB J. 18:1909–1911.
2004.
|
|
25
|
Zheng S, Li W, Xu M, et al: Calcitonin
gene-related peptide promotes angiogenesis via AMP-activated
protein kinase. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 299:C1485–C1492. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Radisavljevic Z, Avraham H and Avraham S:
Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulates ICAM-1 expression
via the phosphatidylinositol 3 OH-kinase/AKT/Nitric oxide pathway
and modulates migration of brain microvascular endothelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 275:20770–20774. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Morrow VA, Foufelle F, Connell JM, Petrie
JR, Gould GW and Salt IP: Direct activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase stimulates nitric-oxide synthesis in human aortic
endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 278:31629–31639. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu Z, Fu C, Li X, et al: Prostaglandin E2
promotes endothelial differentiation from bone marrow-derived cells
through AMPK activation. PLoS One. 6:e235542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Su KH, Yu YB, Hou HH, et al: AMP-activated
protein kinase mediates erythropoietin-induced activation of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Cell Physiol. 227:3053–3062.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Izumi Y, Shiota M, Kusakabe H, et al:
Pravastatin accelerates ischemia-induced angiogenesis through
AMP-activated protein kinase. Hypertens Res. 32:675–679. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tao J, Zhu W, Li Y, et al: Apelin-13
protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through
inhibition of ER-dependent apoptotic pathways in a time-dependent
fashion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1471–H1486. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rastaldo R, Cappello S, Folino A, et al:
Apelin-13 limits infarct size and improves cardiac postischemic
mechanical recovery only if given after ischemia. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H2308–H2315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|