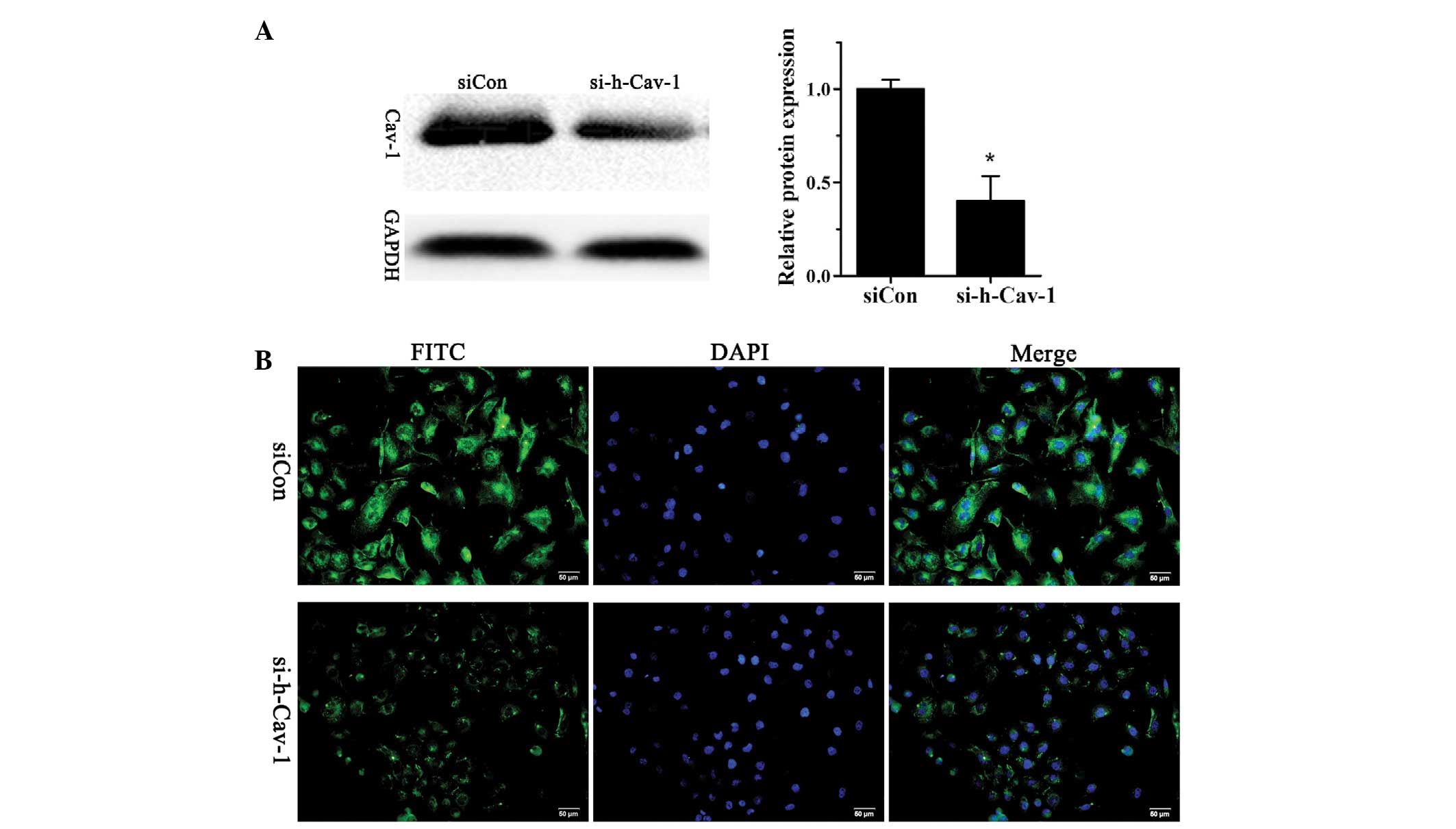
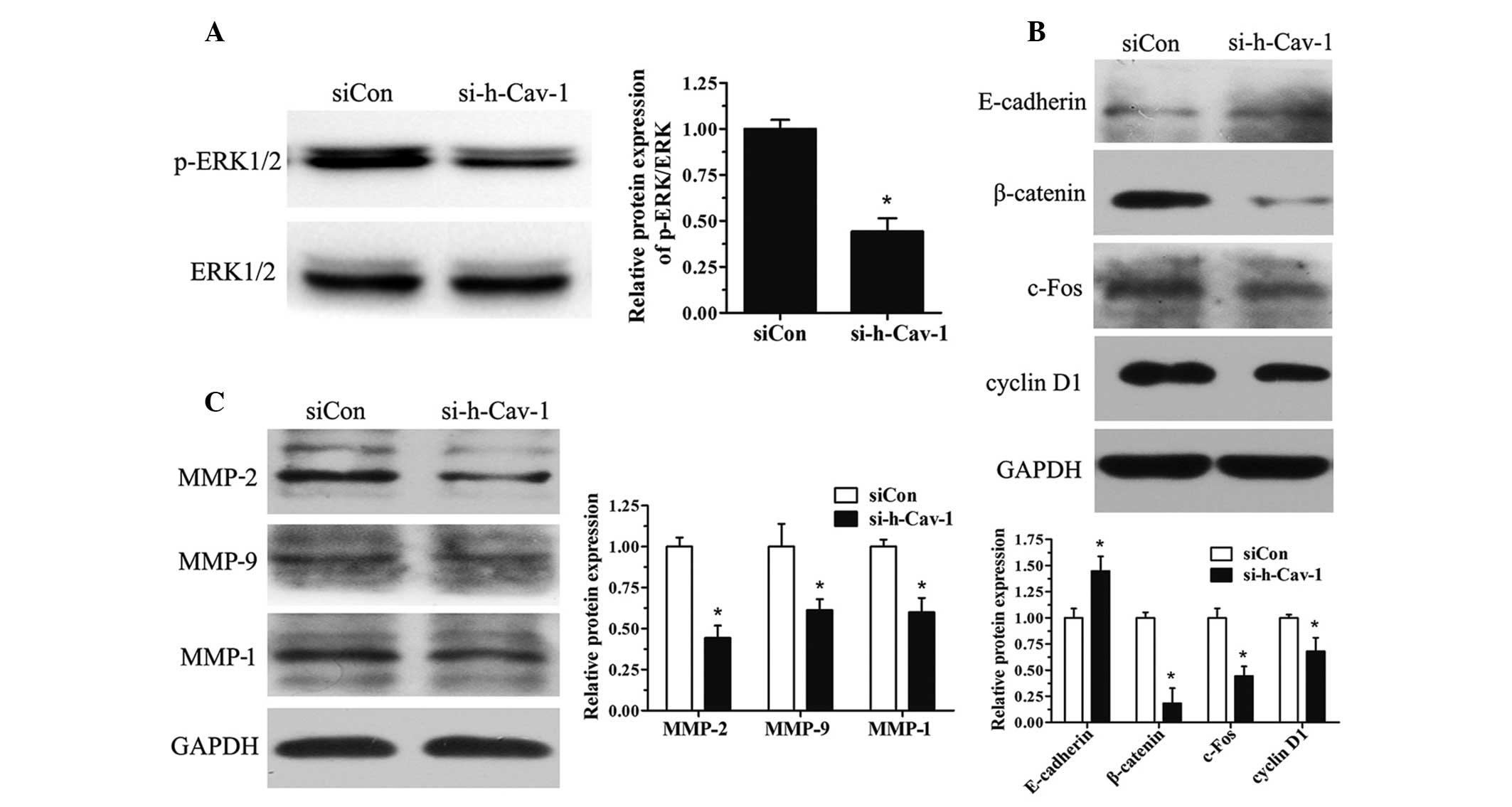
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shaul PW and Anderson RG: Role of
plasmalemmal caveolae in signal transduction. Am J Physiol.
275:L843–L851. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Williams TM and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 in
oncogenic transformation, cancer, and metastasis. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 288:C494–C506. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cokakli M, Erdal E, Nart D, et al:
Differential expression of Caveolin-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma:
correlation with differentiation state, motility and invasion. BMC
Cancer. 9:652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cerezo A, Guadamillas MC, Goetz JG, et al:
The absence of caveolin-1 increases proliferation and
anchorage-independent growth by a Rac-dependent, Erk-independent
mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 29:5046–5059. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang G, Truong LD, Wheeler TM and Thompson
TC: Caveolin-1 expression in clinically confined human prostate
cancer: a novel prognostic marker. Cancer Res. 59:5719–5723.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Joo HJ, Oh DK, Kim YS, Lee KB and Kim SJ:
Increased expression of caveolin-1 and microvessel density
correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis in clear cell renal
cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 93:291–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kato K, Hida Y, Miyamoto M, et al:
Overexpression of caveolin-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
correlates with lymph node metastasis and pathologic stage. Cancer.
94:929–933. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu P, Wang X, Li F, Qi B, Zhu H, et al:
Growth suppression of MCF-7 cancer cell-derived xenografts in nude
mice by caveolin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 376:215–220. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Urra H, Torres VA, Ortiz RJ, et al:
Caveolin-1-enhanced motility and focal adhesion turnover require
tyrosine-14 but not accumulation to the rear in metastatic cancer
cells. PLoS One. 7:e330852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Elsheikh SE, Green AR, Rakha EA, et al:
Caveolin 1 and Caveolin 2 are associated with breast cancer
basal-like and triple-negative immunophenotype. Br J Cancer.
99:327–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han F, Gu D, Chen Q and Zhu H: Caveolin-1
acts as a tumor suppressor by down-regulating epidermal growth
factor receptor-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Pancreas. 38:766–774. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sunaga N, Miyajima K, Suzuki M, et al:
Different roles for caveolin-1 in the development of non-small cell
lung cancer versus small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
64:4277–4285. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Felicetti F, Parolini I, Bottero L, et al:
Caveolin-1 tumor-promoting role in human melanoma. Int J Cancer.
125:1514–1522. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Savage K, Lambros MB, Robertson D, et al:
Caveolin 1 is overexpressed and amplified in a subset of basal-like
and metaplastic breast carcinomas: a morphologic, ultrastructural,
immunohistochemical, and in situ hybridization analysis. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:90–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Van den Eynden GG, Van Laere SJ, Van der
Auwera I, et al: Overexpression of caveolin-1 and -2 in cell lines
and in human samples of inflammatory breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 95:219–228. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fiucci G, Ravid D, Reich R and Liscovitch
M: Caveolin-1 inhibits anchorage-independent growth, anoikis and
invasiveness in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
21:2365–2375. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Williams TM, Medina F, Badano I, et al:
Caveolin-1 gene disruption promotes mammary tumorigenesis and
dramatically enhances lung metastasis in vivo. Role of Cav-1 in
cell invasiveness and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-2/9) secretion.
J Biol Chem. 279:51630–51646. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salatino M, Beguelin W, Peters MG, et al:
Progestin-induced caveolin-1 expression mediates breast cancer cell
proliferation. Oncogene. 25:7723–7739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams TM, Lee H, Cheung MW, et al:
Combined loss of INK4a and caveolin-1 synergistically enhances cell
proliferation and oncogene-induced tumorigenesis: role of
INK4a/CAV-1 in mammary epithelial cell hyperplasia. J Biol Chem.
279:24745–24756. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Williams TM, Sotgia F, Lee H, et al:
Stromal and epithelial caveolin-1 both confer a protective effect
against mammary hyperplasia and tumorigenesis: Caveolin-1
antagonizes cyclin D1 function in mammary epithelial cells. Am J
Pathol. 169:1784–1801. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Boström P, Söderström M, Palokangas T, et
al: Analysis of cyclins A, B1, D1 and E in breast cancer in
relation to tumour grade and other prognostic factors. BMC Res
Notes. 2:1402009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arteaga CL and Holt JT: Tissue-targeted
antisense c-fos retroviral vector inhibits established breast
cancer xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res. 56:1098–1103.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wend P, Runke S, Wend K, et al:
WNT10B/β-catenin signalling induces HMGA2 and proliferation in
metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 5:264–279.
2013.
|
|
25
|
Selleri S, Arnaboldi F, Palazzo M, Hussein
U, Balsari A and Rumio C: Caveolin-1 is expressed on multipotent
cells of hair follicles and might be involved in their resistance
to chemotherapy. Br J Dermatol. 153:506–513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ho CC, Kuo SH, Huang PH, Huang HY, Yang CH
and Yang PC: Caveolin-1 expression is significantly associated with
drug resistance and poor prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer patients treated with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Lung
Cancer. 59:105–110. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu Z, Ghosh S, Wang Z and Hunter T:
Downregulation of caveolin-1 function by EGF leads to the loss of
E-cadherin, increased transcriptional activity of beta-catenin, and
enhanced tumor cell invasion. Cancer Cell. 4:499–515. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu D, Guo H, Li Y, Xu X, Yang K and Bai
Y: Association between polymorphisms in the promoter regions of
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and risk of cancer metastasis: a
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e312512012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumour cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Prasad CP, Chaurasiya SK, Axelsson L and
Andersson T: WNT-5A triggers Cdc42 activation leading to an ERK1/2
dependent decrease in MMP9 activity and invasive migration of
breast cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 7:870–883. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|