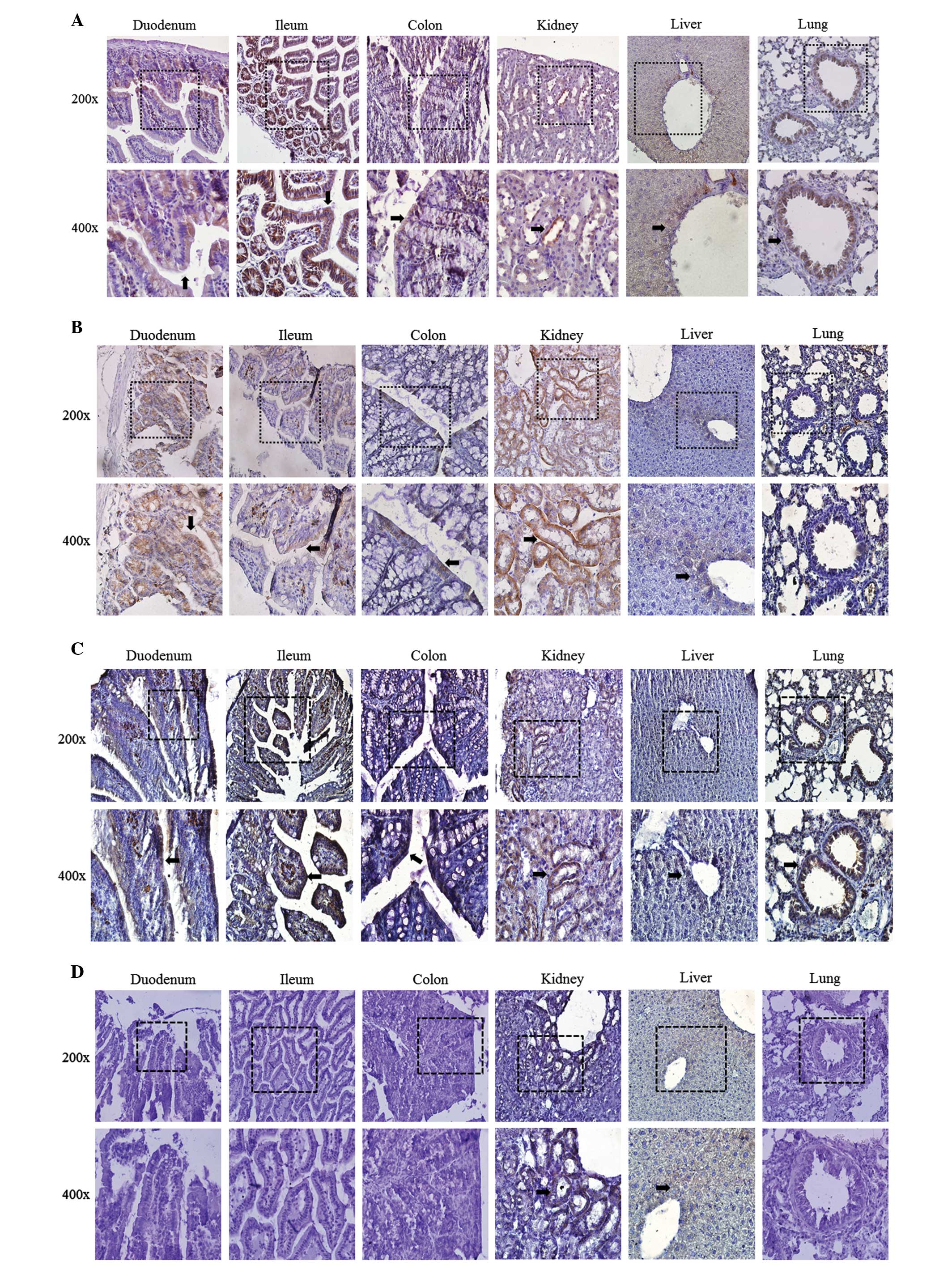
|
1
|
Wen H, Watry DD, Marcondes MC and Fox HS:
Selective decrease in paracellular conductance of tight junctions:
role of the first extracellular domain of claudin-5. Mol Cell Biol.
24:8408–8417. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, et al:
Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight
junctions of epithelial cells. J Cell Sci. 115:4969–4976. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hou J, Paul DL and Goodenough DA:
Paracellin-1 and the modulation of ion selectivity of tight
junctions. J Cell Sci. 118:5109–5118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Colegio OR, Van Itallie C, Rahner C and
Anderson JM: Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular
charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril
architecture. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 284:C1346–C1354. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Alexandre MD, Jeansonne BG, Renegar RH,
Tatum R and Chen YH: The first extracellular domain of claudin-7
affects paracellular Cl- permeability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
357:87–91. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van Itallie CM, Rogan S, Yu A, Vidal LS,
Holmes J and Anderson JM: Two splice variants of claudin-10 in the
kidney create paracellular pores with different ion selectivities.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 291:F1288–F1299. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM: Claudins
and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol.
68:403–429. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krug SM, Günzel D, Conrad MP, et al:
Charge-selective claudin channels. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1257:20–28.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schulzke JD, Günzel D, John LJ and Fromm
M: Perspectives on tight junction research. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1257:1–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Günzel D, Stuiver M, Kausalya PJ, et al:
Claudin-10 exists in six alternatively spliced isoforms that
exhibit distinct localization and function. J Cell Sci.
122:1507–1517. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Myal Y, Leygue E and Blanchard AA: Claudin
1 in breast tumorigenesis: revelation of a possible novel ‘claudin
high’ subset of breast cancers. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:9568972010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inai T, Kobayashi J and Shibata Y:
Claudin-1 contributes to the epithelial barrier function in MDCK
cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 78:849–855. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weber CR, Nalle SC, Tretiakova M, Rubin DT
and Turner JR: Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in
inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic
transformation. Lab Invest. 88:1110–1120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Van Itallie C, Rahner C and Anderson JM:
Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular
conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J
Clin Invest. 107:1319–1327. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hou J, Renigunta A, Yang J and Waldegger
S: Claudin-4 forms paracellular chloride channel in the kidney and
requires claudin-8 for tight junction localization. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 107:18010–18015. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujita H, Sugimoto K, Inatomi S, et al:
Tight junction proteins claudin-2 and -12 are critical for vitamin
D-dependent Ca2+ absorption between enterocytes. Mol
Biol Cell. 19:1912–1921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hou J, Renigunta A, Konrad M, et al:
Claudin-16 and claudin-19 interact and form a cation-selective
tight junction complex. J Clin Invest. 118:619–628. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chao YC, Pan SH, Yang SC, et al: Claudin-1
is a metastasis suppressor and correlates with clinical outcome in
lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:123–133. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kitajiri SI, Furuse M, Morita K, et al:
Expression patterns of claudins, tight junction adhesion molecules,
in the inner ear. Hear Res. 187:25–34. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Brännström M, Janson PO and
Sundfeldt K: Differences in expression patterns of the tight
junction proteins, claudin 1, 3, 4 and 5, in human ovarian surface
epithelium as compared to epithelia in inclusion cysts and
epithelial ovarian tumours. Int J Cancer. 118:1884–1891. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H and Tsukita
S: Conversion of zonulae occludentes from tight to leaky strand
type by introducing claudin-2 into Madin-Darby canine kidney I
cells. J Cell Biol. 153:263–272. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reyes JL, Lamas M, Martin D, et al: The
renal segmental distribution of claudins changes with development.
Kidney Int. 62:476–487. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rahner C, Mitic LL and Anderson JM:
Heterogeneity in expression and subcellular localization of
claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in the rat liver, pancreas, and gut.
Gastroenterology. 120:411–422. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wolburg H, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Liebner S
and Engelhardt B: Claudin-1, claudin-2 and claudin-11 are present
in tight junctions of choroid plexus epithelium of the mouse.
Neurosci Lett. 307:77–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Muto S, Hata M, Taniguchi J, et al:
Claudin-2-deficient mice are defective in the leaky and
cation-selective paracellular permeability properties of renal
proximal tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:8011–8016. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hawkins BT and Davis TP: The blood-brain
barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev.
57:173–185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Belanger M, Asashima T, Ohtsuki S,
Yamaguchi H, Ito S and Terasaki T: Hyperammonemia induces transport
of taurine and creatine and suppresses claudin-12 gene expression
in brain capillary endothelial cells in vitro. Neurochem Int.
50:95–101. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujita H, Chiba H, Yokozaki H, et al:
Differential expression and subcellular localization of claudin-7,
-8, -12, -13 and -15 along the mouse intestine. J Histochem
Cytochem. 54:933–944. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brandner JM, McIntyre M, Kief S,
Wladykowski E and Moll I: Expression and localization of tight
junction-associated proteins in human hair follicles. Arch Dermatol
Res. 295:211–221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Simon DB, Lu Y, Choate KA, et al:
Paracellin-1, a renal tight junction protein required for
paracellular Mg2+ resorption. Science. 285:103–106.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Konrad M, Schaller A, Seelow D, et al:
Mutations in the tight-junction gene claudin 19 (CLDN19) are
associated with renal magnesium wasting, renal failure, and severe
ocular involvement. Am J Hum Genet. 79:949–957. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|