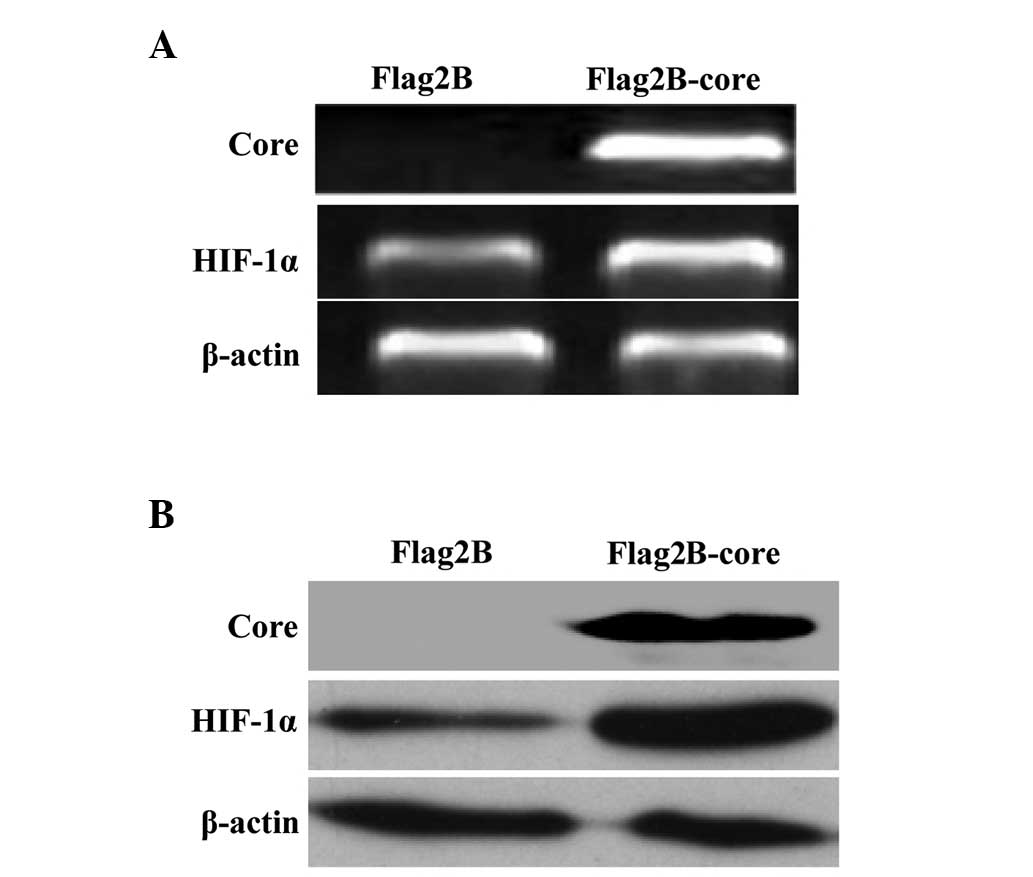
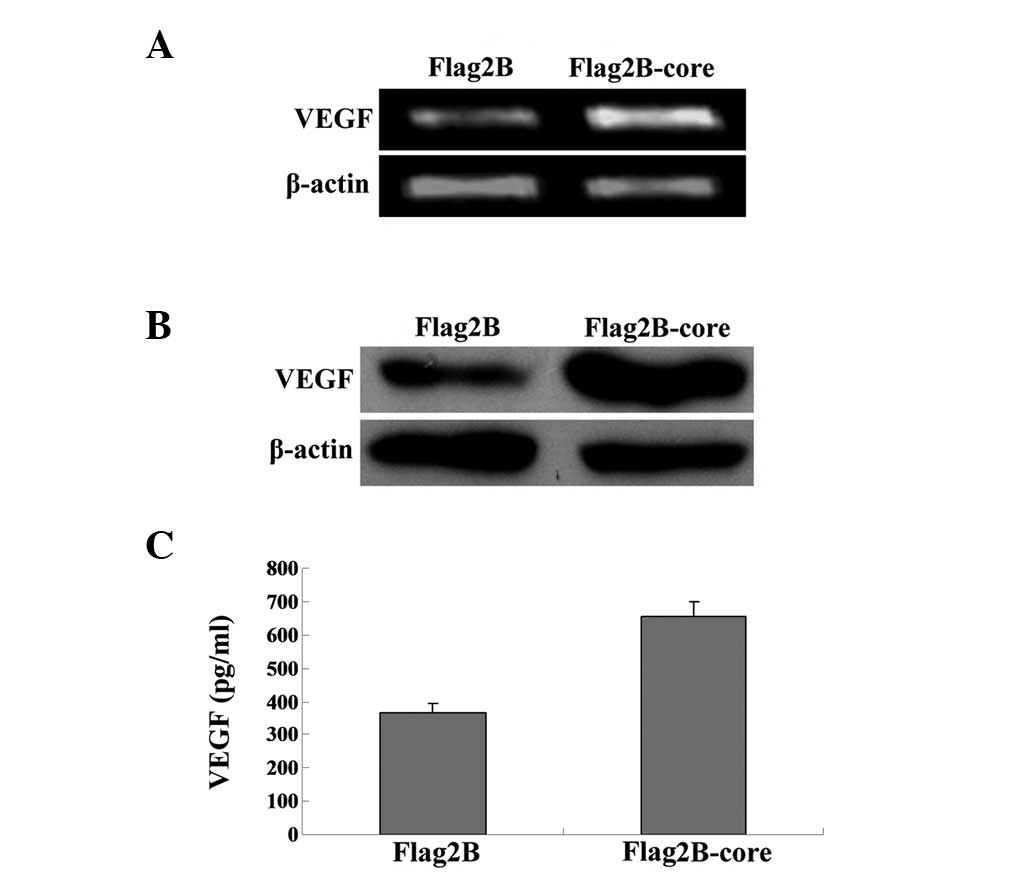
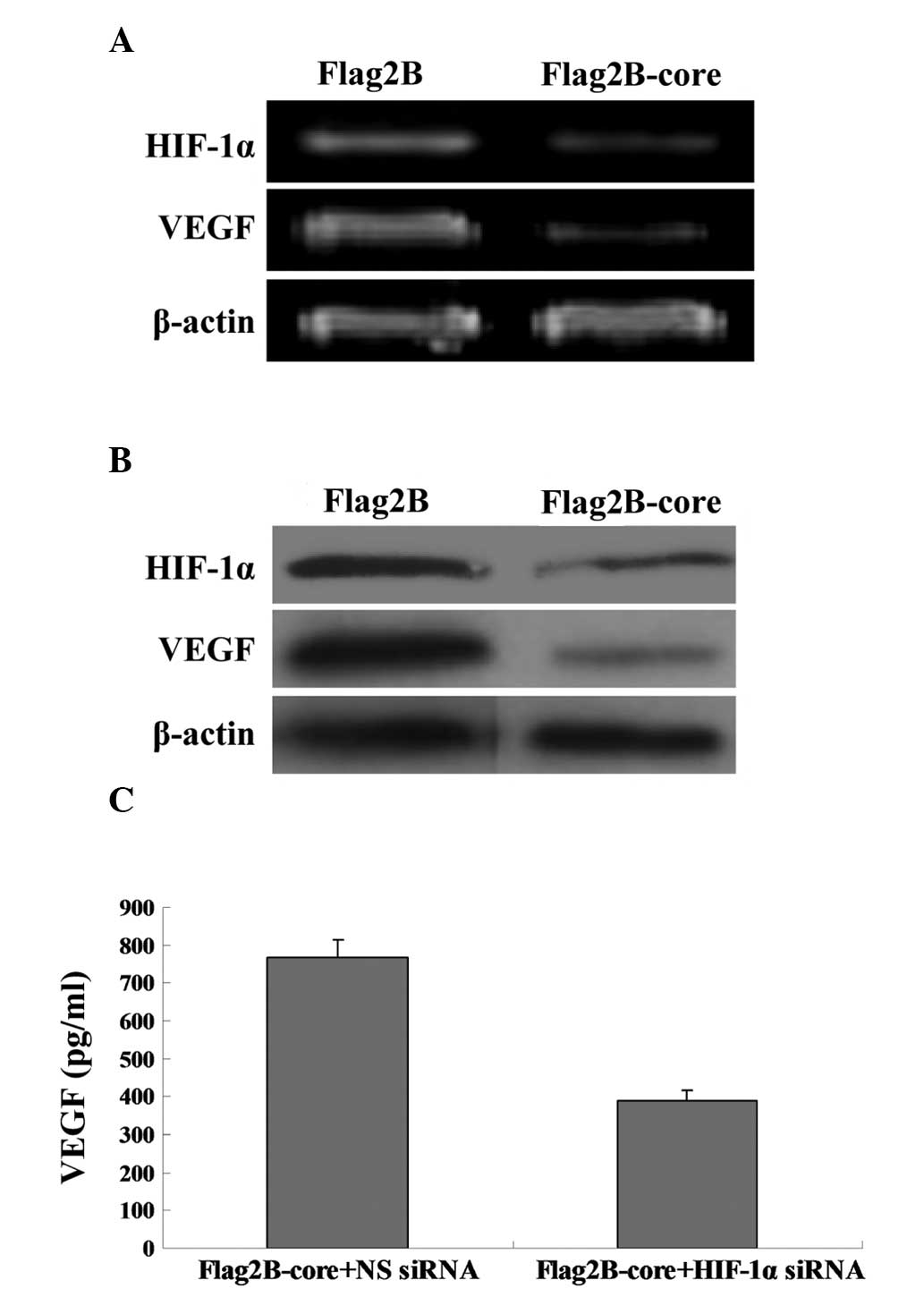
|
1
|
Raimondi S, Bruno S, Mondelli MU and
Maisonneuve P: Hepatitis C virus genotype 1b as a risk factor for
hepatocellular carcinoma development: a meta-analysis. J Hepatol.
50:1142–1154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yotsuyanagi H, Koike K, Yasuda K, et al:
Hepatitis C virus genotypes and development of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer. 76:1352–1355. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Francesco R: Molecular virology of the
hepatitis C virus. J Hepatol. 31(Suppl 1): 47–53. 1999.
|
|
4
|
Rosenberg S: Recent advances in the
molecular biology of hepatitis C virus. J Mol Biol. 313:451–464.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suzuki R, Suzuki T, Ishii K, Matsuura Y
and Miyamura T: Processing and functions of Hepatitis C virus
proteins. Intervirology. 42:145–152. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duong FH, Filipowicz M, Tripodi M, La
Monica N and Heim MH: Hepatitis C virus inhibits interferon
signaling through up-regulation of protein phosphatase 2A.
Gastroenterology. 126:263–277. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones DM, Patel AH, Targett-Adams P and
McLauchlan J: The hepatitis C virus NS4B protein can
trans-complement viral RNA replication and modulates production of
infectious virus. J Virol. 83:2163–2177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park CY, Jun HJ, Wakita T, Cheong JH and
Hwang SB: Hepatitis C virus nonstructural 4B protein modulates
sterol regulatory element-binding protein signaling via the AKT
pathway. J Biol Chem. 284:9237–9246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wagoner J, Austin M, Green J, et al:
Regulation of CXCL-8 (interleukin-8) induction by double-stranded
RNA signaling pathways during hepatitis C virus infection. J Virol.
81:309–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yi M, Ma Y, Yates J and Lemon SM:
Trans-complementation of an NS2 defect in a late step in hepatitis
C virus (HCV) particle assembly and maturation. PLoS Pathog.
5:e10004032009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Semenza GL: Regulation of oxygen
homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Physiology (Bethesda).
24:97–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roos-Mattjus P and Sistonen L: The
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Ann Med. 36:285–295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shemirani B and Crowe DL: Hypoxic
induction of HIF-1alpha and VEGF expression in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma lines is mediated by stress activated
protein kinases. Oral Oncol. 38:251–257. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi YH and Fang WG: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 in tumour angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
10:1082–1087. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nasimuzzaman M, Waris G, Mikolon D,
Stupack DG and Siddiqui A: Hepatitis C virus stabilizes
hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and stimulates the synthesis of
vascular endothelial growth factor. J Virol. 81:10249–10257. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gillespie DL, Flynn JR, Ragel BT, et al:
Silencing of HIF-1alpha by RNA interference in human glioma cells
in vitro and in vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 487:283–301.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katoh R, Miyagi E, Kawaoi A, et al:
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human
thyroid neoplasms. Hum Pathol. 30:891–897. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Machein MR and Plate KH: VEGF in brain
tumors. J Neurooncol. 50:109–120. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Banerjee A, Ray RB and Ray R: Oncogenic
potential of hepatitis C virus proteins. Viruses. 2:2108–2133.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McGivern DR and Lemon SM: Virus-specific
mechanisms of carcinogenesis in hepatitis C virus associated liver
cancer. Oncogene. 30:1969–1983. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moriya K, Fujie H, Shintani Y, et al: The
core protein of hepatitis C virus induces hepatocellular carcinoma
in transgenic mice. Nat Med. 4:1065–1067. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chun SY, Johnson C, Washburn JG,
Cruz-Correa MR, Dang DT and Dang LH: Oncogenic KRAS modulates
mitochondrial metabolism in human colon cancer cells by inducing
HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha target genes. Mol Cancer. 9:2932010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Doronkin S, Djagaeva I, Nagle ME, Reiter
LT and Seagroves TN: Dose-dependent modulation of HIF-1alpha/sima
controls the rate of cell migration and invasion in Drosophila
ovary border cells. Oncogene. 29:1123–1134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, et al: The
expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors
HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and
tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol. 157:411–421. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wong C, Wellman TL and Lounsbury KM: VEGF
and HIF-1alpha expression are increased in advanced stages of
epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 91:513–517. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moon EJ, Jeong CH, Jeong JW, et al:
Hepatitis B virus × protein induces angiogenesis by stabilizing
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. FASEB J. 18:382–384. 2004.
|
|
27
|
Tomita M, Semenza GL, Michiels C, et al:
Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in human T-cell leukaemia
virus type 1-infected cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukaemia
cells. Biochem J. 406:317–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wakisaka N, Kondo S, Yoshizaki T, Murono
S, Furukawa M and Pagano JS: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane
protein 1 induces synthesis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:5223–5234. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang EY and Tang XD: Human papillomavirus
type 16/18 oncoproteins: potential therapeutic targets in
non-smoking associated lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:5363–5369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Markert EK, Levine AJ and Vazquez A:
Proliferation and tissue remodeling in cancer: the hallmarks
revisited. Cell Death Dis. 3:e3972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Smirnova IS, Aksenov ND, Kashuba EV, et
al: Hepatitis C virus core protein transforms murine fibroblasts by
promoting genomic instability. Cell Oncol. 28:177–190.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|