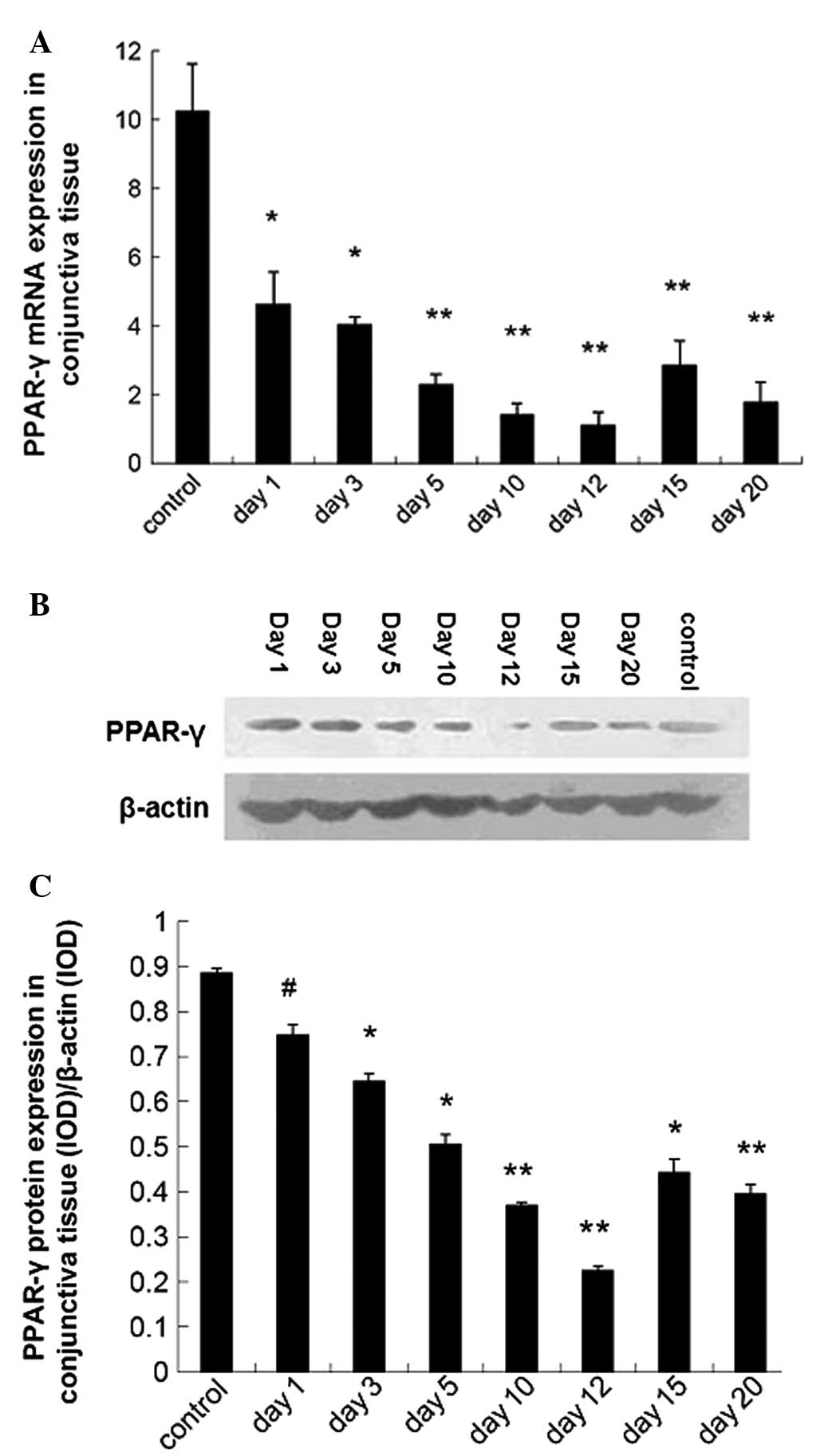
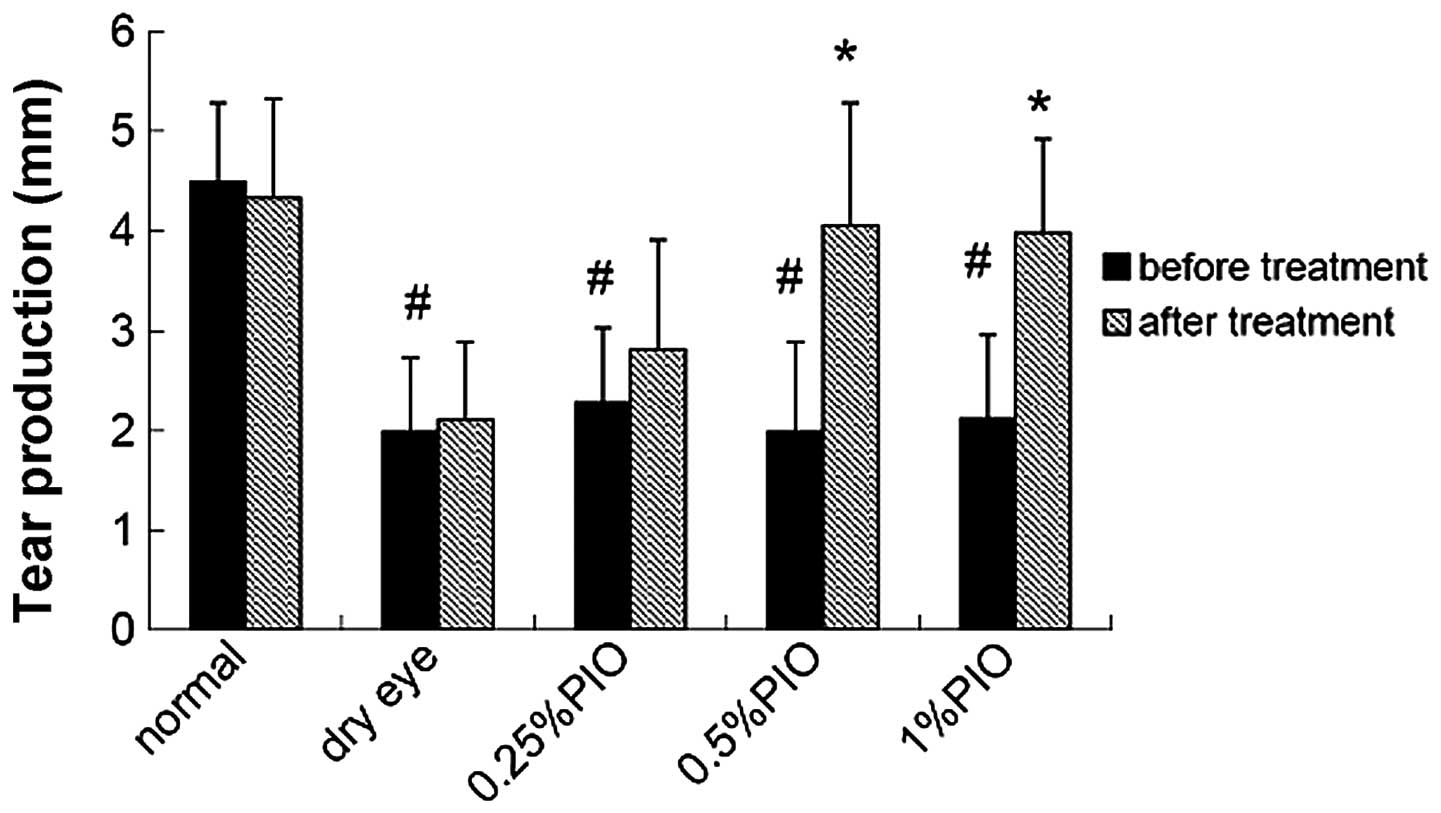
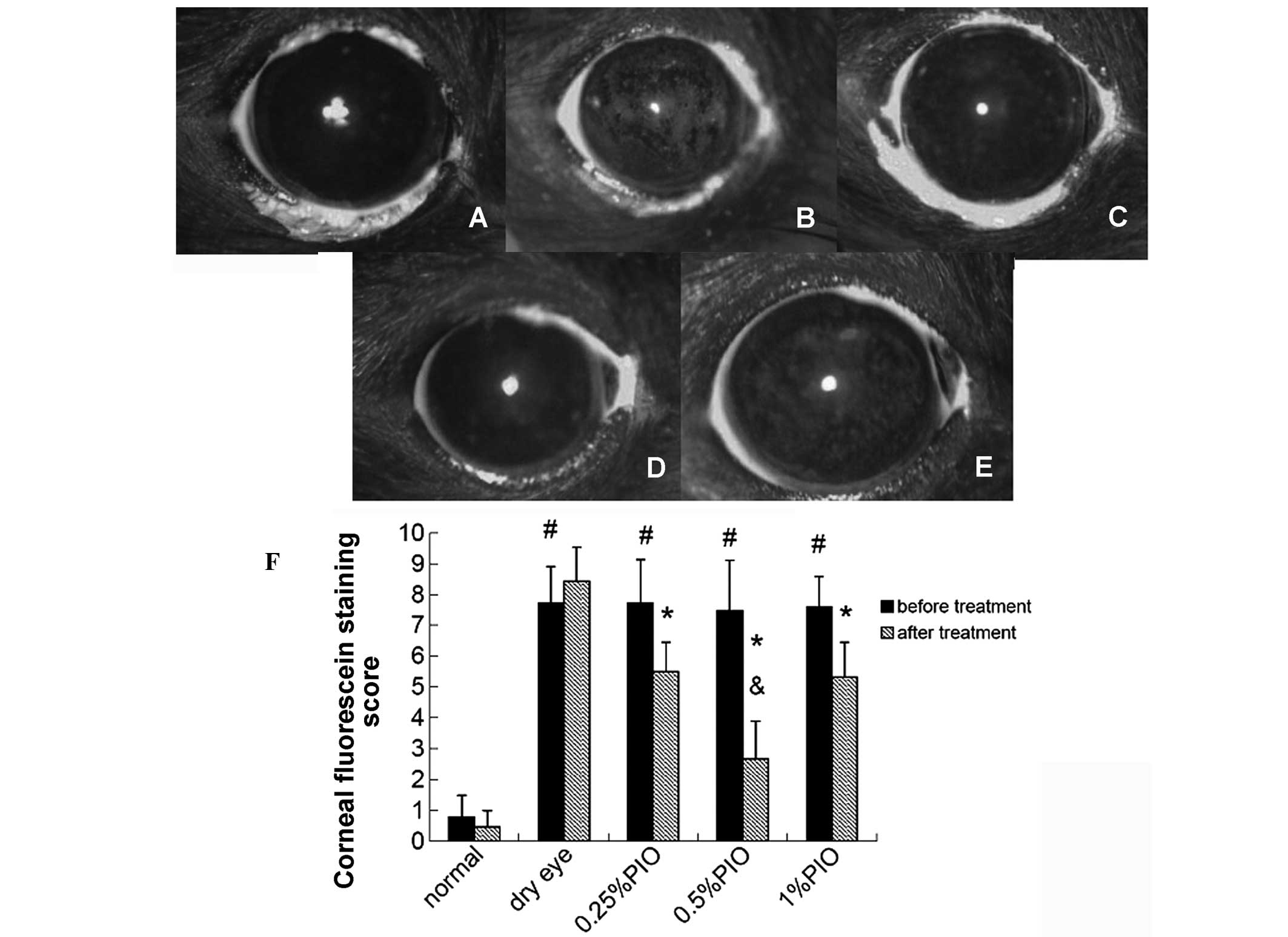
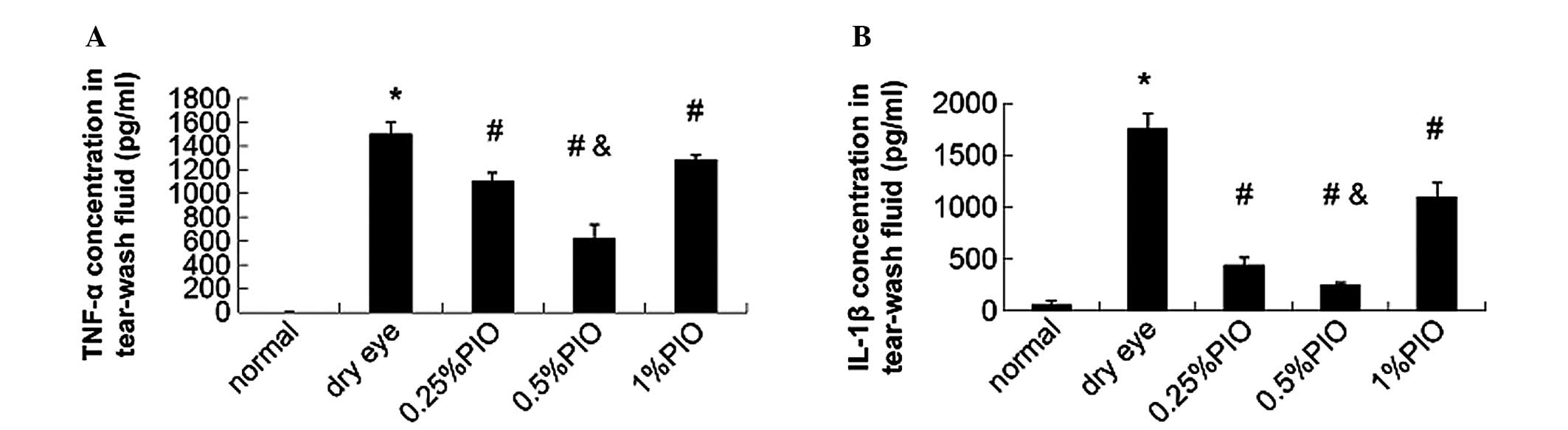
|
1
|
No authors listed. The definition and
classification of dry eye disease: report of the Definition and
Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop
(2007). Ocul Surf. 5:75–92. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Massingale ML, Li X, Vallabhajosyula M,
Chen D, Wei Y and Asbell PA: Analysis of inflammatory cytokines in
the tears of dry eye patients. Cornea. 28:1023–1027. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berger JP, Akiyama TE and Meinke PT:
PPARs: therapeutic targets for metabolic disease. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 26:244–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang C, Ting AT and Seed B: PPAR-gamma
agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines.
Nature. 391:82–86. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tugwood JD, Issemann I, Anderson RG,
Bundell KR, McPheat WL and Green S: The mouse peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor recognizes a response element in
the 5′ flanking sequence of the rat acyl CoA oxidase gene. EMBO J.
11:433–439. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chinetti G, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation: from
basic science to clinical applications. Int J Obes Relat Metab
Disord. 27(Suppl 3): S41–S45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Standiford TJ, Keshamouni VG and Reddy RC:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-{gamma} as a regulator
of lung inflammation and repair. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2:226–231.
2005.
|
|
8
|
Ramakers JD, Verstege MI, Thuijls G, Te
Velde AA, Mensink RP and Plat J: The PPARgamma agonist
rosiglitazone impairs colonic inflammation in mice with
experimental colitis. J Clin Immunol. 27:275–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ricote M, Li AC, Willson TM, Kelly CJ and
Glass CK: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a
negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature. 391:79–82.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beauregard C and Brandt PC: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor agonists inhibit
interleukin-1beta-mediated nitric oxide production in cultured
lacrimal gland acinar cells. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 19:579–587.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sarayba MA, Li L, Tungsiripat T, et al:
Inhibition of corneal neovascularization by a peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligand. Exp Eye Res.
80:435–442. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dursun D, Wang M, Monroy D, et al: A mouse
model of keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
43:632–638. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park CY, Zhuang W, Lekhanont K, et al:
Lacrimal gland inflammatory cytokine gene expression in the
botulinum toxin B-induced murine dry eye model. Mol Vis.
13:2222–2232. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song XJ, Li DQ, Farley W, et al:
Neurturin-deficient mice develop dry eye and keratoconjunctivitis
sicca. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:4223–4229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pflugfelder SC, Jones D, Ji Z, Afonso A
and Monroy D: Altered cytokine balance in the tear fluid and
conjunctiva of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome
keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Curr Eye Res. 19:201–211.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yoon KC, Jeong IY, Park YG and Yang SY:
Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in tears of
patients with dry eye syndrome. Cornea. 26:431–437. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo L, Li DQ, Doshi A, Farley W, Corrales
RM and Pflugfelder SC: Experimental dry eye stimulates production
of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling
pathways on the ocular surface. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
45:4293–4301. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fahmi H, Di Battista JA, Pelletier JP,
Mineau F, Ranger P and Martel-Pelletier J: Peroxisome proliferator
- activated receptor gamma activators inhibit
interleukin-1beta-induced nitric oxide and matrix metalloproteinase
13 production in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 44:595–607.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li M, Pascual G and Glass CK: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent repression of the
inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 20:4699–4707.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chung SW, Kang BY, Kim SH, et al: Oxidized
low density lipoprotein inhibits interleukin-12 production in
lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse macrophages via direct
interactions between peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma and nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem.
275:32681–32687. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gao Z, He Q, Peng B, Chiao PJ and Ye J:
Regulation of nuclear translocation of HDAC3 by IkappaBalpha is
required for tumor necrosis factor inhibition of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma function. J Biol Chem.
281:4540–4547. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ruan H, Hacohen N, Golub TR, Van Parijs L
and Lodish HF: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppresses
adipocyte-specific genes and activates expression of preadipocyte
genes in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: nuclear factor-kappaB activation by
TNF-alpha is obligatory. Diabetes. 51:1319–1336. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Camp HS, Tafuri SR and Leff T: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase phosphorylates peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma1 and negatively regulates its transcriptional
activity. Endocrinology. 140:392–397. 1999.
|
|
24
|
Delerive P, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in inflammation
control. J Endocrinol. 169:453–459. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moraes LA, Piqueras L and Bishop-Bailey D:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation.
Pharmacol Ther. 110:371–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Houseknecht KL, Cole BM and Steele PJ:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) and
its ligands: a review. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 22:1–23. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xin X, Yang S, Kowalski J and Gerritsen
ME: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligands are
potent inhibitors of angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 274:9116–9121. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murata T, Hata Y, Ishibashi T, et al:
Response of experimental retinal neovascularization to
thiazolidinediones. Arch Ophthalmol. 119:709–717. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|