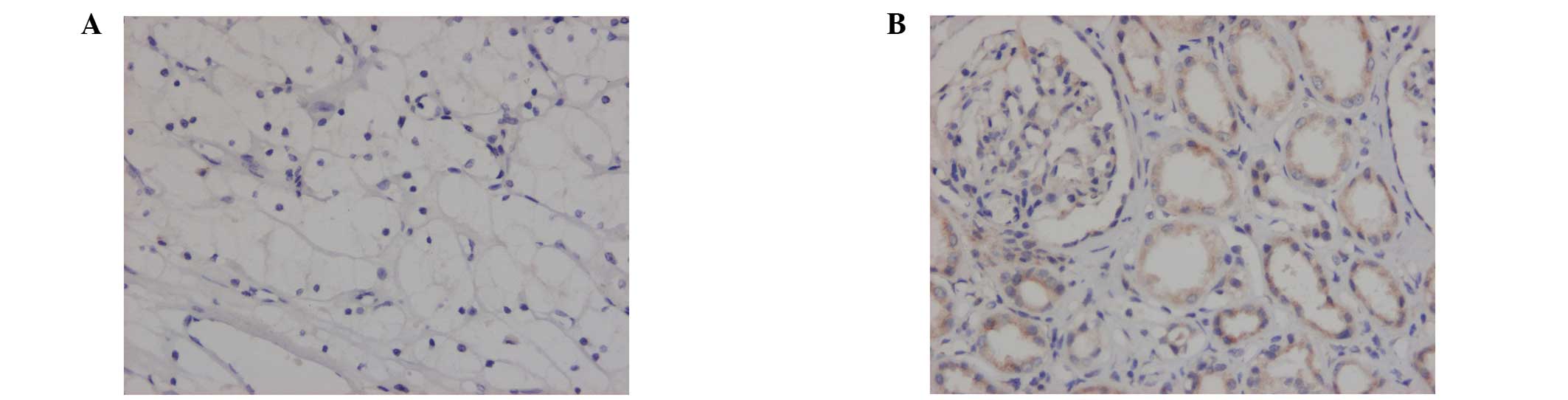
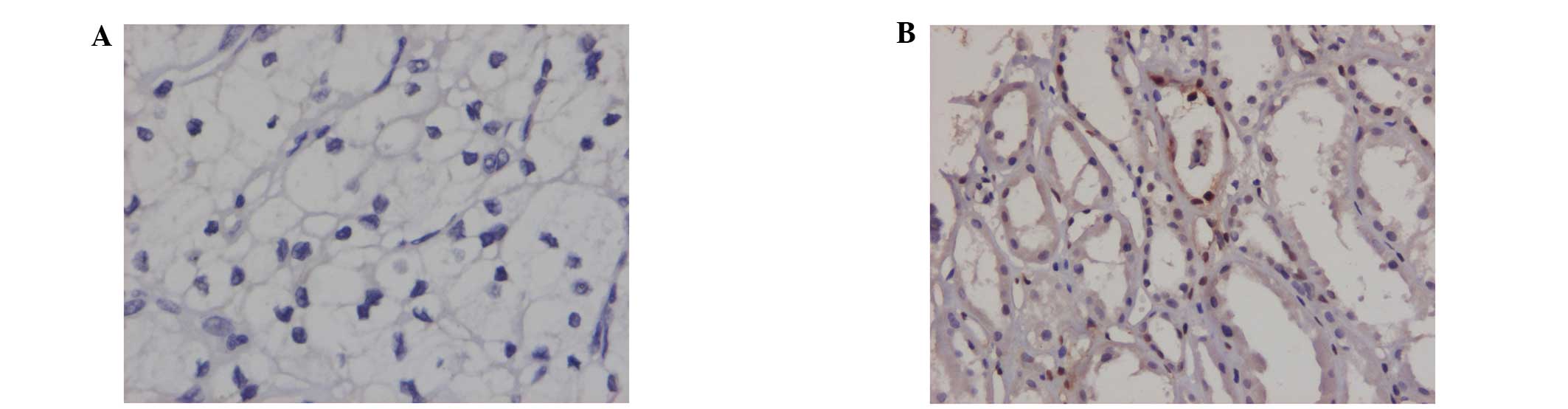
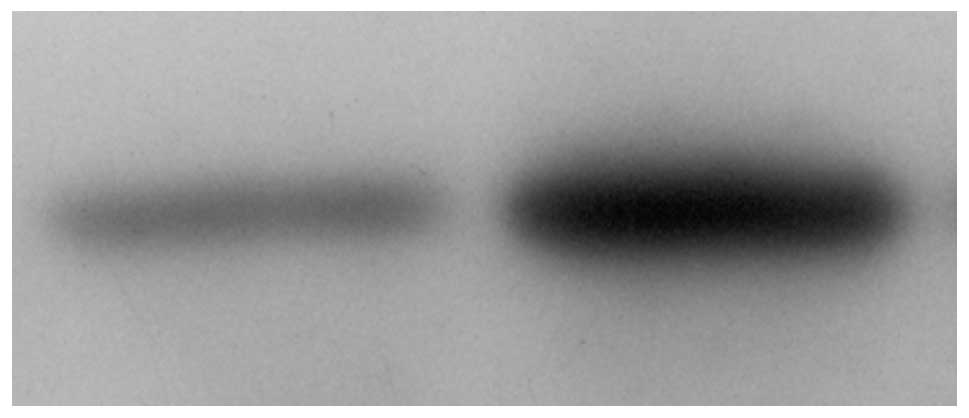
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY, Jacqmin
D, Lee JE, Weikert S and Kiemeney LA: The epidemiology of renal
cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 60:615–621. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Athar U and Gentile TC: Treatment options
for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a review. Can J Urol.
15:3954–3966. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jurado JM, Zarcos I, Delgado M, Blancas I,
Legerén M and García-Puche JL: Temsirolimus in overtreated
metastatic renal cancer with subsequent use of sunitinib: A case
report. Oncol Lett. 5:1382–1384. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tanriverdi O: Review on targeted treatment
of patients with advanced-stage renal cell carcinoma: a medical
oncologist’s perspective. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:609–617.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM and Stark GR:
Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to
IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science.
264:1415–1421. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shang D, Liu Y, Ito N, Kamoto T and Ogawa
O: Defective Jak-Stat activation in renal cell carcinoma is
associated with interferon-alpha resistance. Cancer Sci.
98:1259–1264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eto M, Kamba T, Miyake H, Fujisawa M,
Kamai T, Uemura H, Tsukamoto T, et al; Japan Immunotherapy
SNPs-Study Group for Kidney Cancer. STAT3 polymorphism can predict
the response to interferon-α therapy in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 63:745–752. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Masuda A, Kamai T, Abe H, Arai K and
Yoshida K: Is Stat3 and/or p53 mRNA expression a prognostic marker
for renal cell carcinoma? Biomed Res. 30:171–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed.
Springer Verlag; New York, NY: pp. 547–560. 2009
|
|
11
|
Na Yanqun, Ye Zhangqun and Sun Guang: The
CUA Guideline for Urological Disease. People’s Health Publishing
House; Beijing: pp. 4–16. 2011, (In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Chen L, Zhu YY, Zhang XJ, Wang GL, Li XY,
He S, Zhang JB and Zhu JW: TSPAN1 protein expression: a significant
prognostic indicator for patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 15:2270–2276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng Z, Que T, Zhang J and Hu Y: A study
exploring critical pathways in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp
Ther Med. 7:121–130. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong LH, Krauer KG, Hatzinisiriou I,
Estcourt MJ, Hersey P, Tam ND, Edmondson S, et al:
Interferon-resistant human melanoma cells are deficient in ISGF3
components, STAT1, STAT2, and p48-ISGF3gamma. J Biol Chem.
272:28779–28785. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brinckmann A, Axer S, Jakschies D,
Dallmann I, Grosse J, Patzelt T, Bernier T, et al: Interferon-alpha
resistance in renal carcinoma cells is associated with defective
induction of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
which can be restored by a supernatant of phorbol 12-myristate
13-acetate stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br J
Cancer. 86:449–455. 2002.
|
|
16
|
Caraglia M, Marra M, Pelaia G, Maselli R,
Caputi M, Marsico SA and Abbruzzese A: Alpha-interferon and its
effects on signal transduction pathways. J Cell Physiol.
202:323–335. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lam JS, Shvarts O, Leppert JT, Pantuck AJ,
Figlin RA and Belldegrun AS: Postoperative surveillance protocol
for patients with localized and locally advanced renal cell
carcinoma based on a validated prognostic nomogram and risk group
stratification system. J Urol. 174:466–472. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Noguchi Y, Kurokawa MS, Okuse C, Matsumoto
N, Nagai K, Sato T, Arito M, et al: Serum peptides, represented by
complement 3f des-arginine, are useful for prediction of the
response to pegylated interferon-α plus ribavirin in patients with
chronic hepatitis C. Hepatol Res. 43:743–756. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Azuma T, Matayoshi Y, Nagase Y and Oshi M:
Neutrophil number after interferon-alfa treatment is an independent
predictive marker of overall survival in metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 10:180–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|