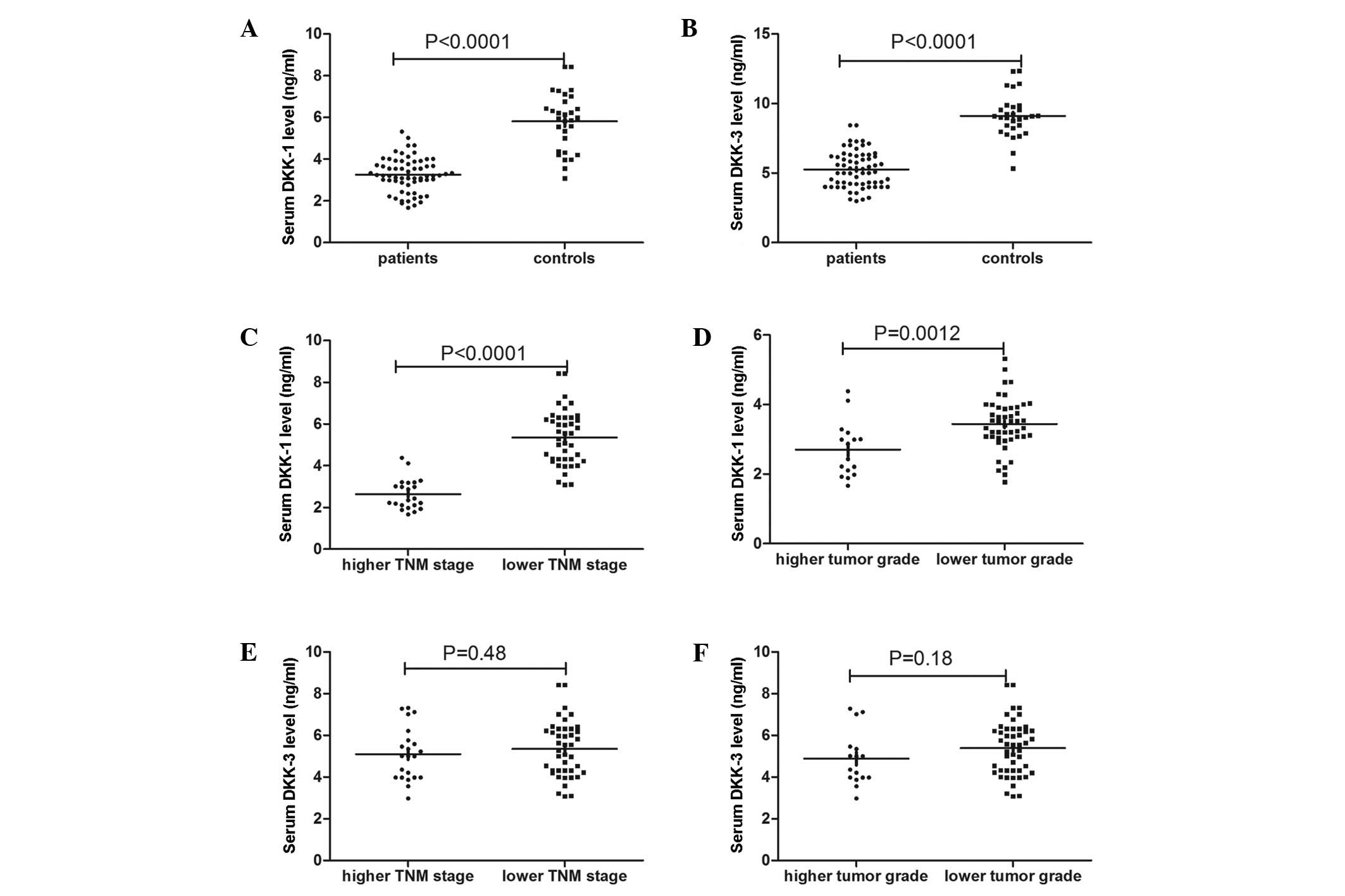
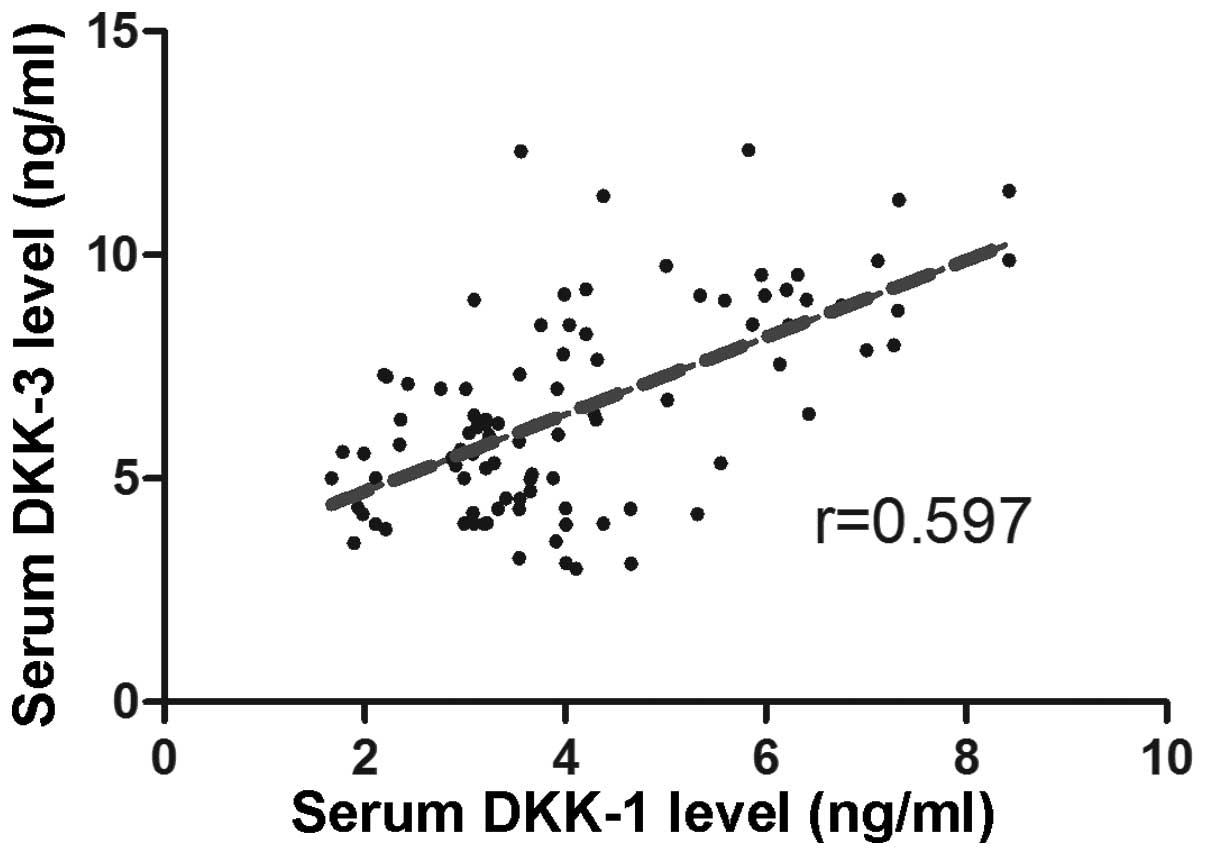
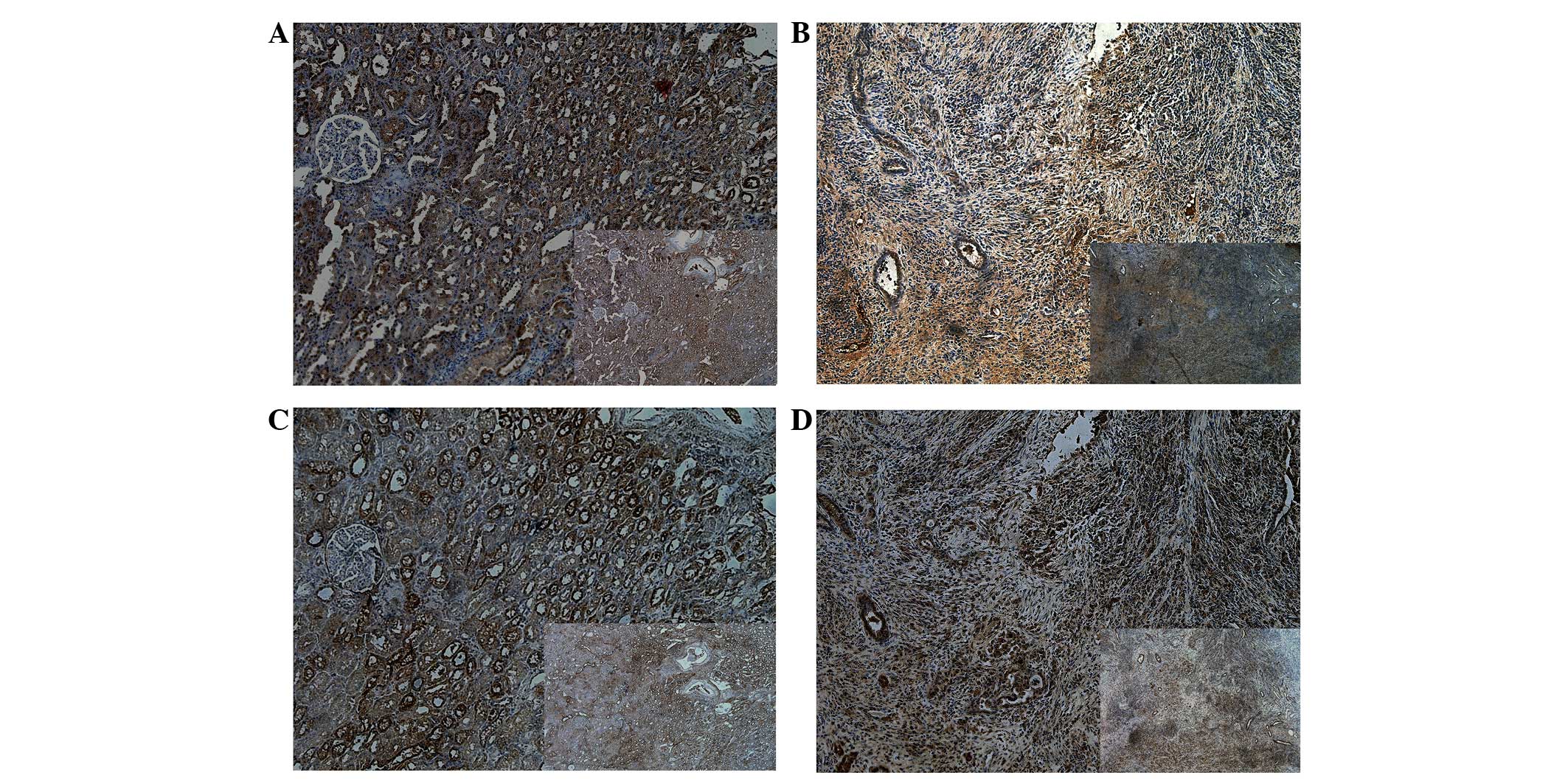
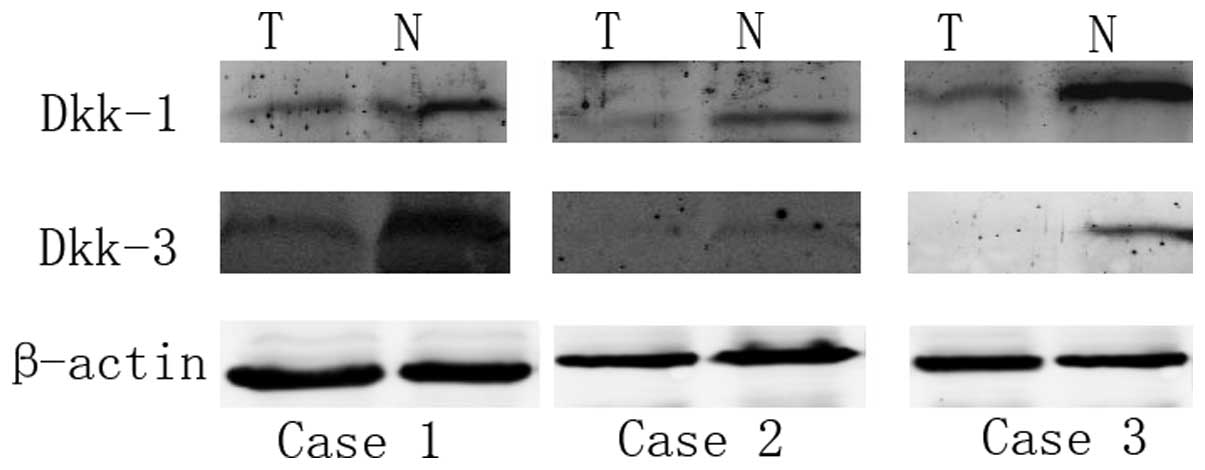
|
1
|
Rini BI, Campbell SC and Escudier B: Renal
cell carcinoma. Lancet. 373:1119–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Deng FM, Melamed J and Zhou M: Pathology
of renal cell carcinoma. Renal Cancer. Libertino JA: Springer; New
York, NY: pp. 51–69. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Vacas E, Bajo AM, Schally AV, et al:
Vasoactive intestinal peptide induces oxidative stress and
suppresses metastatic potential in human clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 365:212–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Escudier B, Szczylik C, Porta C and Gore
M: Treatment selection in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: expert
consensus. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 9:327–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cohen ED, Tian Y and Morrisey EE: Wnt
signaling: an essential regulator of cardiovascular
differentiation, morphogenesis and progenitor self-renewal.
Development. 135:789–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klaus A and Birchmeier W: Wnt signalling
and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:387–398. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Veeck J and Dahl E: Targeting the Wnt
pathway in cancer: the emerging role of Dickkopf-3. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825:18–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, et al:
LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins.
Nature. 411:321–325. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patil MA, Chua MS, Pan KH, et al: An
integrated data analysis approach to characterize genes highly
expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:3737–3747.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wirths O, Waha A, Weggen S, et al:
Overexpression of human Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of wingless/WNT
signaling, in human hepatoblastomas and Wilms’ tumors. Lab Invest.
83:429–434. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takahashi N, Fukushima T, Yorita K, Tanaka
H, Chijiiwa K and Kataoka H: Dickkopf-1 is overexpressed in human
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and is involved in invasive
growth. Int J Cancer. 126:1611–1620. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shizhuo W, Tao J, Shulan Z and Bing Z: The
expression and significance of Dickkopf-1 in epithelial ovarian
carcinoma. Int J Biol Markers. 24:165–170. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
González-Sancho JM, Aguilera O, García JM,
et al: The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 gene is a downstream target of
beta-catenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer.
Oncogene. 24:1098–1103. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kuphal S, Lodermeyer S, Bataille F,
Schuierer M, Hoang BH and Bosserhoff AK: Expression of Dickkopf
genes is strongly reduced in malignant melanoma. Oncogene.
25:5027–5036. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livark KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
16
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Majid S, et al: Wnt
antagonist DICKKOPF-3 (Dkk-3) induces apoptosis in human renal cell
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 50:449–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, et al: Wnt
antagonist family genes as biomarkers for diagnosis, staging, and
prognosis of renal cell carcinoma using tumor and serum DNA. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:6989–6997. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: International Union Against Cancer (UICC) TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumours. 7th edition. Wiley-Liss; New York, NY: pp.
1–336. 2009
|
|
19
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A; American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC).
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition. Springer-Verlag; New York,
NY: pp. 1–649. 2010
|
|
20
|
Winer J, Jung CK, Shackel I and Williams
PM: Development and validation of real-time quantitative reverse
transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for monitoring gene
expression in cardiac myocytes in vitro. Anal Biochem. 270:41–49.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Forget MA, Turcotte S, Beauseigle D, et
al: The Wnt pathway regulator DKK1 is preferentially expressed in
hormone-resistant breast tumours and in some common cancer types.
Br J Cancer. 96:646–653. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kurose K, Sakaguchi M, Nasu Y, et al:
Decreased expression of REIC/Dkk-3 in human renal clear cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 171:1314–1318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang T, Huang L and Zhang S: DKK-1 in
serum as a clinical and prognostic factor in patients with cervical
cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 28:221–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, et al:
Combination analysis of hypermethylated Wnt-antagonist family genes
as a novel epigenetic biomarker panel for bladder cancer detection.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:2109–2116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jin Y, Murata H, Sakaguchi M, et al:
Partial sensitization of human bladder cancer cells to a
gene-therapeutic adenovirus carrying REIC/Dkk-3 by downregulation
of BRPK/PINK1. Oncol Rep. 27:695–699. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niehrs C: The complex world of WNT
receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:767–779. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mikata R, Yokosuka O, Fukai K, et al:
Analysis of genes upregulated by the demethylating agent
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine in gastric cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer.
119:1616–1622. 2006.
|
|
29
|
Niida A, Hiroko T, Kasai M, et al: DKK1, a
negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the
beta-catenin/TCF pathway. Oncogene. 23:8520–8526. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsieh SY, Hsieh PS, Chiu CT and Chen WY:
Dickkopf-3/REIC functions as a suppressor gene of tumor growth.
Oncogene. 23:9183–9189. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fukui T, Kondo M, Ito G, et al:
Transcriptional silencing of secreted frizzled related protein 1
(SFRP 1) by promoter hypermethylation in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Oncogene. 24:6323–6327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yue W, Sun Q, Dacic S, et al:
Downregulation of Dkk3 activates beta-catenin/TCF-4 signaling in
lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 29:84–92. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawano Y, Kitaoka M, Hamada Y, Walker MM,
Waxman J and Kypta RM: Regulation of prostate cell growth and
morphogenesis by Dickkopf-3. Oncogene. 25:6528–6537. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abarzua F, Sakaguchi M, Takaishi M, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of REIC/Dkk-3 selectively
induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells through activation
of c-Jun-NH2-kinase. Cancer Res. 65:9617–9622. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mizobuchi Y, Matsuzaki K, Kuwayama K, et
al: REIC/Dkk-3 induces cell death in human malignant glioma. Neuro
Oncol. 10:244–253. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kloten V, Becker B, Winner K, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation of the tumor-suppressor genes ITIH5,
DKK3, and RASSF1A as novel biomarkers for blood-based breast cancer
screening. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R42013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zenzmaier C, Sampson N, Plas E and Berger
P: Dickkopf-related protein 3 promotes pathogenic stromal
remodeling in benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer.
Prostate. 73:1441–1452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Than SS, Kataoka K, Sakaguchi M, et al:
Intraperitoneal administration of an adenovirus vector carrying
REIC/Dkk-3 suppresses peritoneal dissemination of scirrhous gastric
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:989–995. 2011.
|
|
39
|
Koppen A, Ait-Aissa R, Koster J, et al:
Dickkopf-3 expression is a marker for neuroblastic tumor maturation
and is down-regulated by MYCN. Int J Cancer. 122:1455–1464. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoang BH, Kubo T, Healey JH, et al:
Dickkopf 3 inhibits invasion and motility of Saos-2 osteosarcoma
cells by modulating the Wnt-beta-catenin pathway. Cancer Res.
64:2734–2739. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
del Barrantes IB, Montero-Pedrazuela A,
Guadaño-Ferraz A, et al: Generation and characterization of
dickkopf3 mutant mice. Mol Cell Biol. 26:2317–2326. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|