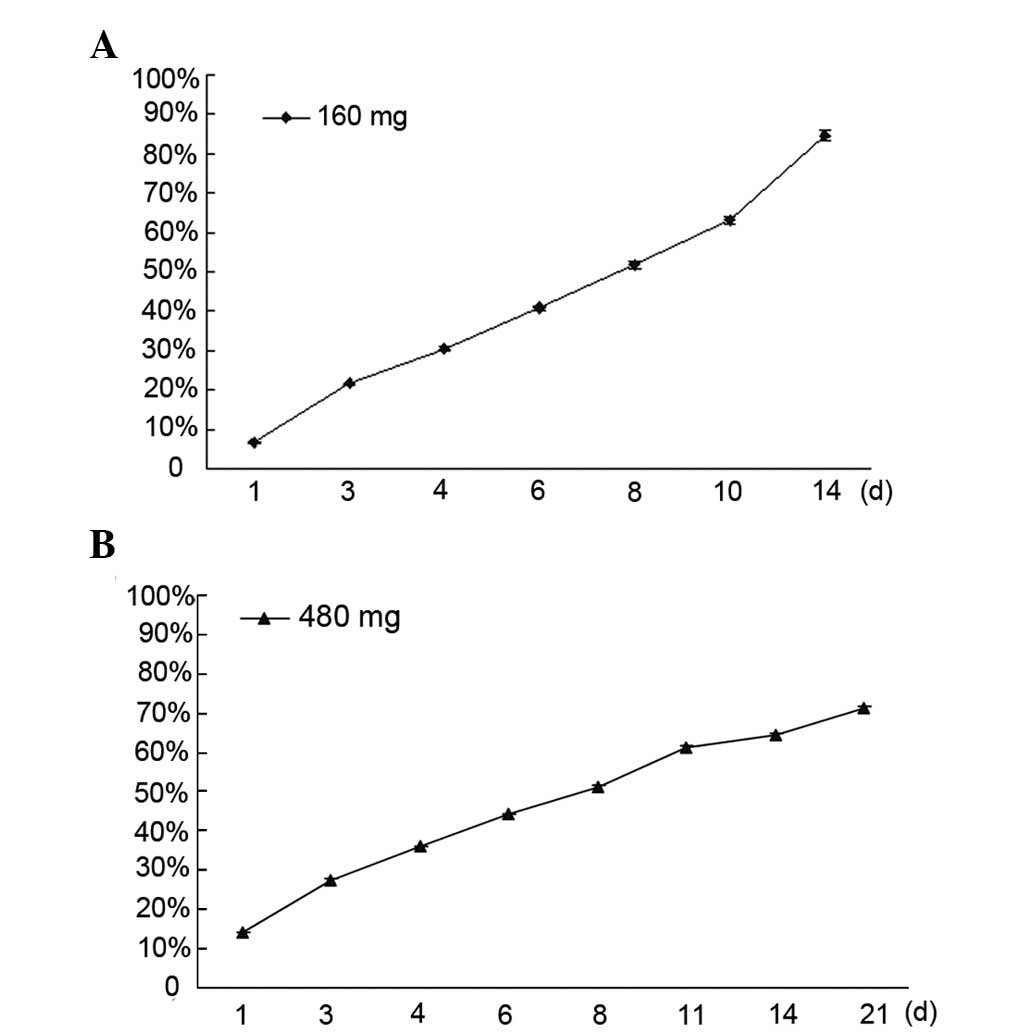
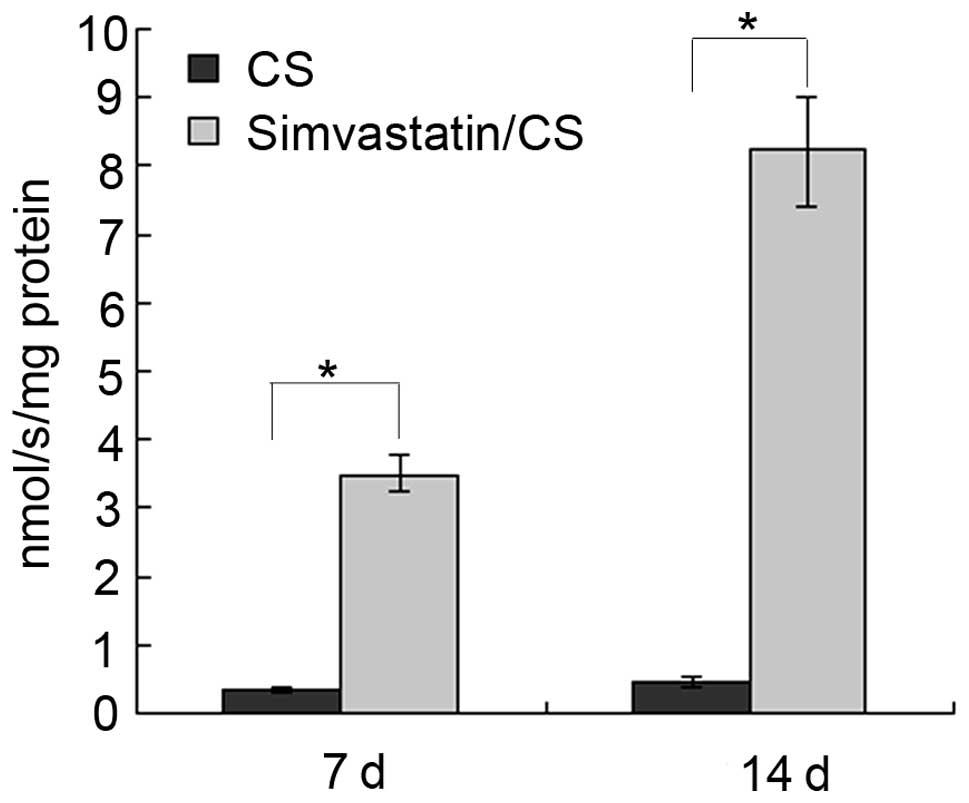
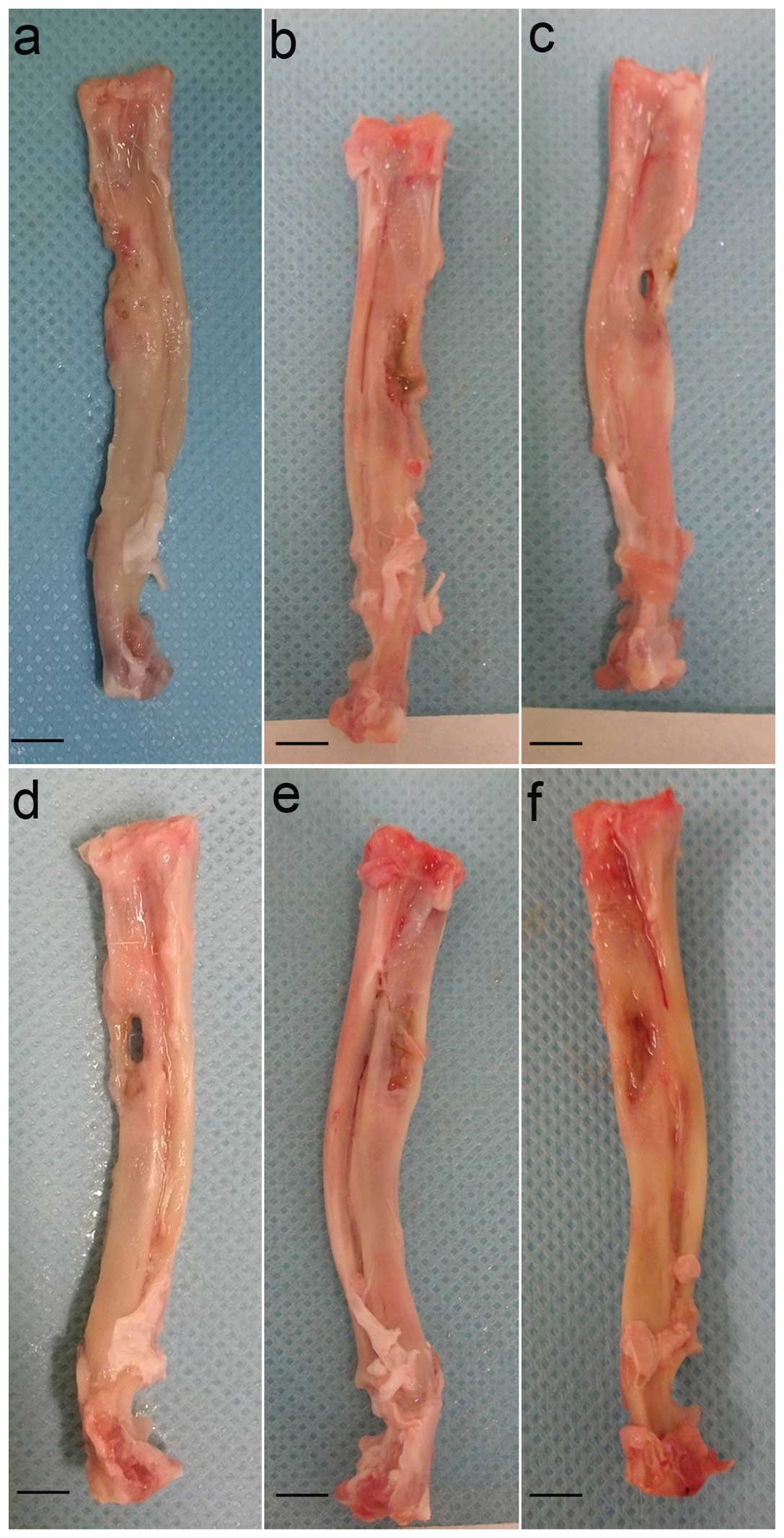
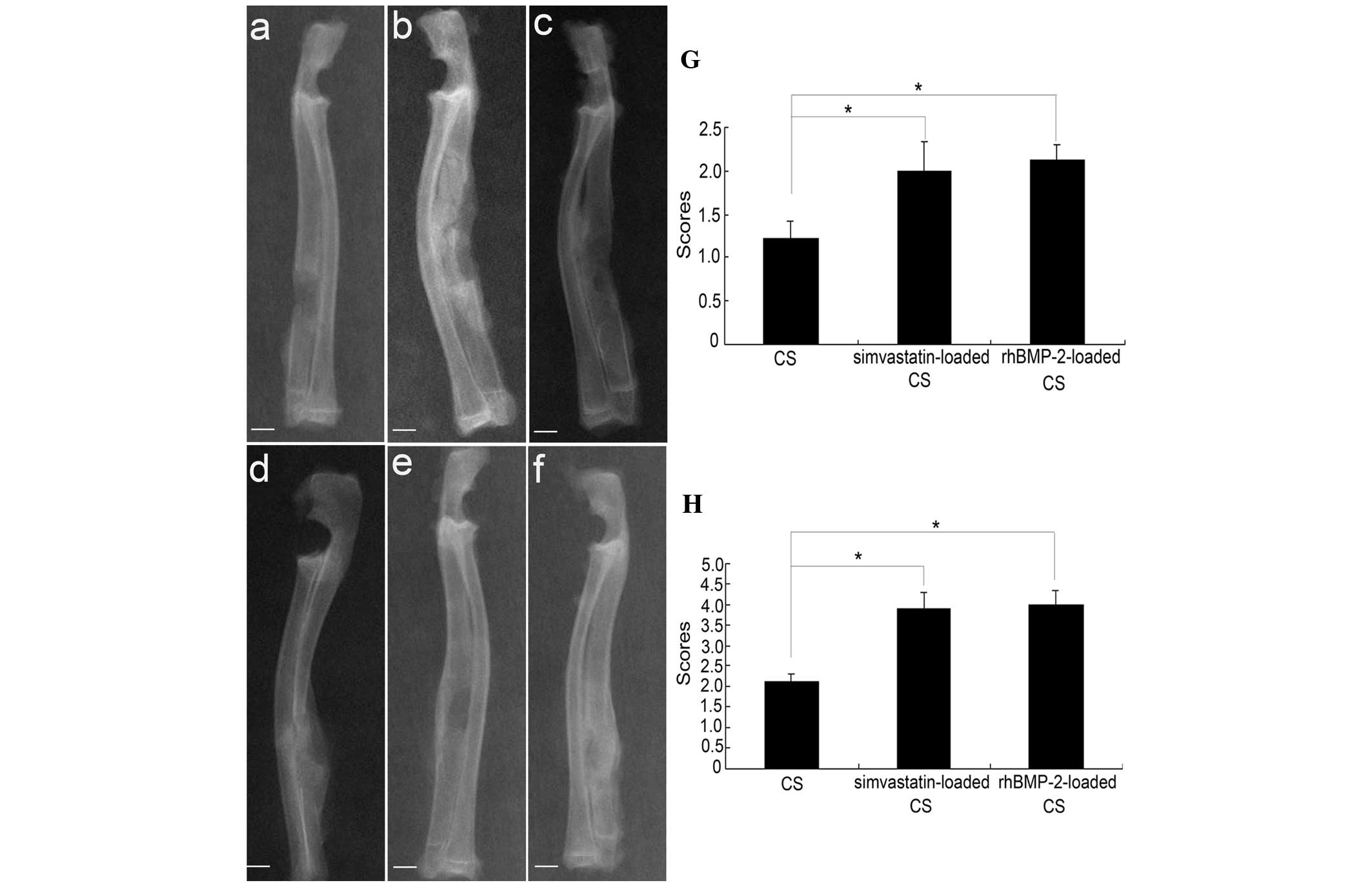
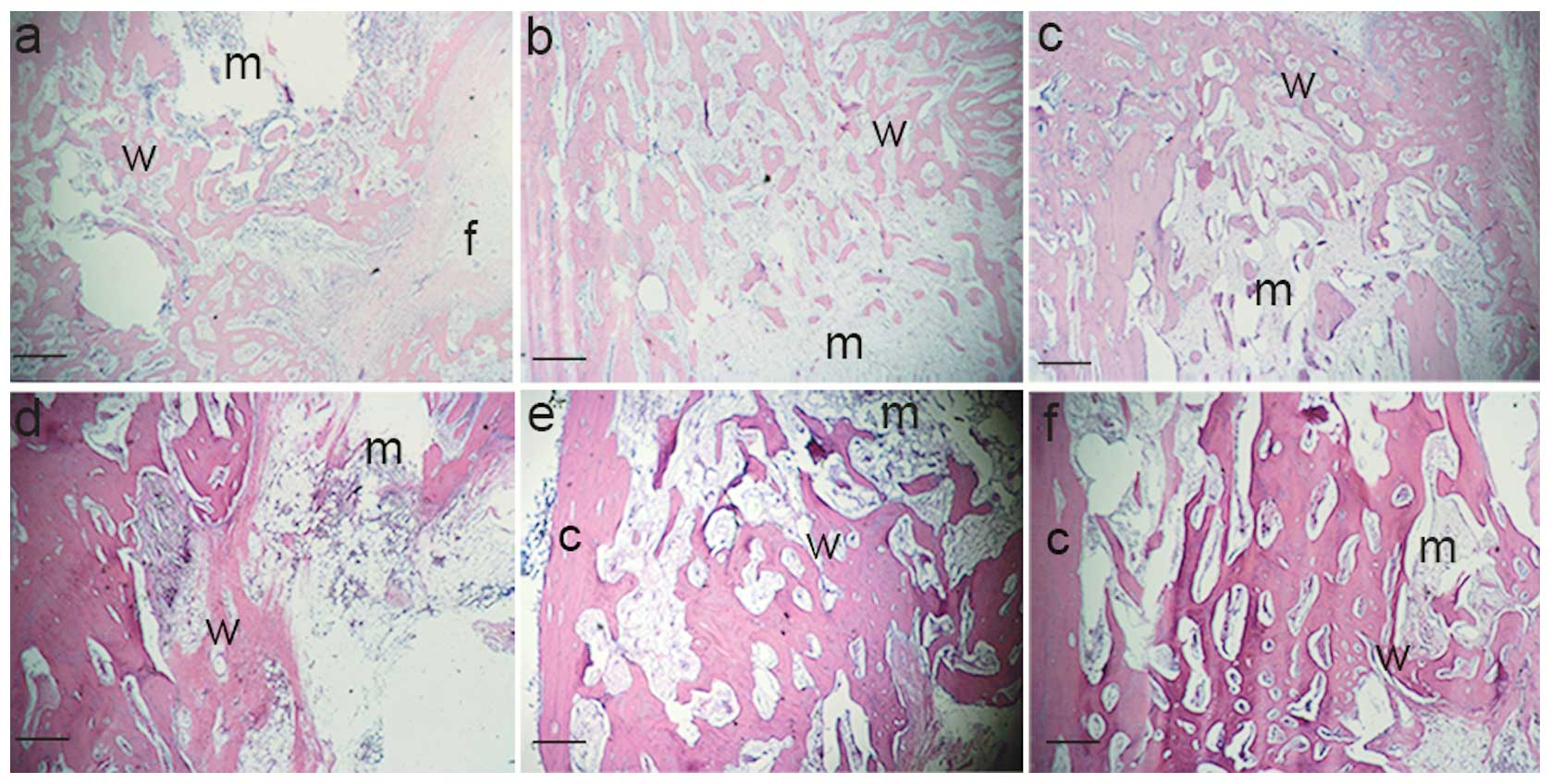
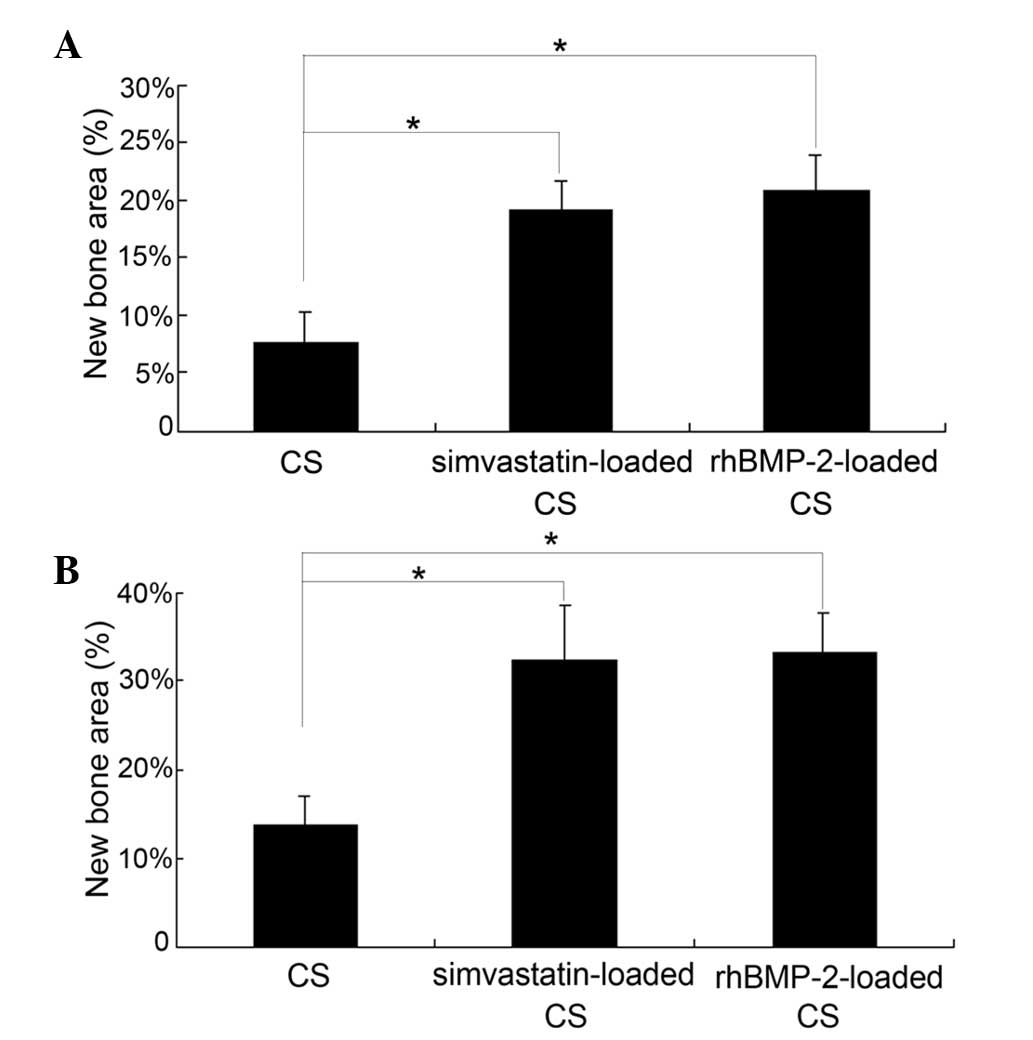
|
1
|
John HD and Wenz B: Histomorphometric
analysis of natural bone mineral for maxillary sinus augmentation.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 19:199–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boyne PJ and James RA: Grafting of the
maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg.
38:613–616. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moy PK, Lundgren S and Holmes RE:
Maxillary sinus augmentation: histomorphometric analysis of graft
materials for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 51:857–862. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Younger EM and Chapman MW: Morbidity at
bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma. 3:192–195. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan H, Yang Z, De Bruij JD, De Groot K
and Zhang X: Material-dependent bone induction by calcium phosphate
ceramics: a 2.5-year study in dog. Biomaterials. 22:2617–2623.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Borrelli J Jr, Prickett WD and Ricci WM:
Treatment of nonunions and osseous defects with bone graft and
calcium sulfate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 245–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gitelis S, Piasecki P, Turner T, Haggard
W, Charters J and Urban R: Use of a calcium sulfate-based bone
graft substitute for benign bone lesions. Orthopedics. 24:162–166.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Turner TM, Urban RM, Gitelis S, Kuo KN and
Andersson GB: Radiographic and histologic assessment of calcium
sulfate in experimental animal models and clinical use as a
resorbable bone-graft substitute, a bone-graft expander, and a
method for local antibiotic delivery. One institution’s experience.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A(Suppl 2): S8–S18. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McKee MD, Wild LM, Schemitsch EH and
Waddell JP: The use of an antibiotic-impregnated, osteoconductive,
bioabsorbable bone substitute in the treatment of infected long
bone defects: early results of a prospective trial. J Orthop
Trauma. 16:622–627. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mousset B, Benoit MA, Delloye C, Bouillet
R and Gillard J: Biodegradable implants for potential use in bone
infection. An in vitro study of antibiotic-loaded calcium sulphate.
Int Orthop. 19:157–161. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dacquet V, Varlet A, Tandogan RN, Tahon
MM, Fournier L, Jehl F, Monteil H and Bascoulergue G:
Antibiotic-impregnated plaster of Paris beads. Trials with
teicoplanin. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 241–249. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benoit MA, Mousset B, Delloye C, Bouillet
R and Gillard J: Antibiotic-loaded plaster of Paris implants coated
with poly lactide-co-glycolide as a controlled release delivery
system for the treatment of bone infections. Int Orthop.
21:403–408. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mundy G, Garrett R, Harris S, Chan J, Chen
D, Rossini G, Boyce B, Zhao M and Gutierrez G: Stimulation of bone
formation in vitro and in rodents by statins. Science.
286:1946–1949. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lane JM and Sandhu HS: Current approaches
to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am. 18:213–225.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu F, Wei J, Guo H, Chen F, Hong H and Liu
C: Self-setting bioactive calcium-magnesium phosphate cement with
high strength and degradability for bone regeneration. Acta
Biomater. 4:1873–1884. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wadagaki R, Mizuno D, Yamawaki-Ogata A,
Satake M, Kaneko H, Hagiwara S, Yamamoto N, Narita Y, Hibi H and
Ueda M: Osteogenic induction of bone marrow-derived stromal cells
on simvastatin-releasing, biodegradable, nano- to microscale fiber
scaffolds. Ann Biomed Eng. 39:1872–1881. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou Y, Ni Y, Liu Y, Zeng B, Xu Y and Ge
W: The role of simvastatin in the osteogenesis of injectable
tissue-engineered bone based on human adipose-derived stromal cells
and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 31:5325–5335. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thylin MR, McConnell JC, Schmid MJ,
Reckling RR, Ojha J, Bhattacharyya I, Marx DB and Reinhardt RA:
Effects of simvastatin gels on murine calvarial bone. J
Periodontol. 73:1141–1148. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wong RW and Rabie AB: Statin collagen
grafts used to repair defects in the parietal bone of rabbits. Br J
Oral Maxillofac Surg. 41:244–248. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ozeç I, Kiliç E, Gümüs C and Göze F:
Effect of local simvastatin application on mandibular defects. J
Craniofac Surg. 18:546–550. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stein D, Lee Y, Schmid MJ, Killpack B,
Genrich MA, Narayana N, Marx DB, Cullen DM and Reinhardt RA: Local
simvastatin effects on mandibular bone growth and inflammation. J
Periodontol. 76:1861–1870. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nyan M, Miyahara T, Noritake K, Hao J,
Rodriguez R, Kuroda S and Kasugai S: Molecular and tissue responses
in the healing of rat calvarial defects after local application of
simvastatin combined with alpha tricalcium phosphate. J Biomed
Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 93:65–73. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giannoudis PV: Fracture healing and bone
regeneration: autologous bone grafting or BMPs? Injury.
40:1243–1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ayukawa Y, Okamura A and Koyano K:
Simvastatin promotes osteogenesis around titanium implants. Clin
Oral Implants Res. 15:346–350. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee Y, Schmid MJ, Marx DB, Beatty MW,
Cullen DM, Collins ME and Reinhardt RA: The effect of local
simvastatin delivery strategies on mandibular bone formation in
vivo. Biomaterials. 29:1940–1949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baek KH, Lee WY, Oh KW, Tae HJ, Lee JM,
Lee EJ, Han JH, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY and Kang SK: The
effect of simvastatin on the proliferation and differentiation of
human bone marrow stromal cells. J Korean Med Sci. 20:438–444.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weis M, Heeschen C, Glassford AJ and Cooke
JP: Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation.
105:739–745. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong RW and Rabie AB: Early healing
pattern of statin-induced osteogenesis. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
43:46–50. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pauly S, Luttosch F, Morawski M, Haas NP,
Schmidmaier G and Wildemann B: Simvastatin locally applied from a
biodegradable coating of osteosynthetic implants improves fracture
healing comparable to BMP-2 application. Bone. 45:505–511. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Armitage J: The safety of statins in
clinical practice. Lancet. 370:1781–1790. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|