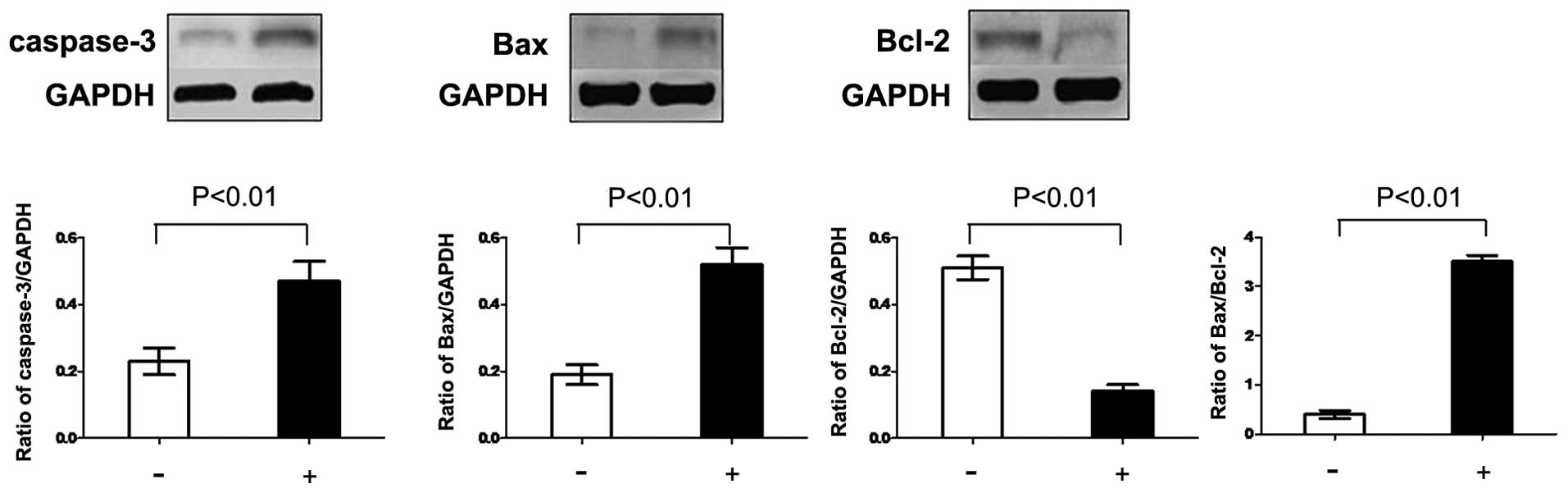
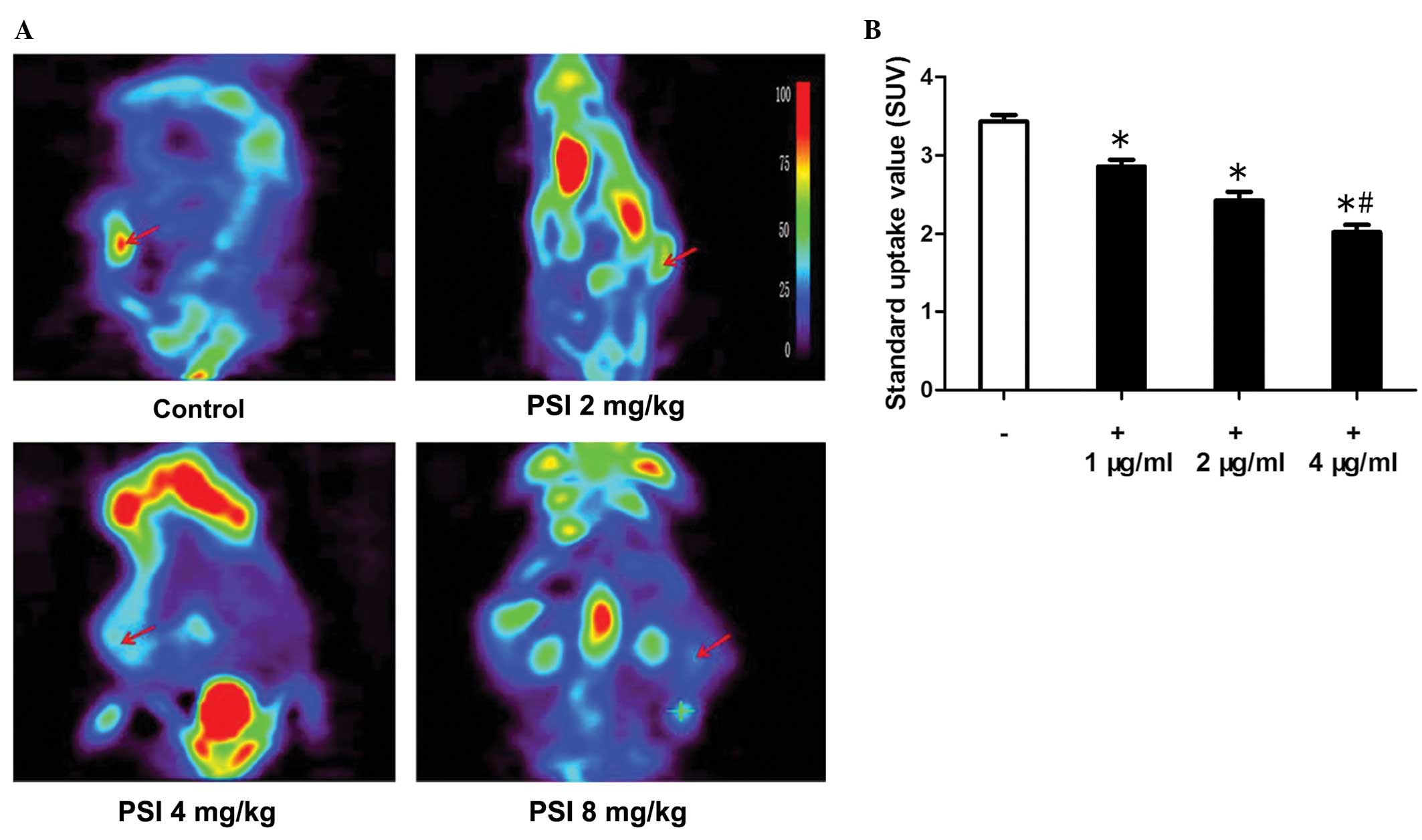
|
1
|
Peters S, Adjei AA, Gridelli C, et al;
ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Metastatic non-small-cell lung
cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. (Suppl 7): vii56–vii64.
2012.
|
|
2
|
Yang JJ, Chen HJ, Yan HH, et al: Clinical
modes of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure and subsequent
management in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
79:33–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Milella M, Nuzzo C, Bria E, et al: EGFR
molecular profiling in advanced NSCLC: a prospective phase II study
in molecularly/clinically selected patients pretreated with
chemotherapy. J Thorac Oncol. 7:672–680. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al;
North-East Japan Study Group. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for
non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med.
362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al:
Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for
previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial). J Clin Oncol. 21:2237–2246. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kris MG, Natale RB, Herbst RS, et al:
Efficacy of gefitinib, an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor
receptor tyrosine kinase, in symptomatic patients with non-small
cell lung cancer: a randomized trial. JAMA. 290:2149–2158. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin L and Bivona TG: Mechanisms of
resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and novel
therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance in NSCLC patients.
Chemother Res Pract. 2012:8172972012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ji Y, Ma SL, Zhang YP, et al: Combined
treatment with TNF-alpha/gefitinib alleviates the resistance to
gefitinib in PC-9 cells. Anticancer Drugs. 20:832–837. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ramalingam S and Sandler AB: Salvage
therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: factors
influencing treatment selection. Oncologist. 11:655–665. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grabley S and Thiericke R: Bioactive
agents from natural sources: trends in discovery and application.
Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 64:101–154. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiao X, Bai P, Bui Nguyen TM, et al: The
antitumoral effect of Paris Saponin I associated with the induction
of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:1179–1188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun J, Liu BR, Hu WJ, et al: In vitro
anticancer activity of aqueous extracts and ethanol extracts of
fifteen traditional Chinese medicines on human digestive tumor cell
lines. Phytother Res. 21:1102–1104. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao M, Dai X, He X, et al: Paris saponin
I induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric
carcinoma SGC7901 cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
31:768–772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Sun Y, Fan L, et al: Paris saponin
VII inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells through Ras
signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:150–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
GuangLie C, WeiShi G, GaiLing H, et al:
Effect of paris saponin on antitumor and immune function in U14
tumor-bearing mice. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 10:503–507.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Gu JF, Zou X, et al: The anti-lung
cancer activities of steroidal saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var.
chinensis (Franch) Hara through enhanced immunostimulation in
experimental Lewis tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice and induction of
apoptosis in the A549 cell line. Molecules. 18:12916–12936. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xiao X, Zou J, Bui-Nguyen TM, et al: Paris
saponin II of Rhizoma Paridis - a novel inducer of apoptosis in
human ovarian cancer cells. Biosci Trends. 6:201–211. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wen F, Yin H, Chen C, et al: Chemical
characteristics of saponins from Paris fargesii var.
brevipetala and cytotoxic activity of its main ingredient,
paris saponin H. Fitoterapia. 83:627–635. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheung JY, Ong RC, Suen YK, et al:
Polyphyllin D is a potent apoptosis inducer in drug-resistant HepG2
cells. Cancer Lett. 217:203–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan JY, Koon JC, Liu X, et al:
Polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin from Paris polyphylla,
inhibits endothelial cell functions in vitro and angiogenesis in
zebrafish embryos in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:64–69.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiao M, Dai X, He X, et al: Paris saponin
I induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
gastric carcinoma SGC7901 cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 31:768–772. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang B, Johnson TS, Thomas GL, et al: A
shift in the Bax/Bcl-2 balance may activate caspase-3 and modulate
apoptosis in experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int.
62:1301–1313. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marneros AG, Grossman ME, Silvers DN, et
al: Pralatrexate-induced tumor cell apoptosis in the epidermis of a
patient with HTLV-1 adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia causing skin
erosions. Blood. 113:6338–6341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smith W and Khuri FR: The care of the lung
cancer patient in the 21st century: a new age. Semin Oncol. 31(2
Suppl 4): 11–15. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pfister DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, et al;
American Society of Clinical Oncology. American Society of Clinical
Oncology treatment of unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer
guideline: update 2003. J Clin Oncol. 22:330–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gerber DE and Schiller JH: Maintenance
chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: new life for
an old idea. J Clin Oncol. 31:1009–1020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Videtic GM: Locally advanced non-small
cell lung cancer: what is the optimal concurrent chemoradiation
regimen? Cleve Clin J Med. 79(Suppl 1): eS32–eS37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bonomi M, Pilotto S, Milella M, et al:
Adjuvant chemotherapy for resected non-small-cell lung cancer:
future perspectives for clinical research. J Exp Clin Canc Res.
30:1152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saintigny P and Burger JA: Recent advances
in non-small cell lung cancer biology and clinical management.
Discov Med. 13:287–297. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, et al:
Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 53:5–26. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Morgillo F, Bareschino MA, Bianco R, et
al: Primary and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR targeted drugs in
cancer therapy. Differentiation. 75:788–799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morgillo F, Cantile F, Fasano M, et al:
Resistance mechanisms of tumour cells to EGFR inhibitors. Clin
Transl Oncol. 11:270–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Zhang YJ, Gao WY and Yan LL:
Anti-tumor constituents from Paris polyphylla var.
yunnanensis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 32:1425–1428.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Sun J, Liu BR, Hu WJ, et al: In vitro
anticancer activity of aqueous extracts and ethanol extracts of
fifteen traditional Chinese medicines on human digestive tumor cell
lines. Phytother Res. 21:1102–1104. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee MS, Yuet-Wa JC, Kong SK, et al:
Effects of polyphyllin D, a steroidal saponin in Paris
polyphylla, in growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells
and in xenograft. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:1248–1254. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cheung JY, Ong RC, Suen YK, et al:
Polyphyllin D is a potent apoptosis inducer in drug-resistant HepG2
cells. Cancer Lett. 217:203–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siu FM, Ma DL, Cheung YW, et al: Proteomic
and transcriptomic study on the action of a cytotoxic saponin
(Polyphyllin D): induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathways. Proteomics. 8:3105–3117.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang H, Su D and Ma SL: The effect of
Chonglou Saponin I on proliferation and apoptosis in lung
adenocarcinoma cell line PC9. J Chin Oncol. 18:166–169. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Hua YH, Ma SL, Fu ZF, et al: Effect of
Polyphyllin I on radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell
line CNE-2 in vitro. Chin Arch Trad Chin Med. 29:1387–1390.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Xiao M, Dai X, He X, et al: Paris saponin
I induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric
carcinoma SGC7901 cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
31:768–772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xiao X, Bai P, Bui Nguyen TM, et al: The
antitumoral effect of Paris Saponin I associated with the induction
of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:1179–1188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan LL, Zhang YJ, Gao WY, et al: In vitro
and in vivo anticancer activity of steroid saponins of Paris
polyphylla var. yunnanensis . Exp Oncol. 31:27–32.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shroff EH, Snyder C and Chandel NS: Bcl-2
family members regulate anoxia-induced cell death. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 9:1405–1409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Reed JC, Miyashita T, Takayama S, et al:
BCL-2 family proteins: regulators of cell death involved in the
pathogenesis of cancer and resistance to therapy. J Cell Biochem.
60:23–32. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sedlak TW, Oltvai ZN, Yang E, et al:
Multiple Bcl-2 family members demonstrate selective dimerizations
with Bax. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:7834–7838. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu F, Tian Y, Huang Y, et al: EGFR
inhibitors sensitize non-small cell lung cancer cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Chin J Cancer. 30:701–711. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mudd SR, Voorbach MJ, Reuter DR, et al:
FDG-PET as a pharmacodynamic biomarker for early assessment of
treatment response to linifanib (ABT-869) in a non-small cell lung
cancer xenograft model. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:1669–1672.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|