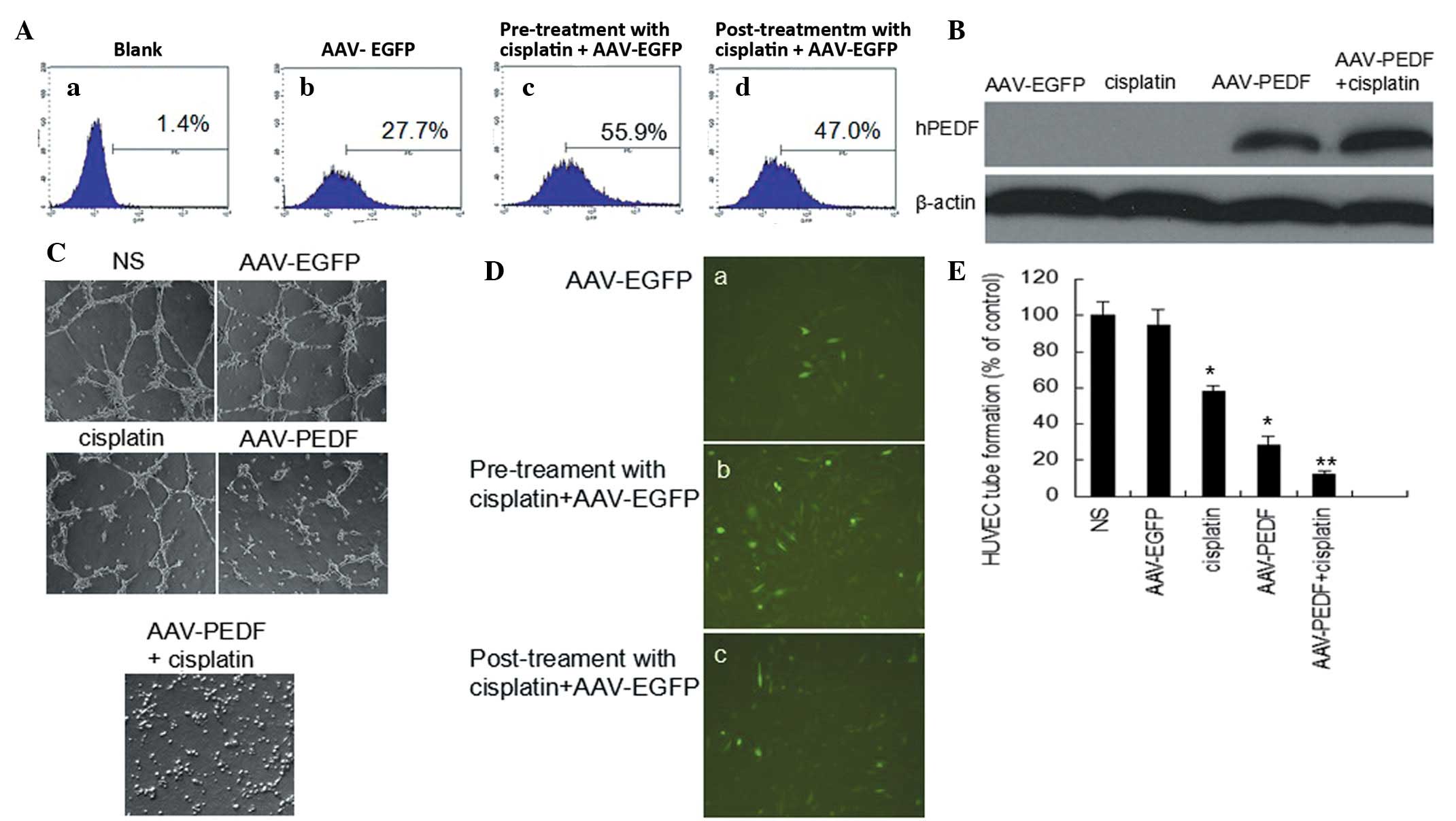
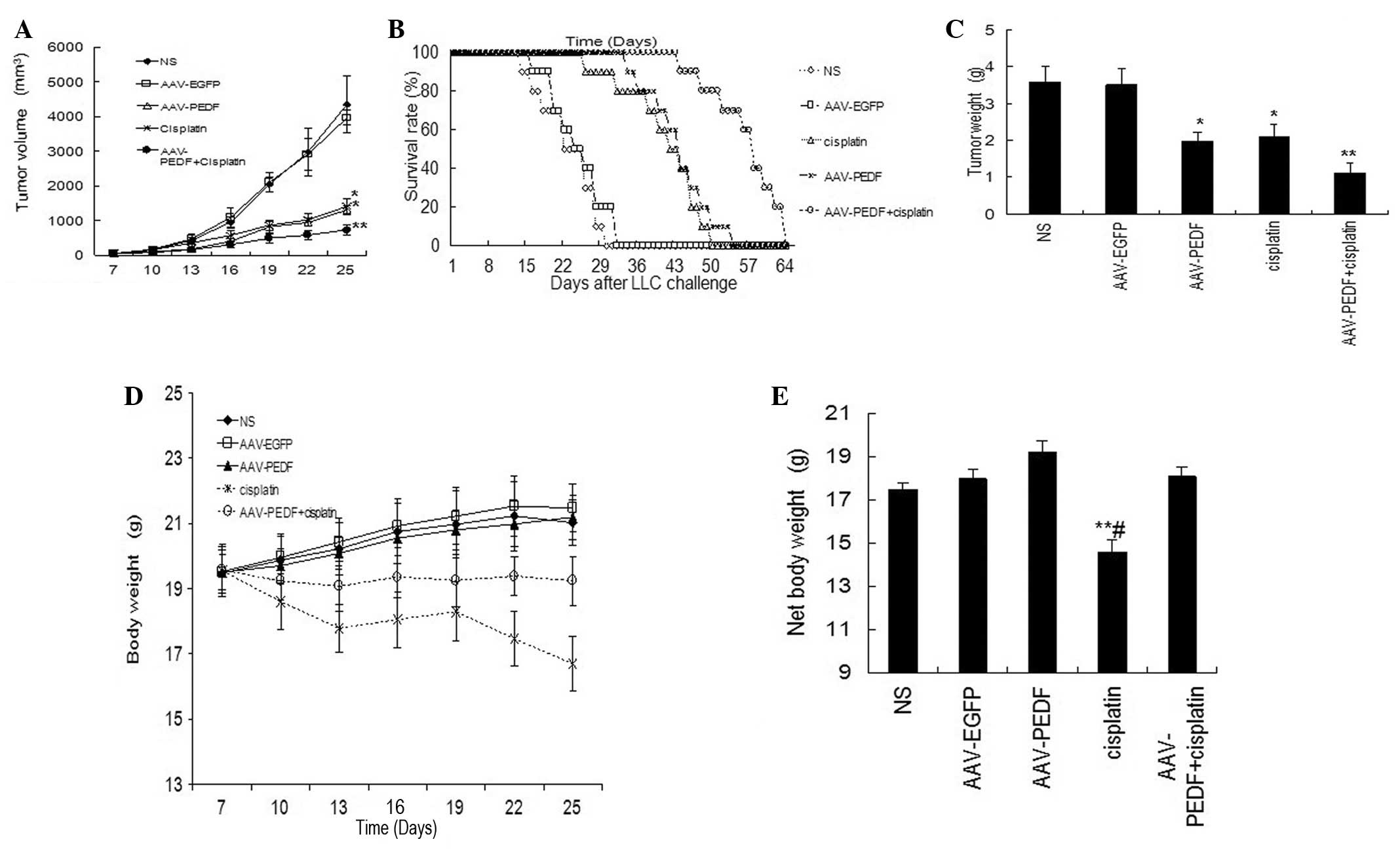
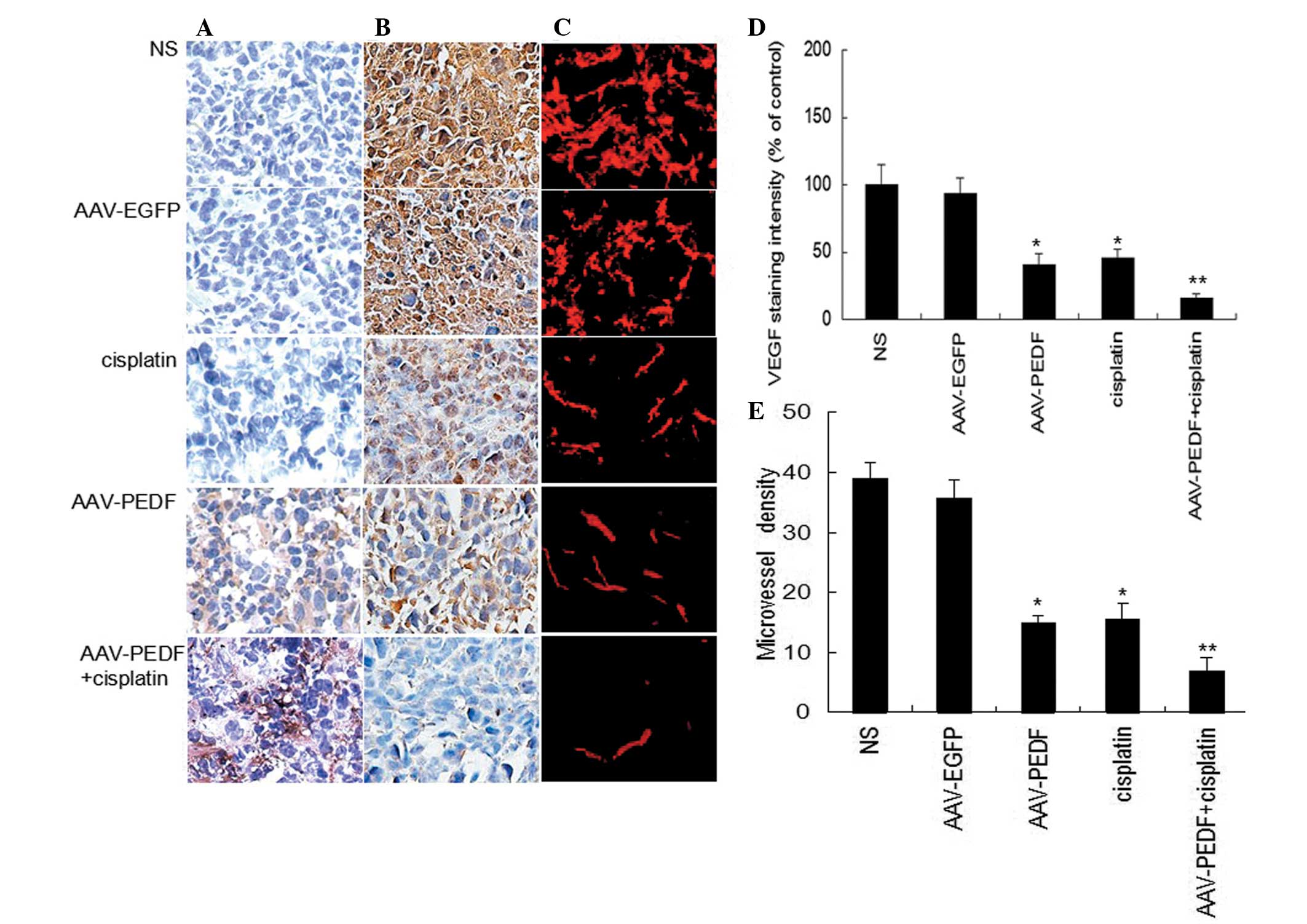
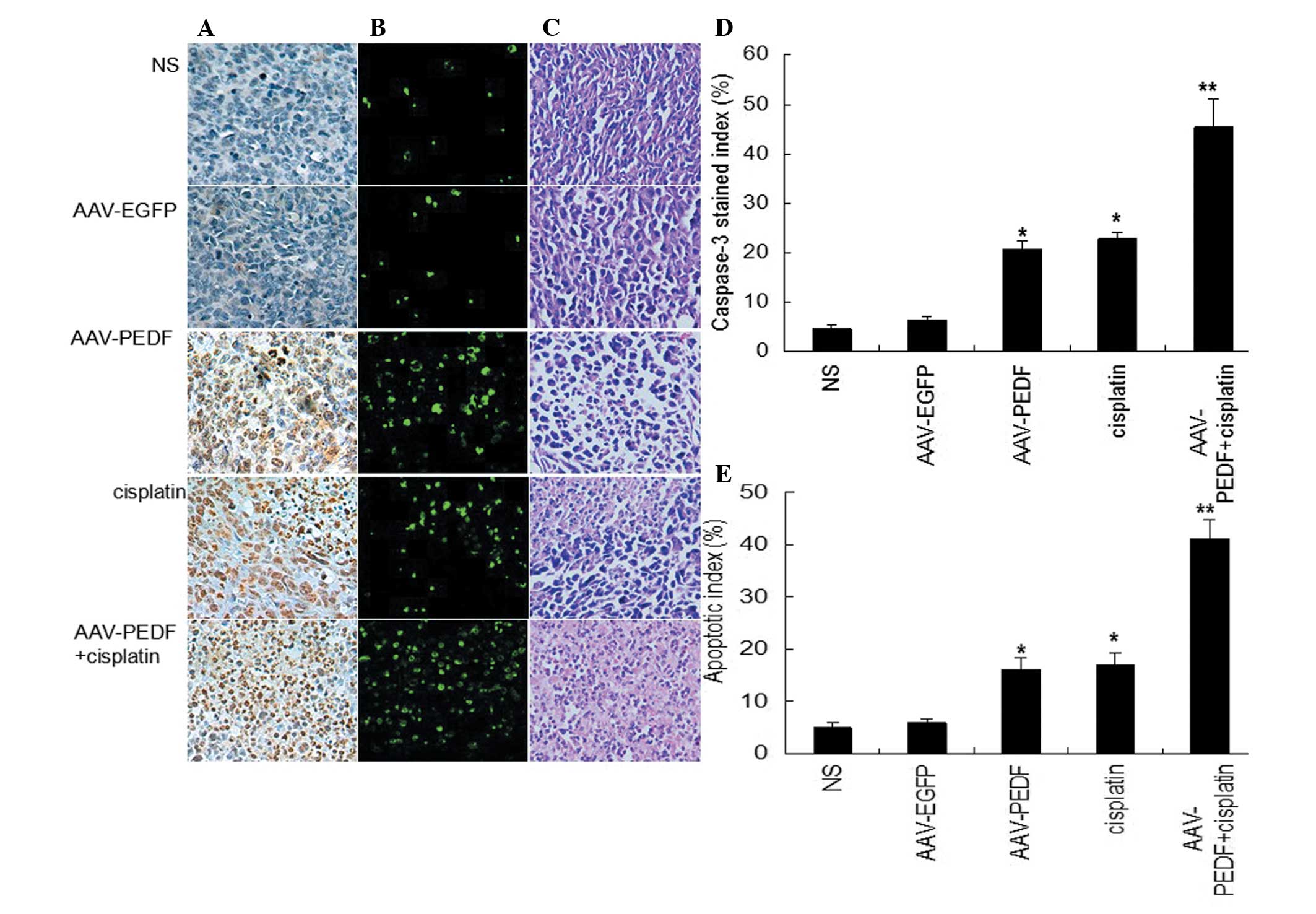
|
1
|
Adam M, Bayer C, Henke J, et al:
Tirapazamine plus cisplatin and irradiation in a mouse model:
improved tumor control at the cost of increased toxicity. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 134:137–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Verweij J, de Wit R and de Mulder PH:
Optimal control of acute cisplatin-induced emesis. Oncology.
53(Suppl 1): 56–64. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jiang M, Liu Z, Xiang Y, et al:
Synergistic antitumor effect of AAV-mediated TRAIL expression
combined with cisplatin on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
BMC Cancer. 11:542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanazawa T, Mizukami H, Okada T, et al:
Suicide gene therapy using AAV-HSVtk/ganciclovir in combination
with irradiation results in regression of human head and neck
cancer xenografts in nude mice. Gene Ther. 10:51–58. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, Huang F, Cai H, et al: The
efficacy of combination therapy using adeno-associated virus-TRAIL
targeting to telomerase activity and cisplatin in a mice model of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1827–1837.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Monahan PE, Jooss K and Sands MS: Safety
of adeno-associated virus gene therapy vectors: a current
evaluation. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 1:79–91. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wagner JA, Reynolds T, Moran ML, et al:
Efficient and persistent gene transfer of AAV-CFTR in maxillary
sinus. Lancet. 351:1702–1703. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Muramatsu S, Fujimoto K, Ikeguchi K, et
al: Behavioral recovery in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease
by triple transduction of striatal cells with adeno-associated
viral vectors expressing dopamine synthesizing enzymes. Hum Gene
Ther. 13:345–354. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kay MA, Manno CS, Ragni MV, et al:
Evidence for gene transfer and expression of factor IX in
haemophilia B patients treated with an AAV vector. Nat Genet.
24:257–261. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Becerra SP, Sagasti A, Spinella P and
Notario V: Pigment epithelium-derived factor behaves like a
noninhibitory serpin. Neurotrophic activity does not require the
serpin reactive loop. J Biol Chem. 270:25992–25999. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Broadhead ML, Dass CR and Choong PF: In
vitro and in vivo biological activity of PEDF against a range of
tumours. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 13:1429–1438. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tombran-Tink J and Barnstable CJ: PEDF: a
multifaceted neurotrophic factor. Nat Rev Neurosci. 4:628–636.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dawson D, Volpert OV, Gillis P, et al:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor: a potent inhibitor of
angiogenesis. Science. 285:245–248. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fernandez-Garcia NI, Volpert OV and
Jimenez B: Pigment epithelium-derived factor as a multifunctional
antitumor factor. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:15–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG and Minick
CR: Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical
veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J
Clin Invest. 52:2745–2756. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He SS, Shi HS, Yin T, et al: AAV-mediated
gene transfer of human pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits
Lewis lung carcinoma growth in mice. Oncol Rep. 27:1142–1148.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Dong X, Wu Z, Cao H, Niu D, et al: A
novel method for purification of recombinant adenoassociated virus
vectors on a large scale. Chinese Sci Bull. 46:485–488. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pang X, Yi Z, Zhang X, et al:
Acetyl-11-ketob-boswellic acid inhibits prostate tumor growth by
suppressing vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 69:5893–5900. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Alexander IE, Russell DW and Miller AD:
DNA-damaging agents greatly increase the transduction of
nondividing cells by adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol.
68:8282–8287. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanazawa T, Urabe M, Mizukami H, et al:
Gamma-rays enhance rAAV-mediated transgene expression and cytocidal
effect of AAV-HSVtk/ganciclovir on cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther.
8:99–106. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taraboletti G and Giavazzi R: Modelling
approaches for angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 40:881–889. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hase R, Miyamoto M, Uehara H, et al:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor gene therapy inhibits human
pancreatic cancer in mice. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8737–8744. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang LP, Cheng P, Peng XC, et al:
Anti-tumor effect of adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of pigment
epithelium-derived factor on mouse B16-F10 melanoma. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 28:752009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu QJ, Gong CY, Luo ST, et al:
AAV-mediated human PEDF inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in
murine colorectal peritoneal carcinomatosis model. BMC Cancer.
12:1292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stellmach V, Crawford SE, Zhou W and Bouck
N: Prevention of ischemia-induced retinopathy by the natural ocular
antiangiogenic agent pigment epithelium-derived factor. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:2593–2597. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Siddik ZH: Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic
action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 22:7265–7279.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|