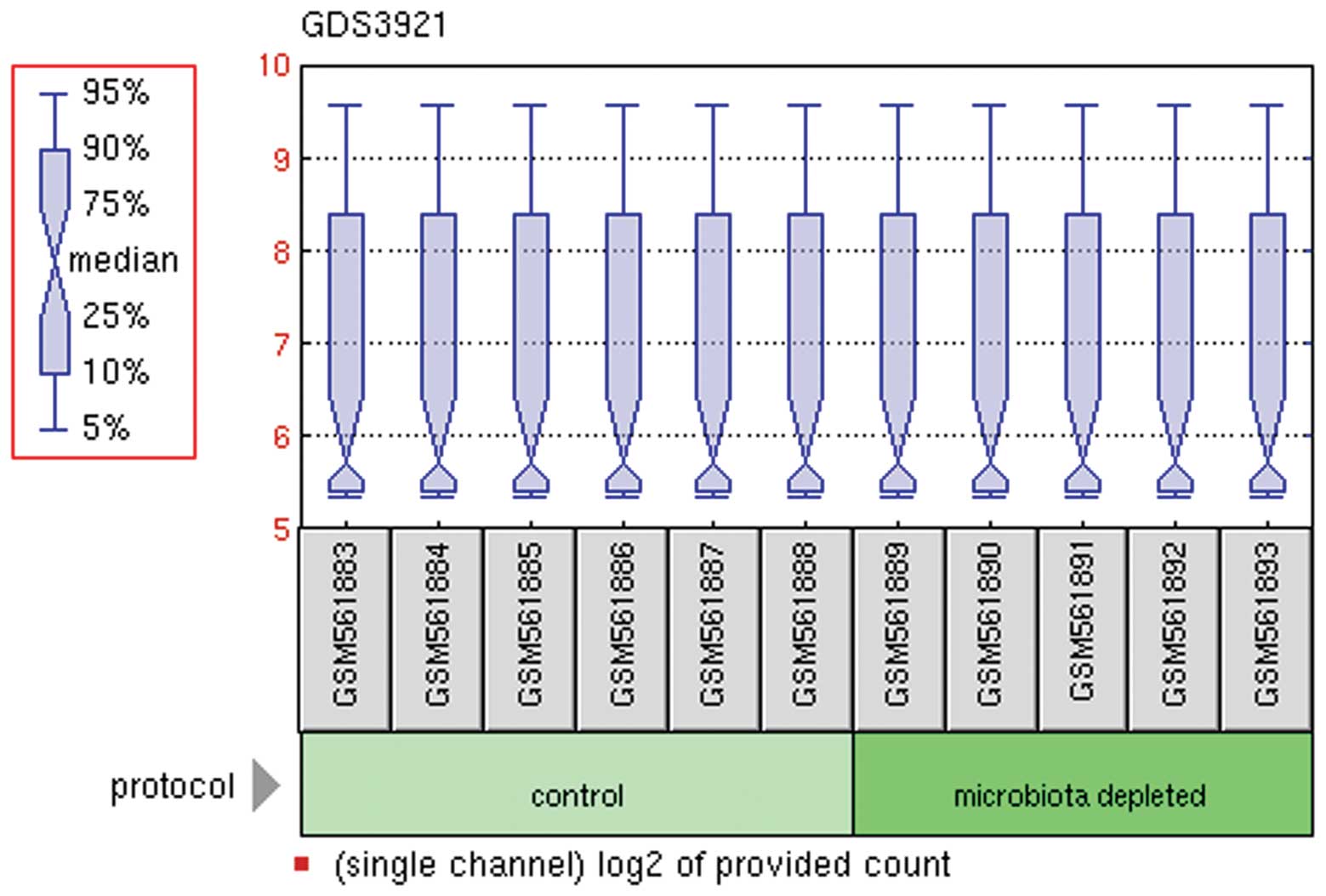
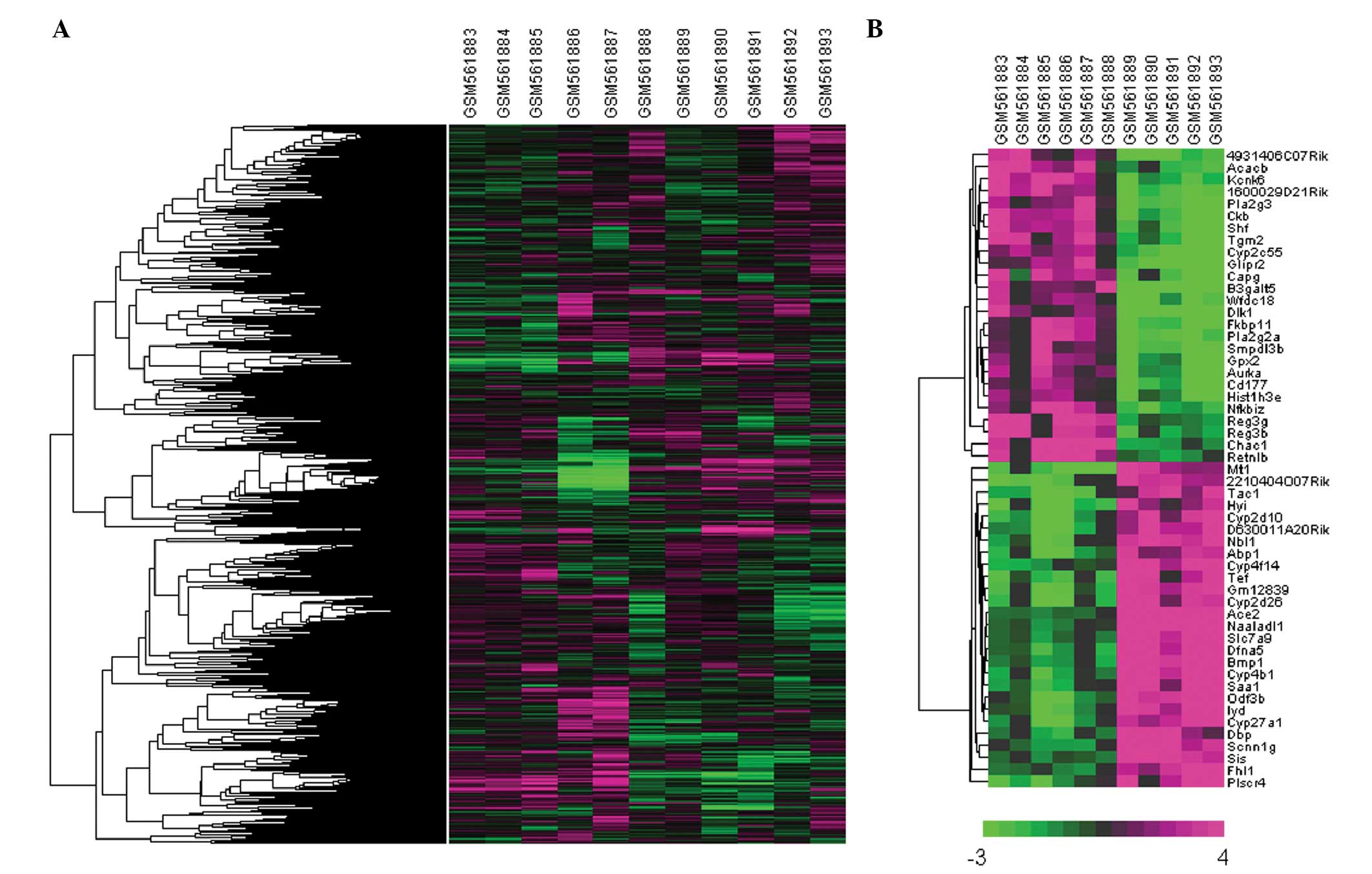
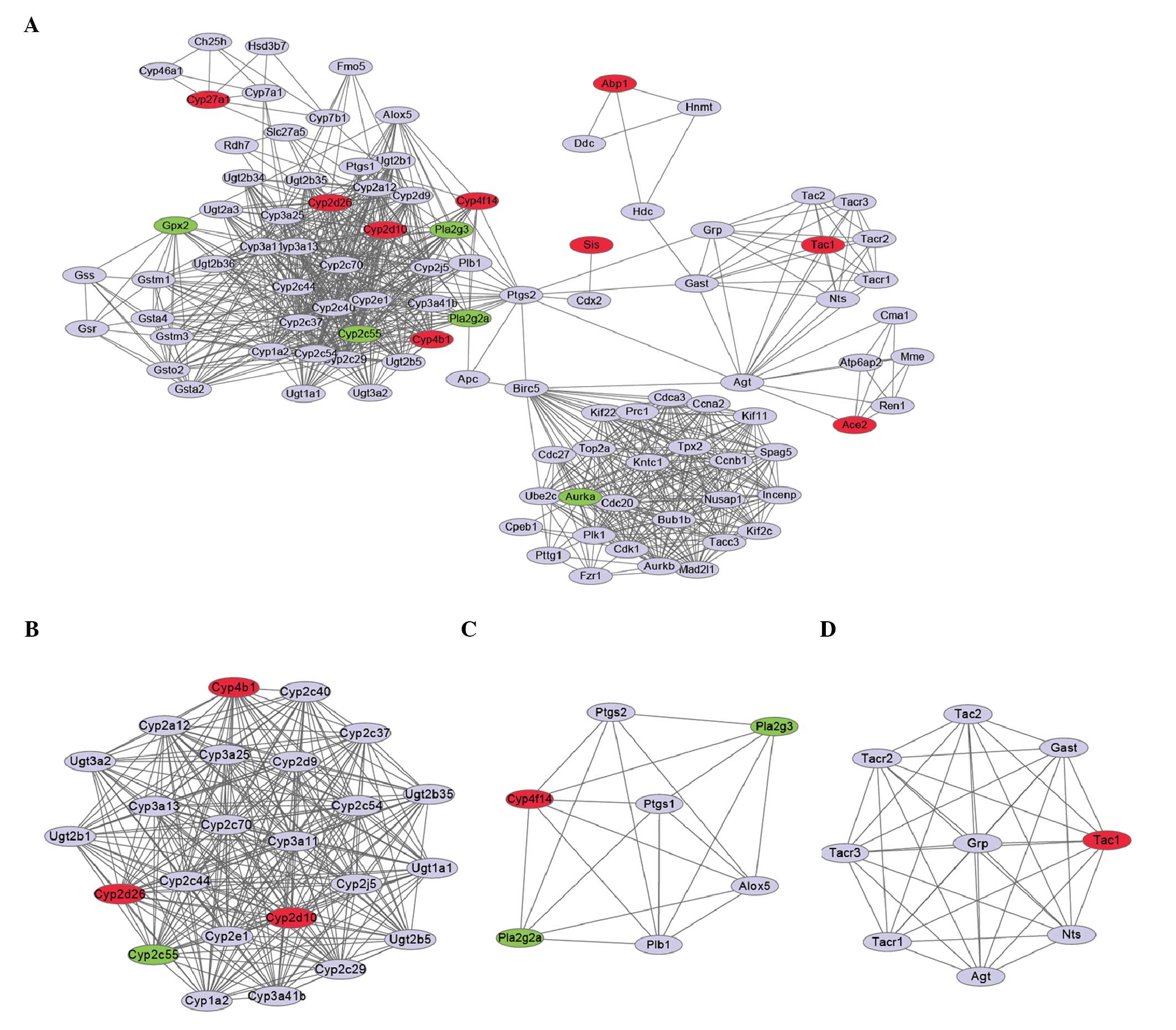
|
1
|
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, et al: A human gut
microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing.
Nature. 464:59–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tremaroli V and Backhed F: Functional
interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism.
Nature. 489:242–249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gerritsen J, Smidt H, Rijkers GT and de
Vos WM: Intestinal microbiota in human health and disease: the
impact of probiotics. Genes Nutr. 6:209–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jernberg C, Lofmark S, Edlund C and
Jansson JK: Long-term impacts of antibiotic exposure on the human
intestinal microbiota. Microbiology. 156:3216–3223. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arroyo G, Penas E, Pedrazuela A and
Prestamo G: Intestinal microbiota in rats fed with tofu (soy curd)
treated under high pressure. Eur Food Res Technol. 220:395–400.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bjorksten B, Sepp E, Julge K, Voor T and
Mikelsaar M: Allergy development and the intestinal microflora
during the first year of life. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 108:516–520.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohigashi S, Sudo K, Kobayashi D, et al:
Changes of the intestinal microbiota, short chain fatty acids, and
fecal pH in patients with colorectal cancer. Dig Dis Sci.
58:1717–1726. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rawls JF: Enteric infection and
inflammation alter gut microbial ecology. Cell Host Microbe.
16:73–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Human Microbiome Jumpstart Reference
Strains Consortium. Nelson KE, Weinstock GM, Highlander SK, et al:
A catalog of reference genomes from the human microbiome. Science.
328:994–999. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reikvam DH, Erofeev A, Sandvik A, et al:
Depletion of murine intestinal microbiota: effects on gut mucosa
and epithelial gene expression. PLoS One. 6:e179962011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Irizarry R, Gautier L and Cope L: An R
package for analyses of Affymetrix oligonucleotide arrays. The
Analysis of Gene Expression Data: Methods and Software. Parmigiani
G, Garrett ES, Irizarry RA and Zeger SL: Springer-Verlag; Berlin:
pp. 102–119. 2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Smyth GK: limma: linear models for
microarray data. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions
Using R and Bioconductor. Gentleman R, Carey VJ, Huber W, Irizarry
RA and Dudoit S: Springer; New York, NY: pp. 397–420. 2005,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shao X, Huang B, Lee JM, Xu F and Espejo
A: Bayesian method for multirate data synthesis and model
calibration. AIChE J. 57:1514–1525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hur AB, Elisseeff A and Guyon I:
Identification of co-regulation patterns by unsupervised cluster
analysis of gene expression data. US Patent 8,489,531. Filed
February 2, 2011; issued July 16, 2013.
|
|
15
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M, et
al: The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of
proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:D561–D568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al:
Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of
biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smoot M, Ono K, Ideker T and Maere S:
PiNGO: a Cytoscape plugin to find candidate genes in biological
networks. Bioinformatics. 27:1030–1031. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue J, Zhao C and Liang A: Pathway
analysis of the differential expression genes of oligonucleotide
microarray of airway allergic diseases using GenMAPP. Lin Chung Er
Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 25:371–373. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Dahlquist KD, Salomonis N, Vranizan K,
Lawlor SC and Conklin BR: GenMAPP, a new tool for viewing and
analyzing microarray data on biological pathways. Nat Genet.
31:19–20. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Velagapudi VR, Hezaveh R, Reigstad CS, et
al: The gut microbiota modulates host energy and lipid metabolism
in mice. J Lipid Res. 51:1101–1112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bäckhed F: Programming of host metabolism
by the gut microbiota. Ann Nutr Metab. 58:44–52. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Espey MG: Role of oxygen gradients in
shaping redox relationships between the human intestine and its
microbiota. Free Radic Biol Med. 55:130–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tamaki Y, Arai T, Sugimura H, et al:
Association between cancer risk and drug-metabolizing enzyme gene
(CYP2A6, CYP2A13, CYP4B1, SULT1A1, GSTM1, and GSTT1) polymorphisms
in cases of lung cancer in Japan. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.
26:516–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roos PH, Belik R, Follmann W, et al:
Expression of cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP1A1, CYP1B1, CYP2E1 and
CYP4B1 in cultured transitional cells from specimens of the human
urinary tract and from urinary sediments. Arch Toxicol. 80:45–52.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang SJ, Kang JH, Lee TS, et al:
Prodrug-activating gene therapy with rabbit cytochrome P450
4B1/4-ipomeanol or 2-aminoanthracene system in glioma cells. Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 44:193–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Antonovic L: A physiological role of
cytochromes P450 4Fs: mouse model (unpublished dissertation). The
University of Texas. AAI3218710. 2006
|
|
29
|
Li N, Liu JY, Qiu H, et al: Use of
metabolomic profiling in the study of arachidonic acid metabolism
in cardiovascular disease. Congest Heart Fail. 17:42–46. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gaullier JM, Halse J, Hoye K, et al:
Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid for 24 months is well
tolerated by and reduces body fat mass in healthy, overweight
humans. J Nutr. 135:778–784. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gaullier JM, Halse J, Hoye K, et al:
Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation for 1 y reduces body fat
mass in healthy overweight humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 79:1118–1125.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kreider RB, Ferreira MP, Greenwood M,
Wilson M and Almada AL: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid
supplementation during resistance training on body composition,
bone density, strength, and selected hematological markers. J
Strength Cond Res. 16:325–334. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Graham GJ, Stevens JM, Page NM, et al:
Tachykinins regulate the function of platelets. Blood.
104:1058–1065. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brain SD: Sensory neuropeptides: their
role in inflammation and wound healing. Immunopharmacology.
37:133–152. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mayer EA: Gut feelings: the emerging
biology of gut-brain communication. Nat Rev Neurosci. 12:453–466.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, et
al: Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking
Toll-like receptor 5. Science. 328:228–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|