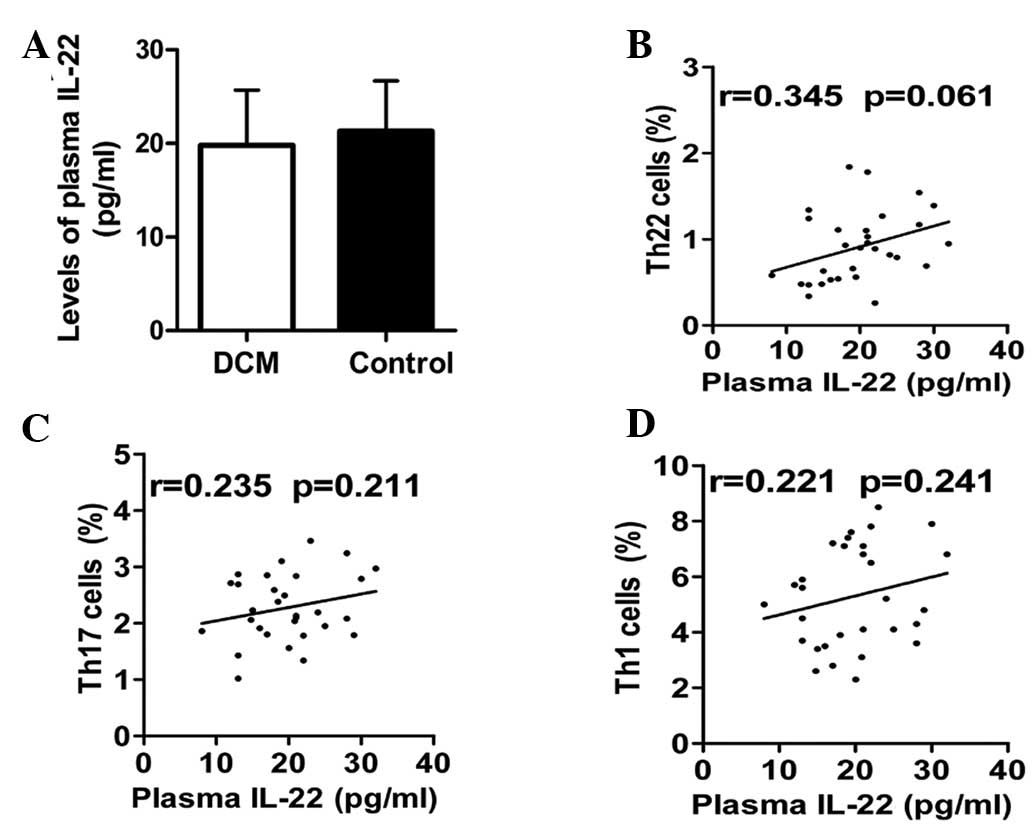
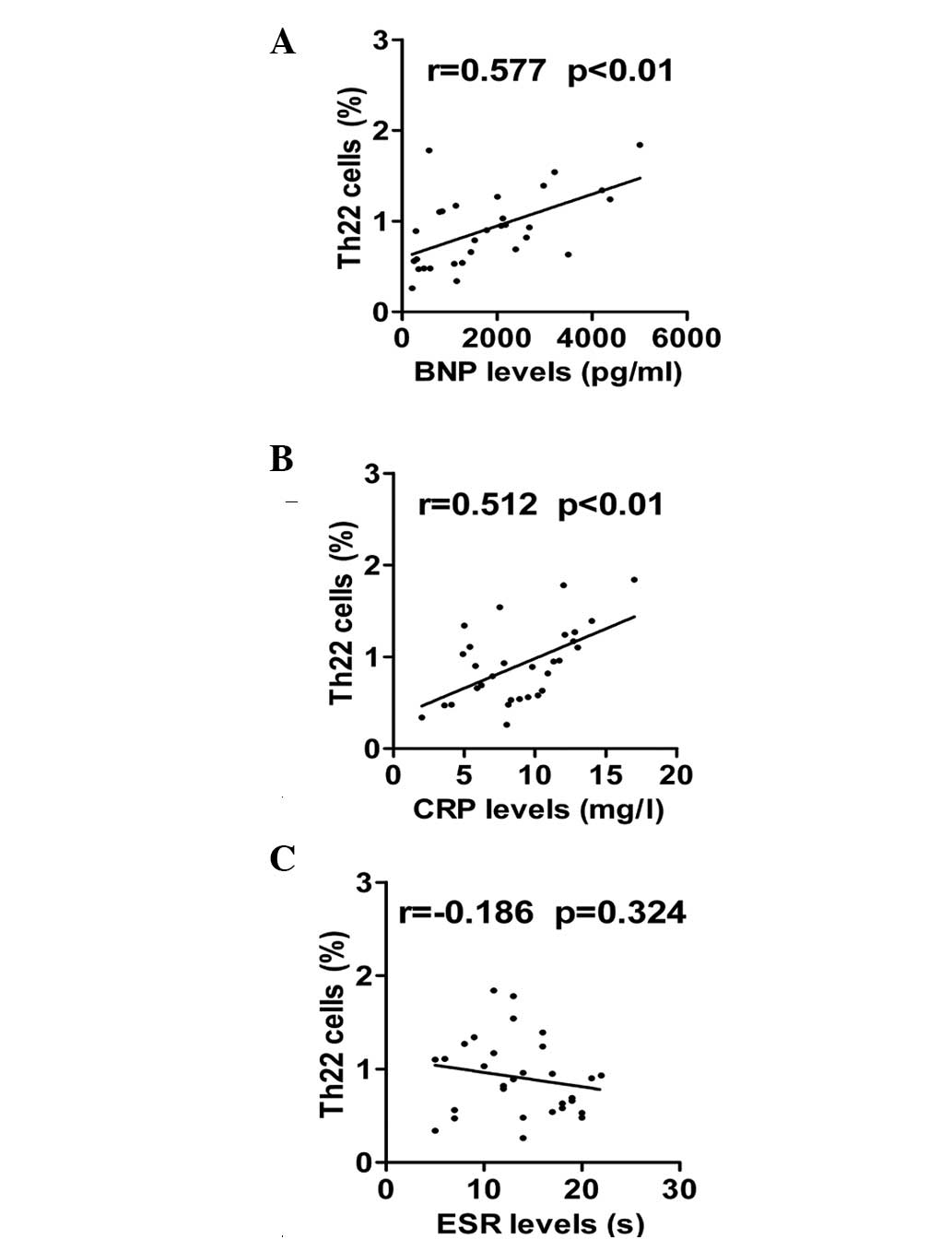
|
1
|
Richardson P, McKenna W, Bristow M, et al:
Report of the 1995 World Health Organisation/International Society
and Federation of Cardiology Task Force on the Definition and
Classification of Cardiomyopathies. Circulation. 93:841–842. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luk A, Ahn E, Soor GS and Butany J:
Dilated cardiomyopathy: a review. J Clin Pathol. 62:219–225. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Grogan M, Redfield MM, Bailey KR, et al:
Long-term outcome of patients with biopsy-proven myocarditis:
comparison with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 26:80–84. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan J, Cao AL, Yu M, et al: Th17 cells
facilitate the humoral immune response in patients with acute viral
myocarditis. J Clin Immunol. 30:226–234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guedes PM, Gutierrez FR, Silva GK, et al:
Deficient regulatory T cell activity and low frequency of
IL-17-producing T cells correlate with the extent of cardiomyopathy
in human Chagas’ disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis.
6:e16302012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J, Wang L, Wang S, et al: The Treg/Th17
imbalance in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Scand
J Immunol. 71:298–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi A, Jian L, Xiaojing H and Hui X: The
prevalence of Th17 cells in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
Clin Invest Med. 32:E144–E150. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: Pathogenic roles of
cardiac autoantibodies in dilated cardiomyopathy. Trends Mol Med.
11:322–326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duhen T, Geiger R, Jarrossay D,
Lanzavecchia A and Sallusto F: Production of interleukin 22 but not
interleukin 17 by a subset of human skin-homing memory T cells. Nat
Immunol. 10:857–863. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang N, Pan HF and Ye DQ: Th22 in
inflammatory and autoimmune disease: prospects for therapeutic
intervention. Mol Cell Biochem. 353:41–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tian T, Yu S and Ma D: Th22 and related
cytokines in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:113–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen H, Goodall JC and Hill Gaston JS:
Frequency and phenotype of peripheral blood Th17 cells in
ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1647–1656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Truchetet ME, Brembilla NC, Montanari E,
Allanore Y and Chizzolini C: Increased frequency of circulating
Th22 in addition to Th17 and Th2 lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis:
association with interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Res Ther.
13:R1662011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baba N, Rubio M, Kenins L, et al: The aryl
hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligand VAF347 selectively acts on
monocytes and naïve CD4(+) Th cells to promote the development of
IL-22-secreting Th cells. Hum Immunol. 73:795–800. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu Y, Li H, Zhang L, et al: Elevated
profiles of Th22 cells and correlations with Th17 cells in patients
with immune thrombocytopenia. Hum Immunol. 73:629–635. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kong Q, Wu W, Yang F, et al: Increased
expressions of IL-22 and Th22 cells in the coxsackievirus
B3-induced mice acute viral myocarditis. Virol J. 9:2322012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maron BJ, Towbin JA, Thiene G, et al:
Contemporary definitions and classification of the
Cardiomyopathies: an American Heart Association Scientific
Statement From the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure
and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes
Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology
Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and
Prevention. Circulation. 113:1807–1816. 2006.
|
|
18
|
Liao YH: Functional analysis of
autoantibodies against ADP/ATP carrier from dilated cardiomyopathy.
Int J Cardiol. 54:165–169. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schulze K, Witzenbichler B, Christmann C
and Schultheiss HP: Disturbance of myocardial energy metabolism in
experimental virus myocarditis by antibodies against the adenine
nucleotide translocator. Cardiovasc Res. 44:91–100. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
De Gennaro L, Brunetti ND, Cuculo A,
Pellegrino PL and Di Biase M: Systemic inflammation in nonischemic
dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart Vessels. 23:445–450. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kones R: Rosuvastatin, inflammation,
C-reactive protein, JUPITER, and primary prevention of
cardiovascular disease - a perspective. Drug Des Devel Ther.
4:383–413. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang F, Wu Y, Tang L, et al: Brain
natriuretic peptide for prediction of mortality in patients with
sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care.
16:R742012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goetze JP, Christoffersen C, Perko M,
Arendrup H, Rehfeld JF, Kastrup J and Nielsen LB: Increased cardiac
BNP expression associated with myocardial ischemia. FASEB J.
17:1105–1107. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishii M, Inomata T, Takehana H, et al:
Prognostic utility of B-type natriuretic peptide assessment in
stable low-risk outpatients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy after
decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 51:2329–2335. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shimazu S, Hirashiki A, Okumura T, et al:
Association between indoxyl sulfate and cardiac dysfunction and
prognosis in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ J.
77:390–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peng D, Xu B, Wang Y, Guo H and Jiang Y: A
high frequency of circulating Th22 and Th17 cells in patients with
new onset graves’ disease. PLoS One. 8:e684462013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang XY, Wang HY, Zhao XY, Wang LJ, Lv QH
and Wang QQ: Th22, but not Th17 might be a good index to predict
the tissue involvement of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin
Immunol. 33:767–774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wolk K, Kunz S, Asadullah K and Sabat R:
Cutting edge: immune cells as sources and targets of the IL-10
family members? J Immunol. 168:5397–5402. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolk K, Witte E, Wallace E, et al: IL-22
regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial
defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a
potential role in psoriasis. Eur J Immunol. 36:1309–1323. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Simonian PL, Wehrmann F, Roark CL, Born
WK, O’Brien RL and Fontenot AP: gammadelta T cells protect against
lung fibrosis via IL-22. J Exp Med. 207:2239–2253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|