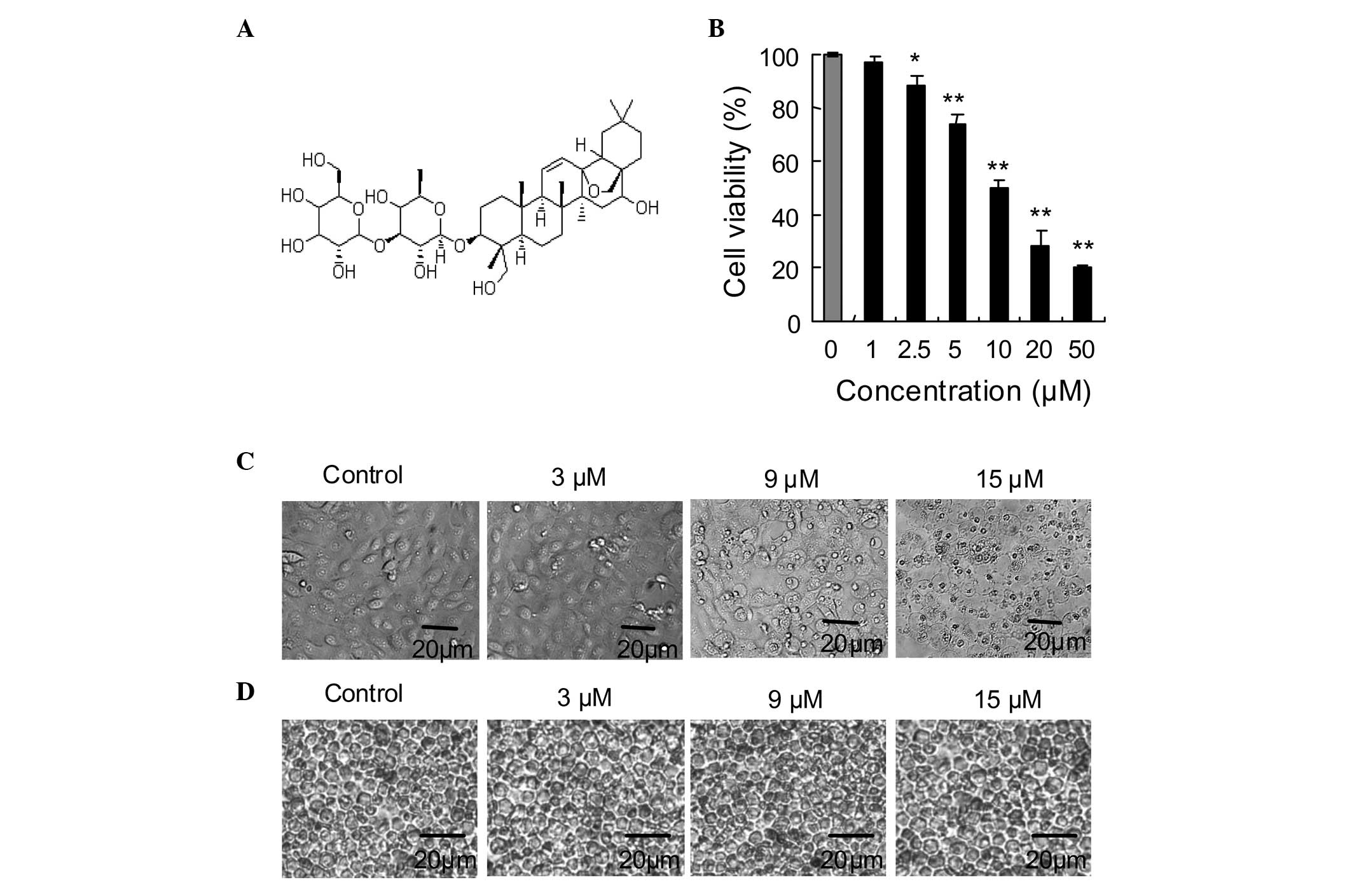
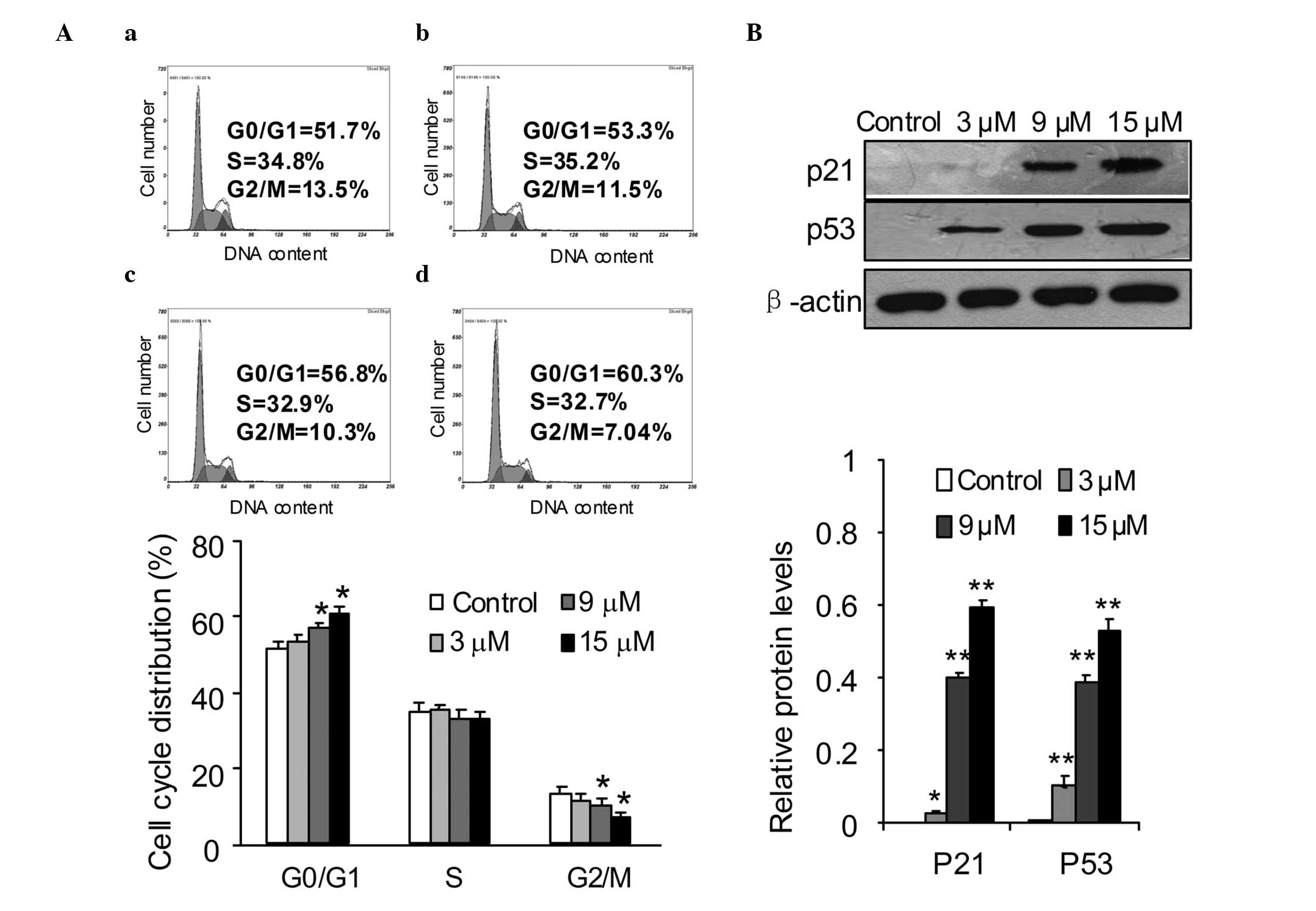
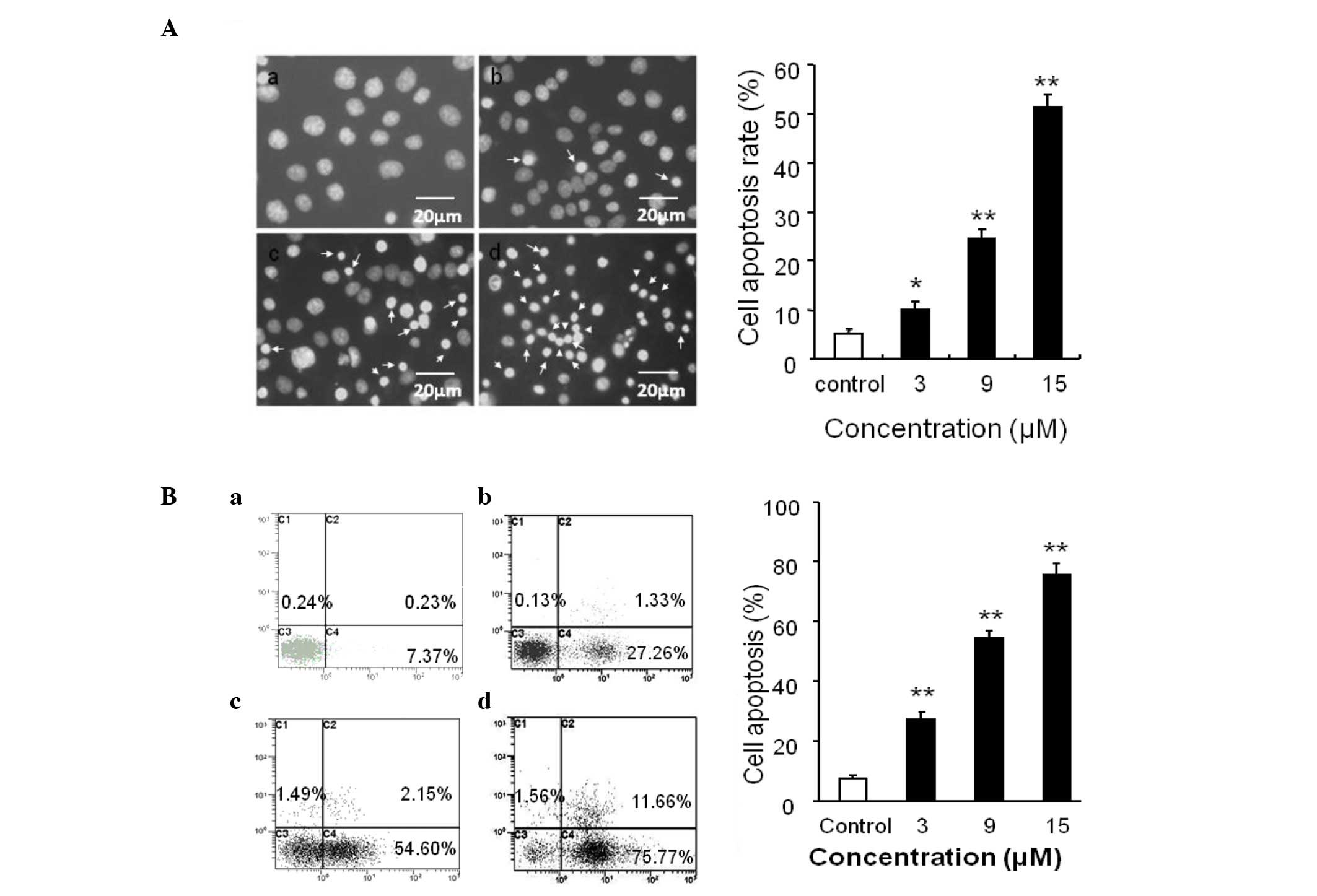
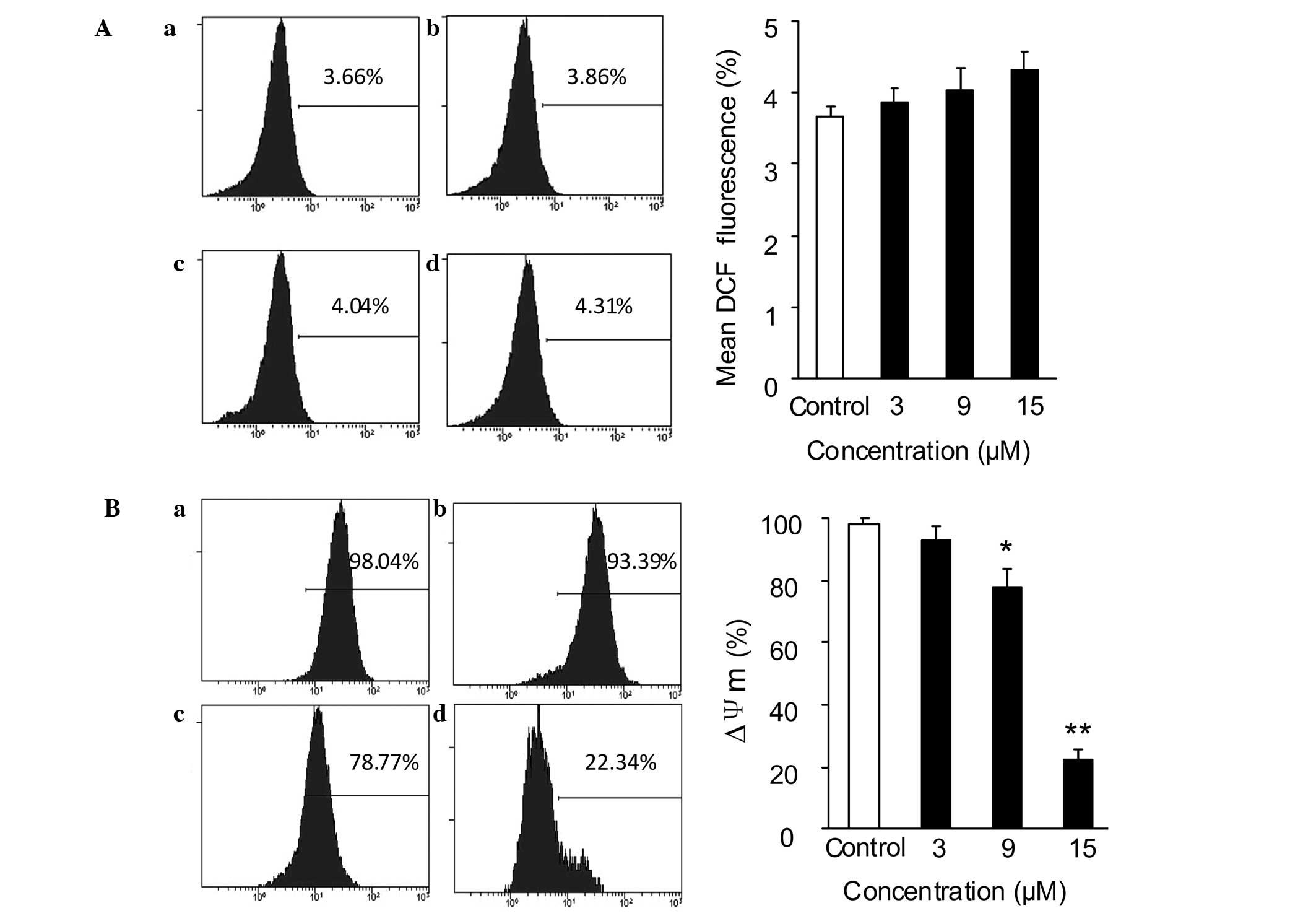
|
1
|
Lee J, Yang DH, Suh JH, Kim U, Eom HY, Kim
J, Lee MY, Kim J and Han SB: Species discrimination of Radix
Bupleuri through the simultaneous determination of ten
saikosaponins by high performance liquid chromatography with
evaporative light scattering detection and electrospray ionization
mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
879:3887–3895. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kato M, Pu MY, Isobe K, Iwamoto T, Nagase
F, Lwin T, Zhang YH, Hattori T, Yanagita N and Nakashima I:
Characterization of the immunoregulatory action of saikosaponin-d.
Cell Immunol. 159:15–25. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kato M, Pu MY, Isobe K, Hattori T,
Yanagita N and Nakashima I: Cell type-oriented differential
modulatory actions of saikosaponin-d on growth responses and DNA
fragmentation of lymphocytes triggered by receptor-mediated and
receptor-bypassed pathways. Immunopharmacology. 29:207–213. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chang JS, Wang KC, Liu HW, Chen MC, Chiang
LC and Lin CC: Sho-saiko-to (Xiao-Chai-Hu-Tang) and crude
saikosaponins inhibit hepatitis B virus in a stable HBV-producing
cell line. Am J Chin Med. 35:341–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohtake N, Nakai Y, Yamamoto M, Sakakibara
I, Takeda S, Amagaya S and Aburada M: Separation and isolation
methods for analysis of the active principles of Sho-saiko-to (SST)
oriental medicine. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
812:135–148. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bao Y, Li C, Shen H and Nan F:
Determination of saikosaponin derivatives in Radix bupleuri and in
pharmaceuticals of the chinese multiherb remedy xiaochaihu-tang
using liquid chromatographic tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem.
76:4208–4216. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu GC, Wu H, Fan LY and Pan HF:
Saikosaponins: a potential treatment option for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Ir J Med Sci. 180:259–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Chiang LC and Lin CC:
Involvement of p53, nuclear factor kappaB and Fas/Fas ligand in
induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by saikosaponin d in
human hepatoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 213:213–221. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Q, Zheng XL, Yang L, Shi F, Gao LB,
Zhong YJ, Sun H, He F, Lin Y and Wang X: Reactive oxygen
species-mediated apoptosis contributes to chemosensitization effect
of saikosaponins on cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in cancer cells.
J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:1592010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL and Lin CC: The
proliferative inhibition and apoptotic mechanism of Saikosaponin D
in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Life Sci.
75:1231–1242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim BM and Hong SH: Sequential caspase-2
and caspase-8 activation is essential for saikosaponin a-induced
apoptosis of human colon carcinoma cell lines. Apoptosis.
16:184–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JC, Chang NW, Chung JG and Chen KC:
Saikosaponin-A induces apoptotic mechanism in human breast
MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cancer cells. Am J Chin Med. 31:363–377. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zong Z, Fujikawa-Yamamoto K, Tanino M,
Teraoka K, Yamagishi H and Odashima S: Saikosaponin b2-induced
apoptosis of cultured B16 melanoma cell line through
down-regulation of PKC activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
219:480–485. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
American Cancer Society. [http://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostatecancer/overviewguide/prostate-cancer-overview-key-statistics].
|
|
15
|
Marta GN, Hanna SA, Fernandes da Silva JL
and de Carvalho HA: Screening for prostate cancer: an updated
review. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 13:101–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kollmeier MA and Zelefsky MJ: How to
select the optimal therapy for early-stage prostate cancer. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 84(Suppl 1): e6–e15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Drudge-Coates L and Turner B: Prostate
cancer overview. Part 1: non-metastatic disease. Br J Nurs.
21:S23–S28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Drudge-Coates L and Turner B: Prostate
cancer overview. Part 2: metastatic prostate cancer. Br J Nurs.
21:S23–S24. S26–S28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Twentyman PR and Luscombe M: A study of
some variables in a tetrazolium dye (MTT) based assay for cell
growth and chemosensitivity. Br J Cancer. 56:279–285. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rhind N and Russell P: Signaling pathways
that regulate cell division. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:a0059422012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dash BC and El-Deiry WS: Cell cycle
checkpoint control mechanisms that can be disrupted in cancer.
Methods Mol Biol. 280:99–161. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kitazumi I and Tsukahara M: Regulation of
DNA fragmentation: the role of caspases and phosphorylation. FEBS
J. 278:427–441. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zimmermann KC, Bonzon C and Green DR: The
machinery of programmed cell death. Pharmacol Ther. 92:57–70. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mignotte B and Vayssiere JL: Mitochondria
and apoptosis. Eur J Biochem. 252:1–15. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Armstrong JS: Mitochondria: a target for
cancer therapy. Br J Pharmacol. 147:239–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bras M, Queenan B and Susin SA: Programmed
cell death via mitochondria: different modes of dying. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 70:231–239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brenner D and Mak TW: Mitochondrial cell
death effectors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:871–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chalah A and Khosravi-Far R: The
mitochondrial death pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 615:25–45. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pradelli LA, Bénéteau M and Ricci JE:
Mitochondrial control of caspase-dependent and -independent cell
death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1589–1597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ola MS, Nawaz M and Ahsan H: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biochem. 351:41–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
García-Sáez AJ: The secrets of the Bcl-2
family. Cell Death Differ. 19:1733–1740. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Robertson JD, Orrenius S and Zhivotovsky
B: Review: nuclear events in apoptosis. J Struct Biol. 129:346–358.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wlodkowic D, Skommer J and Darzynkiewicz
Z: Cytometry of apoptosis. Historical perspective and new advances.
Exp Oncol. 34:255–262. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zinkel S, Gross A and Yang E: BCL2 family
in DNA damage and cell cycle control. Cell Death Differ.
13:1351–1359. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Burlacu A: Regulation of apoptosis by
Bcl-2 family proteins. J Cell Mol Med. 7:249–257. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schultz DR and Harrington WJ Jr:
Apoptosis: programmed cell death at a molecular level. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 32:345–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gottlieb RA: Mitochondria and apoptosis.
Biol Signals Recept. 10:147–161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fan J, Li X, Li P, Li N, Wang T, Shen H,
Siow Y, Choy P and Gong Y: Saikosaponin-d attenuates the
development of liver fibrosis by preventing hepatocyte injury.
Biochem Cell Biol. 85:189–195. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Besson A, Dowdy SF and Roberts JM: CDK
inhibitors: cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell. 14:159–169.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Junttila MR and Evan GI: p53 - a Jack of
all trades but master of none. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:821–829. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Abbas T and Dutta A: p21 in cancer:
intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:400–414. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|