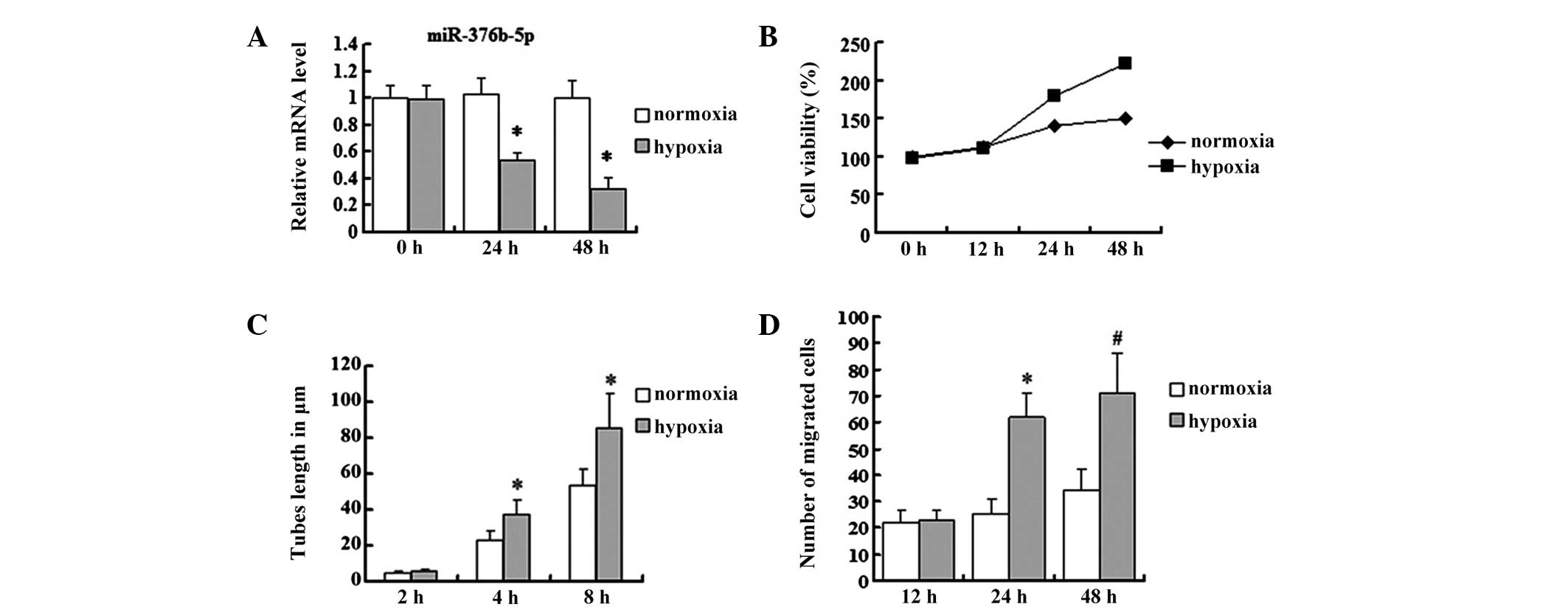
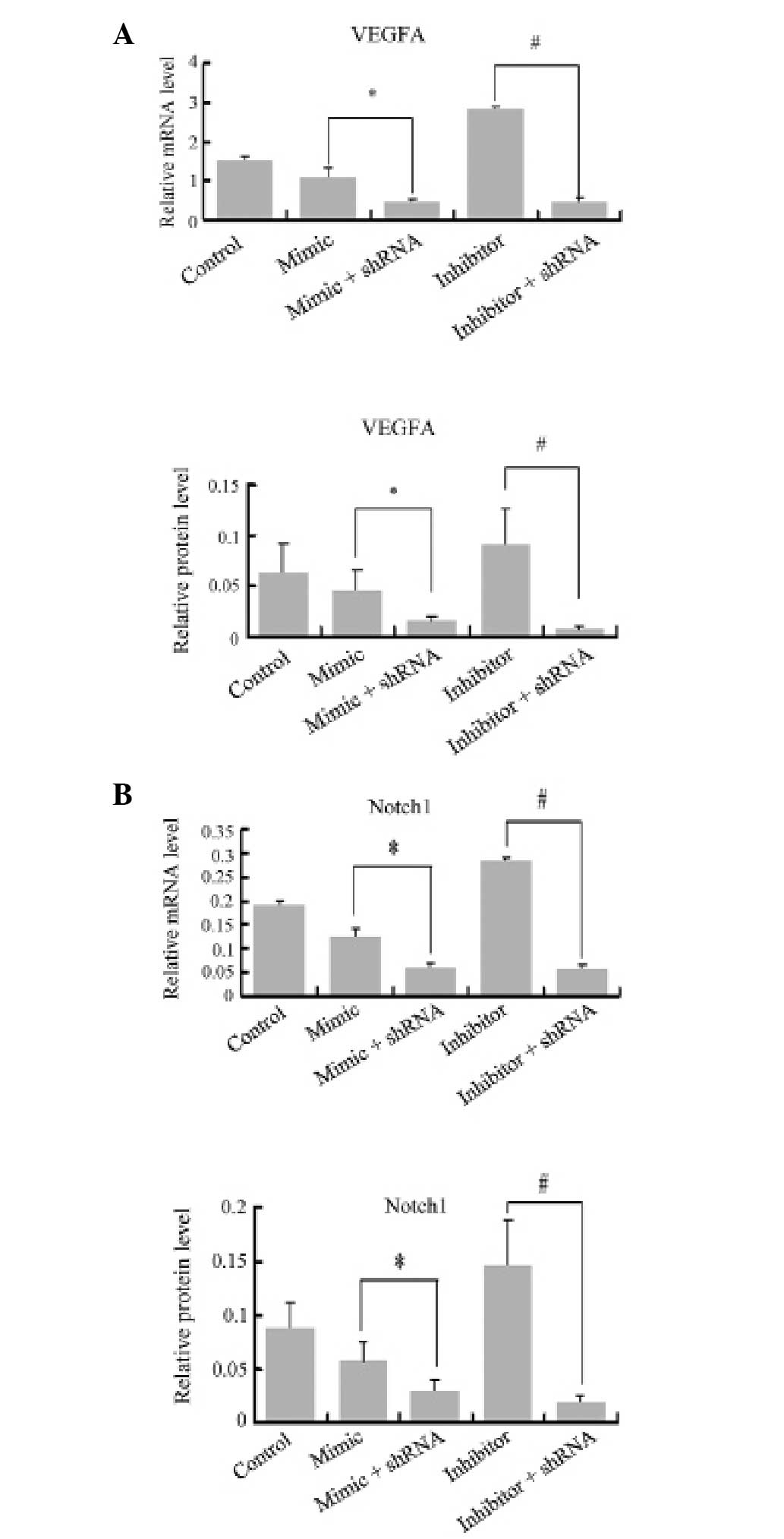
|
1
|
Wang WZ: Neurology. 4th edition. People’s
Medical Publishing House; Beijing: pp. 1302001
|
|
2
|
Zhu XF, Rao ML, Peng J, et al: Dynamis
observed morphologic change of neuron and microcirculation in focal
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion of rat. Chin J Clin Rehabil.
6:1904–1905. 2002.
|
|
3
|
Bang OY, Saver JL, Buck BH, et al; UCLA
Collateral Investigators. Impact of collateral flow on tissue fate
in acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
79:625–629. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liebeskind DS, Cotsonis GA, Saver JL, et
al; Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease (WASID)
Investigators. Collaterals dramatically alter stroke risk in
intracranial atherosclerosis. Ann Neurol. 69:963–974. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miteff F, Levi CR, Bateman GA, et al: The
independent predictive utility of computed tomography angiographic
collateral status in acute ischaemic stroke. Brain. 132:2231–2238.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, et al:
Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke.
Stroke. 25:1794–1798. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu F, Yang Z and Li G: Role of specific
microRNAs for endothelial function and angiogenesis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 386:549–553. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al:
Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in
rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, et al: Potent
and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 391:806–811. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Caplen NJ, Parrish S, Imani F, et al:
Specific inhibition of gene expression by small doublestranded RNAs
in invertebrate and vertebrate systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:9742–9747. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, et al:
Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate
expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans
developmental timing. Cell. 106:23–34. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Humphreys DT, Westman BJ, Martin DI, et
al: MicroRNAs control translation initiation by inhibiting
eukaryotic initiation factor 4E/cap and poly(A) tail function. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:16961–16966. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, et al:
Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA
instability. Cell. 120:623–634. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, et
al: A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 27:1859–1867.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wen QQ, Jia YJ, Wang MC, et al: Expression
analysis of microRNA on acute cerebral ischemia in rats. J
Chongqing Univ. 33:23–26. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Roy S, Khanna S, Hussain SR, et al:
MicroRNA expression in response to murine myocardial infarction:
miR-21 regulates fibroblast metalloprotease-2 via phosphatase and
tensin homologue. Cardiovasc Res. 82:21–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen J, Yang X, Xie B, et al: MicroRNAs
regulate ocular neovascularization. Mol Ther. 16:1208–1216. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dharap A, Bowen K, Place R, et al:
Transient focal ischemia induces extensive temporal changes in rat
cerebral microRNAome. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:675–687. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Velazquez OC, Snyder R, Liu ZJ, et al:
Fibroblast-dependent differentiation of human microvaseular
endothelial cells into capillary-like 3-dimensional networks. FASEB
J. 16:1316–1318. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beck H and Plate KH: Angiogenesis after
cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 117:481–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo X, Liu L, Zhang M, et al: Correlation
of CD34+ cells with tissue angiogenesis after traumatic
brain injury in a rat model. J Neurotrauma. 26:1337–1344. 2009.
|
|
24
|
Yancopoulos GD: Vascular-specific growth
factors and blood vessel formation. Nature. 407:242–248. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Jiang Q, et al: VEGF
enhances angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in
the ischemic brain. J Clin Invest. 106:829–838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abumiya T, Lucero J, Heo JH, et al:
Activated microvessels express vascular endothelial growth factor
and integrin alpha(v)beta3 during focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 19:1038–1050. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sondell M, Lundborg G and Kanje M:
Vascular endothelial growth factor has neurotrophic activity and
stimulates axonal outgrowth, enhancing cell survival and Schwann
cell proliferation in the peripheral nervous system. J Neurosci.
19:5731–5740. 1999.
|
|
29
|
Schratzberger P, Schratzberger G, Silver
M, et al: Favorable effect of VEGF gene transfer on ischemic
peripheral neuropathy. Nat Med. 6:405–413. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang ZJ and He L: Vascular endothelial
growth factor and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Chin J Clin
Rehabil. 8:131972004.
|
|
31
|
Greenberg DA and Jin K: From angiogenesis
to neuropathology. Nature. 438:954–959. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Limbourg FP, Takeshita K, Radtke F, et al:
Essential role of endothelial Notch1 in angiogenesis. Circulation.
111:1826–1832. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song Cai-Li, Zhang Feng-Chun, Xu
Ying-Chun, et al: Effect of breast cancer stromal cells on
expression of Wntl, Notchl and β-catenin and migration of MCF-7
cells. Medical Bulletin of Shanghai Jiaotong University.
28:921–924. 2008.
|
|
34
|
Hainaud P, Contrerès JO, Villemain A, et
al: The role of the vascular endothelial growth factor-Delta-like 4
ligand/Notch4-ephrin B2 cascade in tumor vessel remodeling and
endothelial cell functions. Cancer Res. 66:8501–8510. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin KL, Mao XO, Nagayama T, et al:
Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpHa by global ischemia in rat brain.
Neuroscience. 99:577–585. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sharp FR, Lu A, Tang Y, et al: Multiple
molecular penumbras after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 20:1011–1032. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bonauer A, Carmona G, Iwasaki M, et al:
MicroRNA-92a controls angiogenesis and functional recovery of
ischemic tissues in mice. Science. 324:1710–1713. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jeyaseelan K, Lim KY and Armugam A:
MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to
transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Stroke. 39:959–966. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taguchi A, Yanagisawa K, Tanaka M, et al:
Identification of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha as a novel
target for miR-17–92 microRNA cluster. Cancer Res. 68:5540–5545.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ghosh G, Subramanian IV, Adhikari N, et
al: Hypoxia-induced microRNA-424 expression in human endothelial
cells regulates HIF-alpha isoforms and promotes angiogenesis. J
Clin Invest. 120:4141–4154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cascio S, D’Andrea A, Ferla R, et al:
miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and
STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:242–249.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|