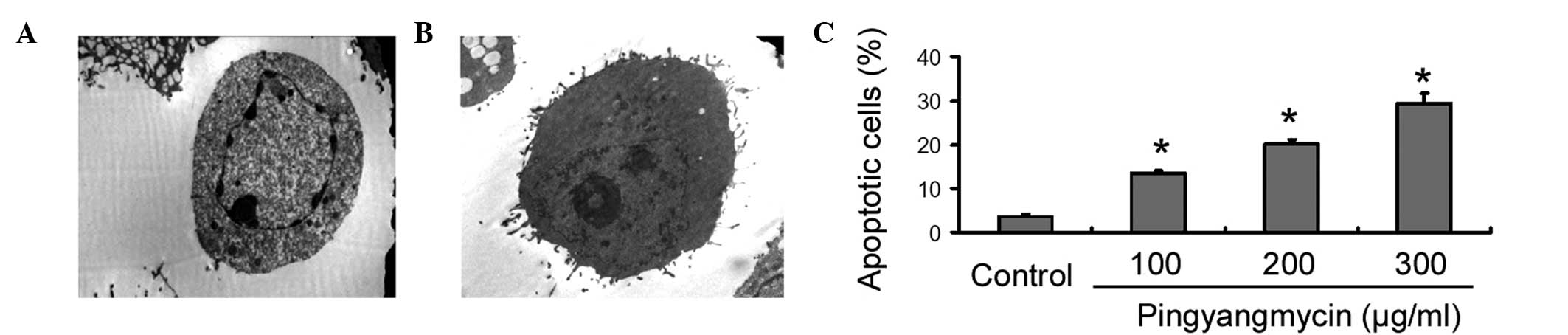
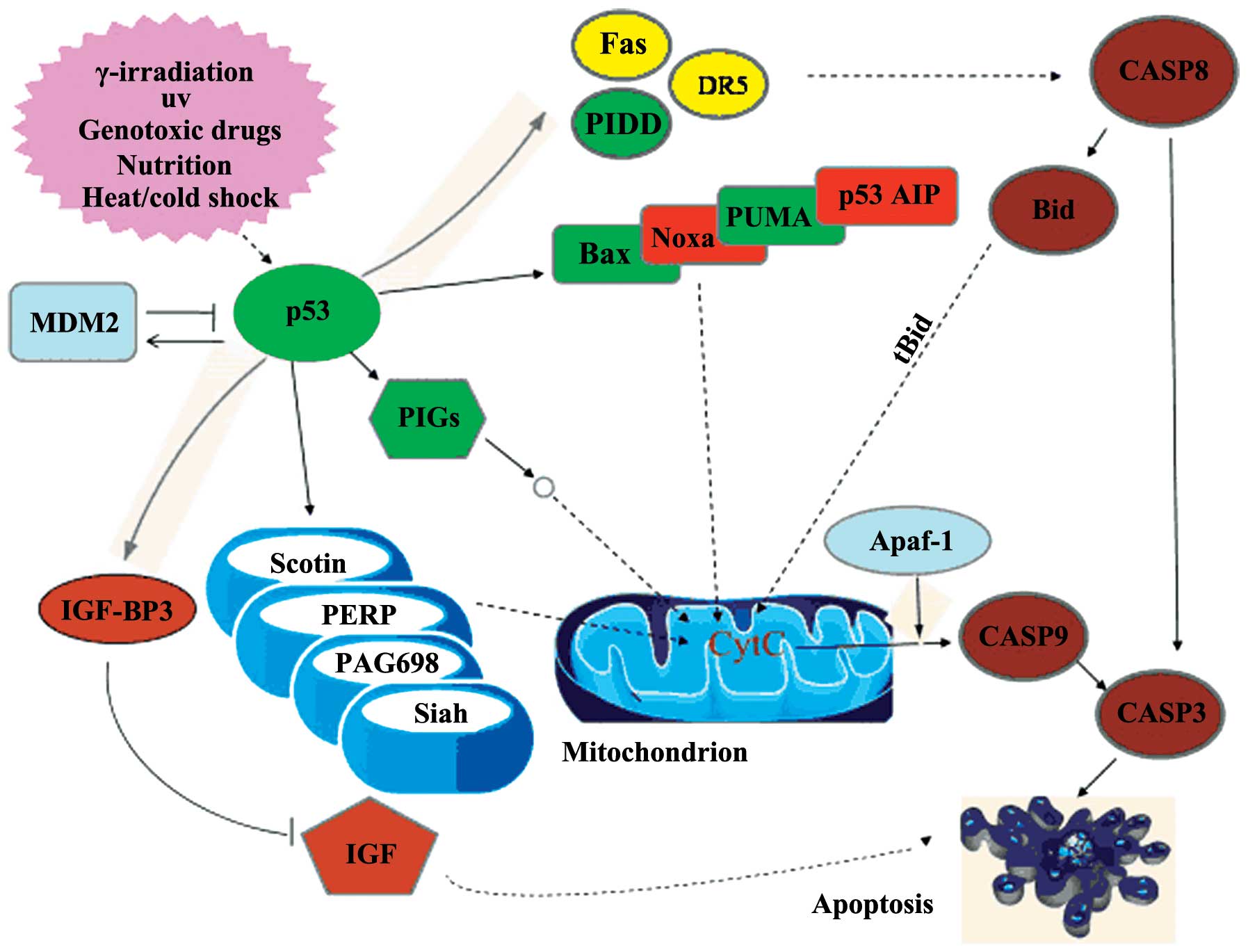
|
1
|
Mendiratta V and Jabeen M: Infantile
hemangioma: an update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol.
76:469–475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwon EK, Seefeldt M and Drolet BA:
Infantile hemangiomas: an update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 14:111–123.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eivazi B and Werner JA: Management of
vascular malformations and hemangiomas of the head and neck - an
update. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 21:157–163. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Itinteang T, Withers AH, Leadbitter P, et
al: Pharmacologic therapies for infantile hemangioma: is there a
rational basis? Plast Reconstr Surg. 128:499–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bischoff J: Monoclonal expansion of
endothelial cells in hemangioma: an intrinsic defect with extrinsic
consequences? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 12:220–224. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Peng Q, Liu W, Zhou F, et al: An
experimental study on the therapy of infantile hemangioma with
recombinant interferon γ. Pediatr Surg. 46:496–501. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Storch CH and Hoeger PH: Propranolol for
infantile haemangiomas: insights into the molecular mechanisms of
action. Br J Dermatol. 163:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, et al: Programmed
cell death pathways in cancer: a review of apoptosis, autophagy and
programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z and Haupt Y:
Apoptosis - the p53 network. J Cell Sci. 116:4077–4085. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai F, Chen Y, Song Y, et al: A natural
small molecule harmine inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses tumour
growth through activation of p53 in endothelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e521622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ji Y, Li K, Xiao X, et al: Effects of
propranolol on the proliferation and apoptosis of
hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. J Pediatr Surg. 47:2216–2223.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen P, Liu B and Hu M: The effect of
hydroxycamptothecin and pingyangmycin on human squamous cell
carcinoma of the tongue. Oncol Lett. 5:947–952. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gong JH, Liu XJ, Li Y and Zhen YS:
Pingyangmycin downregulates the expression of EGFR and enhances the
effects of cetuximab on esophageal cancer cells and the xenograft
in athymic mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:1323–1332. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hou J, Wang M, Tang H, et al:
Pingyangmycin sclerotherapy for infantile hemangiomas in oral and
maxillofacial regions: an evaluation of 66 consecutive patients.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 40:1246–1251. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luo QF and Zhao FY: The effects of
Bleomycin A5 on infantile maxillofacial haemangioma. Head Face Med.
7:112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tu JB, Dong Q, Hu XY, et al: Proteomic
analysis of mitochondria from infantile hemangioma endothelial
cells treated with sodium morrhuate and its liposomal formulation.
J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 26:374–380. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Guan JY, He XF, Chen Y, et al:
Percutaneous intratumoral injection with pingyangmycin lipiodol
emulsion for the treatment of recurrent sacrococcygeal chordomas. J
Vasc Interv Radiol. 22:1216–1220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ho YC, Tai KW and Chang YC: Synergistic
effects of verapamil on pingyangmycin-induced cytotoxicity and
apoptosis in KB cells. Oral Dis. 13:40–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sgonc R, Fuerhapter C, Boeck G, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in human dermal microvascular endothelial
cells and infantile hemangiomas by interferon-alpha. Int Arch
Allergy Immunol. 117:209–214. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sethi G, Shanmugam MK, Ramachandran L, et
al: Multifaceted link between cancer and inflammation. Biosci Rep.
32:1–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lindgren T, Stigbrand T, Riklund K, et al:
Gene expression profiling in MOLT-4 cells during
gamma-radiation-induced apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 33:689–700. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Di J, Zhang Y and Zheng J: Reactivation of
p53 by inhibiting Mdm2 E3 ligase: a novel antitumor approach. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 11:987–994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bradley G, Tremblay S, Irish J, et al: The
expression of p53-induced protein with death domain (Pidd) and
apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
96:1425–1432. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakano K and Vousden KH: PUMA, a novel
proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell. 7:683–694. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nicholls CD, Shields MA, Lee PW, et al:
UV-dependent alternative splicing uncouples p53 activity and PIG3
gene function through rapid proteolytic degradation. J Biol Chem.
279:24171–24178. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee JH, Kang Y, Khare V, et al: The
p53-inducible gene 3 (PIG3) contributes to early cellular response
to DNA damage. Oncogene. 29:1431–1450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thornborrow EC, Patel S, Mastropietro AE,
et al: A conserved intronic response element mediates direct
p53-dependent transcriptional activation of both the human and
murine bax genes. Oncogene. 21:990–999. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z and Haupt Y:
Apoptosis - the p53 network. J Cell Sci. 116:4077–4085. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang H, Deng C, Shen S, et al: Expression
and significance of Bcl-2, Bax, Fas and caspase-3 in different
phases of human hemangioma. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
26:402–404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|