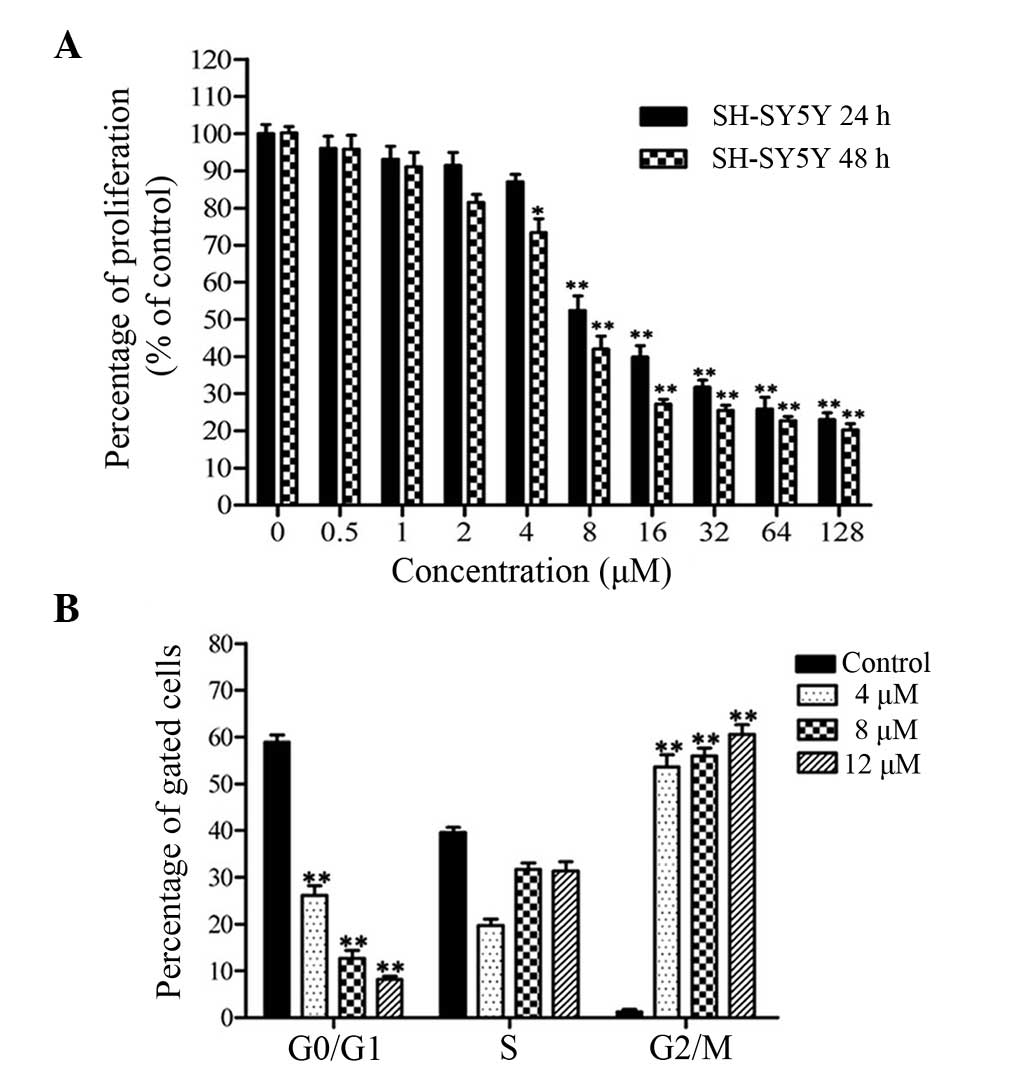
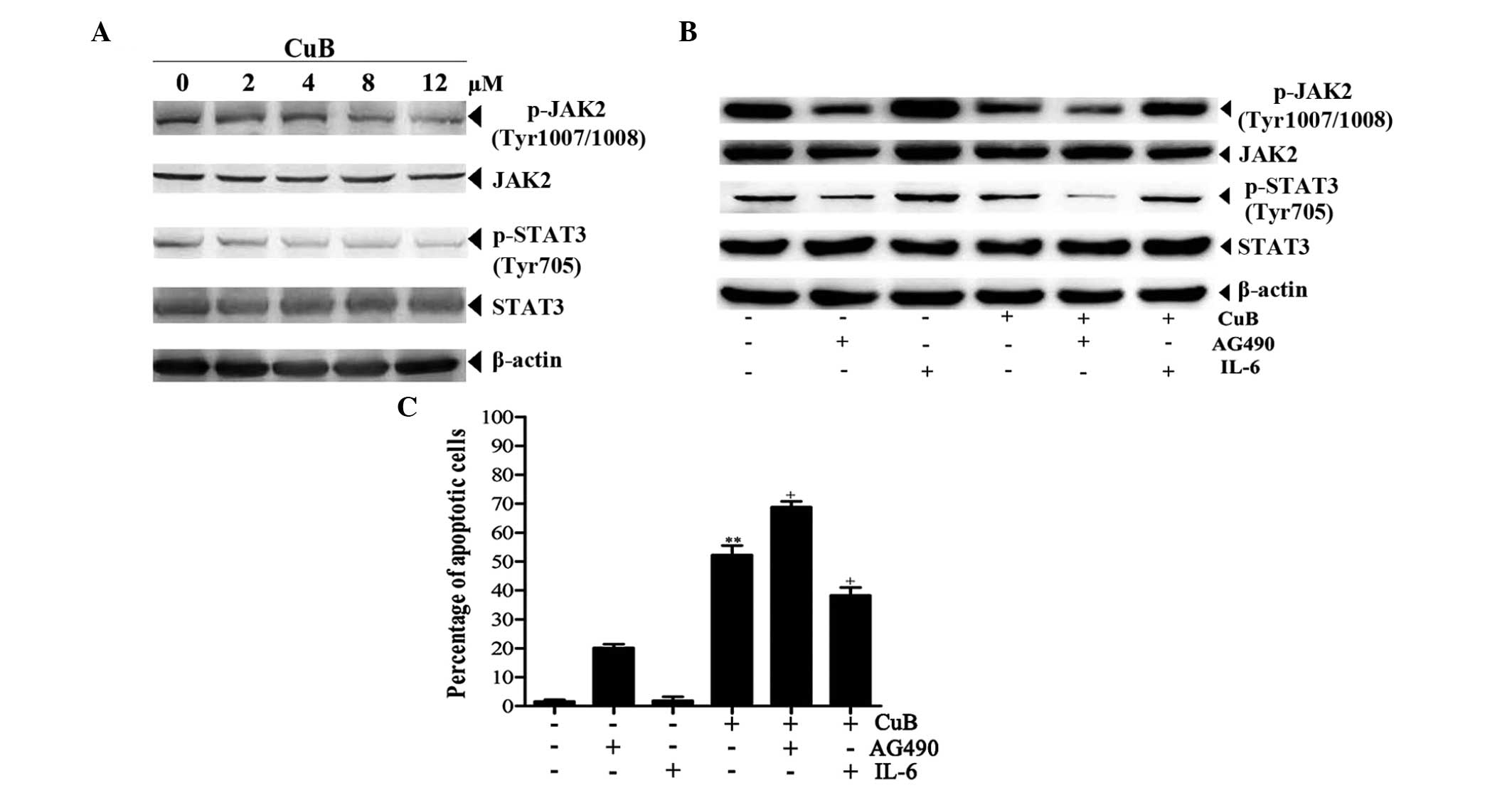
|
1
|
Brodeur GM: Neuroblastoma: Biological
insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:203–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fisher JP and Tweddle DA: Neonatal
neuroblastoma. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 17:207–215. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y, Ouyang D, Xu L, Ji Y, Zha Q, Cai
J and He X: Cucurbitacin B induces rapid depletion of the G-actin
pool through reactive oxygen species-dependent actin aggregation in
melanoma cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:556–567.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jayaprakasam B, Seeram NP and Nair MG:
Anticancer and antiinflammatory activities of cucurbitacins from
Cucurbita andreana. Cancer Lett. 189:11–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen JC, Chiu MH, Nie RL, Cordell GA and
Qiu SX: Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: structures and
biological activities. Nat Prod Rep. 22:386–399. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dzubak P, Hajduch M, Vydra D, et al:
Pharmacological activities of natural triterpenoids and their
therapeutic implications. Nat Prod Rep. 23:394–411. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takasaki M, Konoshima T, Murata Y, et al:
Anticarcinogenic activity of natural sweeteners, cucurbitane
glycosides, from Momordica grosvenori. Cancer Lett. 198:37–42.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu T, Peng H, Zhang M, Deng Y and Wu Z:
Cucurbitacin B, a small molecule inhibitor of the Stat3 signaling
pathway, enhances the chemosensitivity of laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma cells to cisplatin. Eur J Pharmacol. 641:15–22. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Promkan M, Dakeng S, Chakrabarty S, Bögler
O and Patmasiriwat P: The effectiveness of cucurbitacin B in BRCA1
defective breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e557322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Haritunians T, Gueller S, Zhang L, et al:
Cucurbitacin B induces differentiation, cell cycle arrest, and
actin cytoskeletal alterations in myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res.
32:1366–1373. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dakeng S, Duangmano S, Jiratchariyakul W,
U-Pratya Y, Bögler O and Patmasiriwat P: Inhibition of Wnt
signaling by cucurbitacin B in breast cancer cells: reduction of
Wnt-associated proteins and reduced translocation of
galectin-3-mediated β-catenin to the nucleus. J Cell Biochem.
113:49–60. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yin D, Wakimoto N, Xing H, et al:
Cucurbitacin B markedly inhibits growth and rapidly affects the
cytoskeleton in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Cancer.
123:1364–1375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thoennissen NH, Iwanski GB, Doan NB, et
al: Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis by inhibition of the JAK/STAT
pathway and potentiates antiproliferative effects of gemcitabine on
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:5876–5884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu T, Zhang M, Zhang H, Sun C and Deng Y:
Inhibitory effects of cucurbitacin B on laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 265:1225–1232. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oh H, Mun YJ, Im SJ, Lee SY, Song HJ, Lee
HS and Woo WH: Cucurbitacins from Trichosanthes kirilowii as the
inhibitory components on tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis
of B16/F10 melanoma cells. Planta Med. 68:832–833. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee DH, Thoennissen NH, Goff C, et al:
Synergistic effect of low-dose cucurbitacin B and low-dose
methotrexate for treatment of human osteosarcoma. Cancer Lett.
306:161–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin HR, Jin X, Dat NT and Lee JJ:
Cucurbitacin B suppresses the transactivation activity of RelA/p65.
J Cell Biochem. 112:1643–1650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gheeya JS, Chen QR, Benjamin CD, et al:
Screening a panel of drugs with diverse mechanisms of action yields
potential therapeutic agents against neuroblastoma. Cancer Biol
Ther. 8:2386–2395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang M, Zhang H, Sun C, Shan X, Yang X,
Li-Ling J and Deng YH: Targeted constitutive activation of signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by cucurbitacin B. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
63:635–642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mirzayans R, Andrais B, Scott A and Murray
D: New insights into p53 signaling and cancer cell response to DNA
damage: implications for cancer therapy. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012:1703252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kiu H and Nicholson SE: Biology and
significance of the JAK/STAT signalling pathways. Growth Factors.
30:88–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
O’Shea JJ, Gadina M and Schreiber RD:
Cytokine signaling in 2002: new surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway.
Cell. 109(Suppl): S121–S131. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu YY, Zheng Q, Fang B, et al: Germacrone
induces apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells through inhibition
of the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog
Med Sci. 33:339–345. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Epling-Burnette PK, Liu JH,
Catlett-Falcone R, et al: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling leads to
apoptosis of leukemic large granular lymphocytes and decreased
Mcl-1 expression. J Clin Invest. 107:351–362. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nam S, Xie J, Perkins A, et al: Novel
synthetic derivatives of the natural product berbamine inhibit
Jak2/Stat3 signaling and induce apoptosis of human melanoma cells.
Mol Oncol. 6:484–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bill MA, Nicholas C, Mace TA, et al:
Structurally modified curcumin analogs inhibit STAT3
phosphorylation and promote apoptosis of human renal cell carcinoma
and melanoma cell lines. PLoS One. 7:e407242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Um HJ, Min KJ, Kim DE and Kwon TK:
Withaferin A inhibits JAK/STAT3 signaling and induces apoptosis of
human renal carcinoma Caki cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
427:24–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park KR, Nam D, Yun HM, et al:
β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth and induces apoptosis through
the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1 pathways and ROS-mediated
MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett. 312:178–188. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Scuteri A, Galimberti A, Maggioni D, et
al: Role of MAPKs in platinum-induced neuronal apoptosis.
Neurotoxicology. 30:312–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boutros T, Chevet E and Metrakos P:
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase
regulation: roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev.
60:261–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ishdorj G, Johnston JB and Gibson SB:
Cucurbitacin-I (JSI-124) activates the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway
independent of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in B leukemic cells.
BMC Cancer. 11:2682011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cory S and Adams JM: The Bcl2 family:
regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:647–656. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fuster JJ, Sanz-González SM, Moll UM and
Andrés V: Classic and novel roles of p53: prospects for anticancer
therapy. Trends Mol Med. 13:192–199. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|