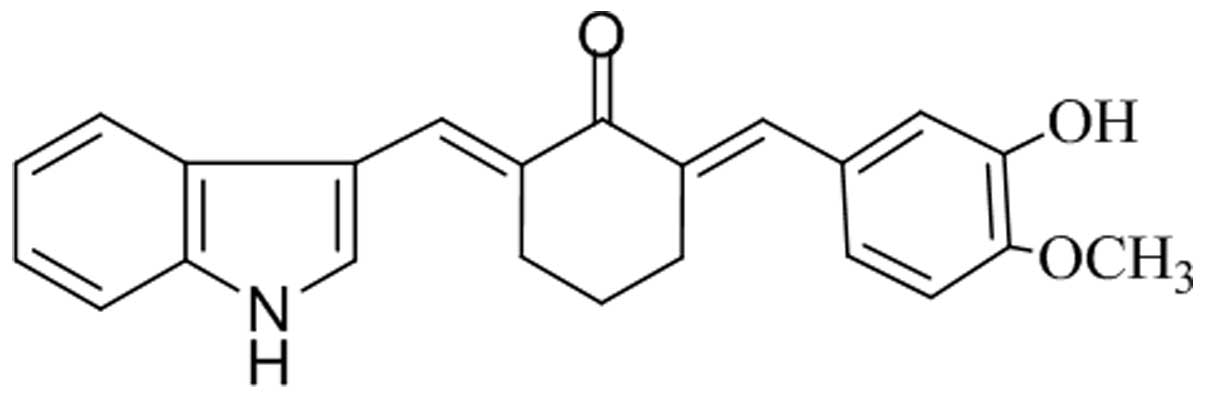
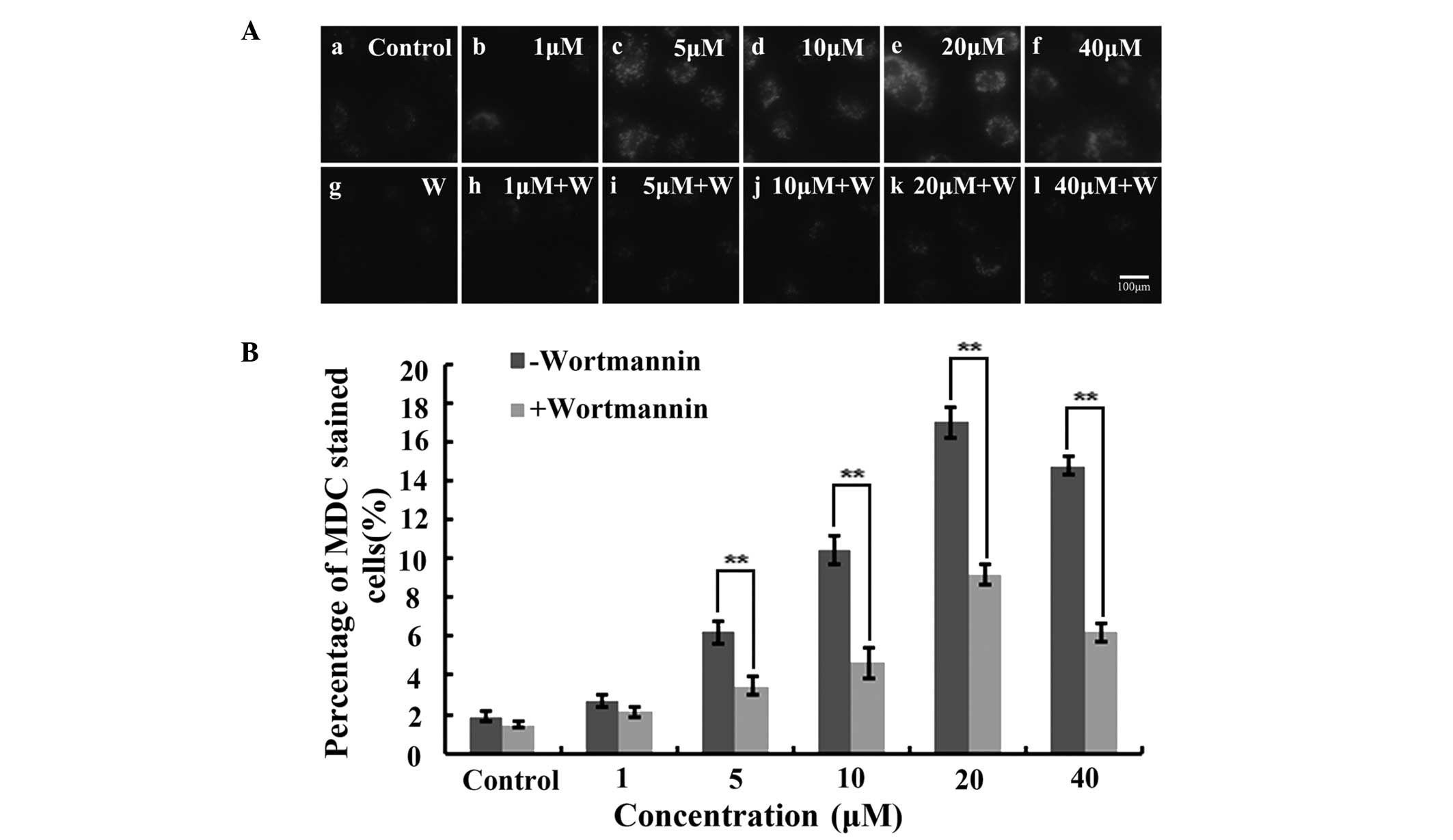
|
1
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiøtz BL, Roos N, Rishovd AL and Gjøen
T: Formation of autophagosomes and redistribution of LC3 upon in
vitro infection with infectious salmon anemia virus. Virus Res.
151:104–107. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gurusamy N and Das DK: Autophagy, redox
signaling, and ventricular remodeling. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:1975–1988. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Q, Liang B, Shirwany NA and Zou MH:
2-Deoxy-D-glucose treatment of endothelial cell induces autophagy
by reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of the AMP-activated
protein kinase. PLoS One. 6:e172342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang PY, Peng SF, Lee CY, et al:
Curcumin-loaded nanoparticles induce apoptotic cell death through
regulation of the function of MDR1 and reactive oxygen species in
cisplatin-resistant CAR human oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:1141–1150. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Norris L, Karmokar A, Howells L, Steward
WP, Gescher A and Brown K: The role of cancer stem cells in the
anti-carcinogenicity of curcumin. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:1630–1637.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ranjan AP, Mukerjee A, Helson L, Gupta R
and Vishwanatha JK: Efficacy of liposomal curcumin in a human
pancreatic tumor xenograft model: inhibition of tumor growth and
angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 33:3603–3609. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Doggui S, Belkacemi A, Paka GD, Perrotte
M, Pi R and Ramassamy C: Curcumin protects neuronal-like cells
against acrolein by restoring Akt and redox signaling pathways. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:1660–1670. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA and
Aggarwal BB: Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises.
Mol Pharm. 4:807–818. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumaravel M, Sankar P and Rukkumani R:
Antiproliferative effect of an analog of curcumin
bis-1,7-(2-hydroxyphenyl)-hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione in human breast
cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 16:1900–1907.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao J, Wang Y, Peng J, et al: A synthetic
compound, 1,5-bis(2-methoxyphenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one (B63),
induces apoptosis and activates endoplasmic reticulum stress in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 131:1455–1465.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Faião-Flores F, Suarez JA, Maria-Engler
SS, Soto-Cerrato V, Pérez-Tomás R and Maria DA: The curcumin analog
DM-1 induces apoptotic cell death in melanoma. Tumor Biol.
34:1119–1129. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arsikin K, Kravic-Stevovic T, Jovanovic M,
et al: Autophagy-dependent and -independent involvement of
AMP-activated protein kinase in 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity to
SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:1826–1836.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, et al:
A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy
and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res. 61:439–444.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buchanan CM, Dickson JM, Lee WJ, Guthridge
MA, Kendall JD and Shepherd PR: Oncogenic mutations of p110a
isoform of PI 3-kinase upregulate its protein kinase activity. PLoS
One. 8:e713372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A,
Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, GABARAP and
GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II
formation. J Cell Sci. 117:2805–2812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aggarwal BB and Shishodia S: Molecular
targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1397–1421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou GZ, Zhang SN, Zhang L, Sun GC and
Chen XB: A synthetic curcumin derivative hydrazinobenzoylcurcumin
induces autophagy in A549 lung cancer cells. Pharm Biol.
52:111–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|