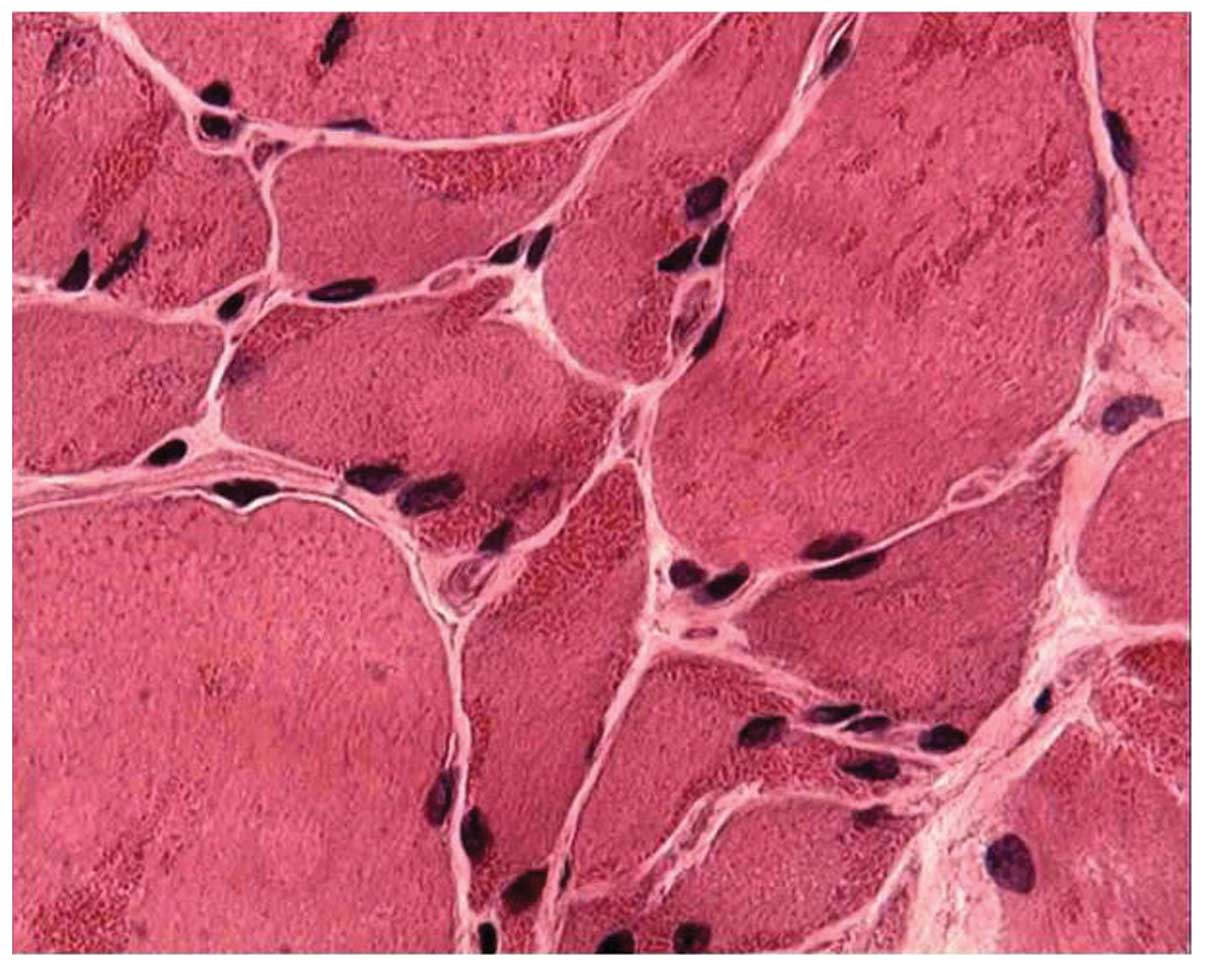
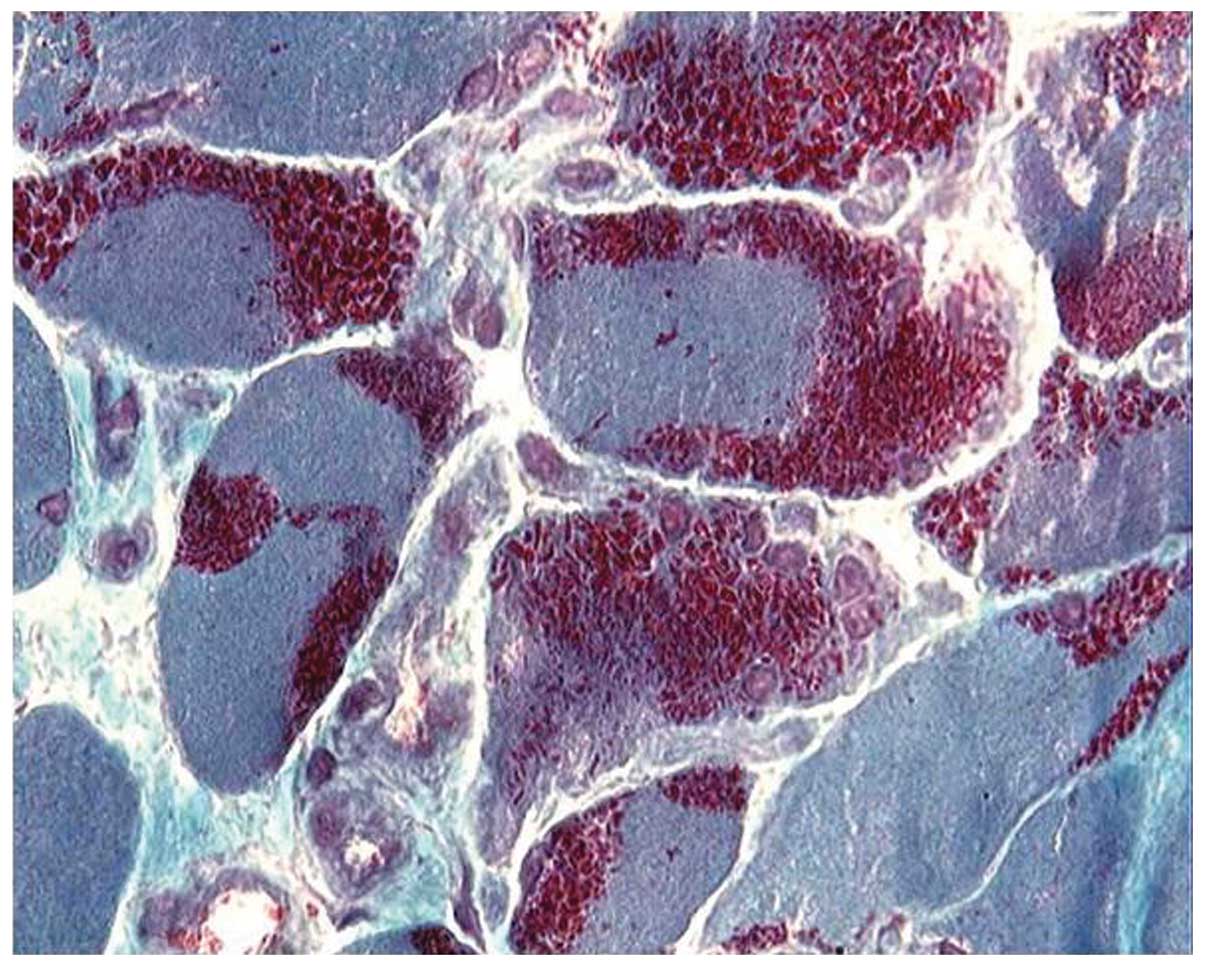
|
1
|
Agrawal PB, Strickland CD, Midgett C, et
al: Heterogeneity of nemaline myopathy cases with skeletal muscle
alpha-actin gene mutations. Ann Neurol. 56:86–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Conen PE, Murphy EG and Donohue WL: Light
and electron microscopic studies of ‘myogranules’ in a child with
hypotonia and muscle weakness. Can Med Assoc J. 89:983–986.
1963.
|
|
3
|
Shy GM, Engel WK, Somers JE and Wanko T:
Nemaline myopathy. A new congenital myopathy. Brain. 86:793–810.
1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wallgren-Pettersson C and Laing NG: Report
of the 70th ENMC International Workshop: nemaline myopathy, 11–13
June 1999, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord.
10:299–306. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wallgren-Pettersson C, Sewry CA, Nowak KJ
and Laing NG: Nemaline myopathies. Semin Pediatr Neurol.
18:230–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao P, Lu D and Feng LF: A case report of
nemaline myopathy. Hered Dis. 7:243–244. 1990.
|
|
7
|
Li YX, Wu LJ, Chen QT, et al: Adult
nemaline myopathy. J Clin Neurol. 11:369–370. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Li YX, Wu LJ and Chen QT: Clinical and
pathological discussion: the 42nd cases. Chin J Neurol. 34:122–124.
2001.
|
|
9
|
Han Y, Zheng HM, Zhou S, Deng BQ, Wu T, et
al: A discussion of clinical and pathological features and
pathogenesis of nemaline myopathy (NM). J Apoplexy Nerv Dis.
19:90–92. 2002.
|
|
10
|
Yan CZ, Liu SP, Wu JL, et al: Adult form
nemaline myopathy: two cases report with clinicopathological and
ultrastructural study. Chin J Neurol. 36:173–175. 2002.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Lai HW, Yang CH, Wang FH and Tang GY:
Electron microscopic observation of nemaline myopathy (report of a
case). J Chin Electr Microsc Soc. 23:77–80. 2004.
|
|
12
|
Yuan JH, Hu J, Chen L, Mei L, Kang ZJ, et
al: The clinical and pathological analysis of the nemaline myopathy
complicated with the uniform type I fiber myopathy. J Apoplexy Nerv
Dis. 22:432–433. 2005.
|
|
13
|
Chen L and Hu J: A case report of nemaline
myopathy. Chin J Pract Pediatr. 21:1542006.
|
|
14
|
Lu Y, Da Y, Wang M, Liu L and Jia JP:
Nemaline myopathy - A 2 cases report and review of literatures.
Chin J Neuroimmunol Neurol. 15:236–238. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Lu HD, Li ZF, Qin DX, Zhang SJ, Qian Q, et
al: Clinical and pathological analysis of 3 nemaline myopathy
cases. Chin J Neurol. 41:465–467. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Jiang H1, Xiao B, Jia DD, Zhang N, Xu XP,
et al: Clinical and pathologic analysis of an autosomal recessive
kindred with nemaline myopathy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
89:3316–3319. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Ryan MM, Schnell C, Strickland CD, Shield
LK, Morgan G, et al: Nemaline myopathy: a clinical study of 143
cases. Ann Neurol. 50:312–320. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goebel HH, Piirsoo A, Warlo I, Schofer O,
Kehr S, et al: Infantile intranuclear rod myopathy. J Child Neurol.
12:22–30. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gurgel-Giannetti J, Reed UC, Marie SK,
Zanoteli E, Fireman MA, et al: Rod distribution and muscle fiber
type modification in the progression of nemaline myopathy. J Child
Neurol. 18:235–240. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhatt JR and Pascuzzi RM: Neuromuscular
disorders in clinical practice: case studies. Neurol Clin.
24:233–265. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luther PK and Squire JM: Muscle Z-band
ultrastructure: Titin Z-repeats and Z-band periodicities do not
match. J Mol Biol. 319:1157–1164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Laing NG, Wilton SD, Akkari PA, Dorosz S,
Boundy K, et al: A mutation in the alpha tropomyosin gene TPM3
associated with autosomal dominant nemaline myopathy NEM1. Nat
Genet. 10:2491995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wallgren-Pettersson C, Avela K, Marchand
S, et al: A gene for autosomal recessive nemaline myopathy assigned
to chromosome 2q by linkage analysis. Neuromuscul Disord.
5:441–443. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nowak KJ, Wattanasirichaigoon D, Goebel
HH, Wilce M, Pelin K, et al: Mutations in the skeletal muscle
alpha-actin gene in patients with actin myopathy and nemaline
myopathy. Nat Genet. 23:208–212. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wattanasirichaigoon D, Swoboda KJ, Takada
F, Tong HQ, Lip V, et al: Mutations of the slow muscle
alpha-tropomyosin gene, TPM3, are a rare cause of nemaline
myopathy. Neurology. 59:613–617. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnston JJ, Kelley RI, Crawford TO,
Morton DH, Agarwala R, et al: A novel nemaline myopathy in the
Amish caused by a mutation in troponin T1. Am J Hum Genet.
67:814–821. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sambuughin N, Yau KS, Olivé M, Duff RM,
Bayarsaikhan M, et al: Dominant mutations in KBTBD13, a member of
the BTB/Kelch family, cause nemaline myopathy with cores. Am J Hum
Genet. 87:842–847. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sanoudou D and Beggs AH: Clinical and
genetic heterogeneity in nemaline myopathy - a disease of skeletal
muscle thin filaments. Trends Mol Med. 7:362–368. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ottenheijm CA, Hooijman P, DeChene ET,
Stienen GJ, Beggs AH, et al: Altered myofilament function depresses
force generation in patients with nebulin-based nemaline myopathy
(NEM2). J Struct Biol. 170:334–343. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wallgren-Pettersson C, Pelin K, Nowak KJ,
Muntoni F, Romero NB, et al: Genotype-phenotype correlations in
nemaline myopathy caused by mutations in the genes for nebulin and
skeletal muscle alpha-actin. Neuromuscul Disord. 14:461–470. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Visegrády B and Machesky LM:
Myopathy-causing actin mutations promote defects in serum response
factor signaling. Biochem J. 427:41–48. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laing NG, Dye DE, Wallgren-Pettersson C,
Richard G, Monnier N, et al: Mutations and polymorphisms of the
skeletal muscle alpha-actin gene (ACTA1). Hum Mutat. 30:1267–1277.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Agrawal PB, Greenleaf RS, Tomczak KK, et
al: Nemaline myopathy with minicores caused by mutation of the CFL2
gene encoding the skeletal muscle actin-binding protein, cofilin-2.
Am J Hum Genet. 80:162–167. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ockeloen CW, Gilhuis HJ, Pfundt R, et al:
Congenital myopathy caused by a novel missense mutation in the CFL2
gene. Neuromuscul Disord. 22:632–639. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|