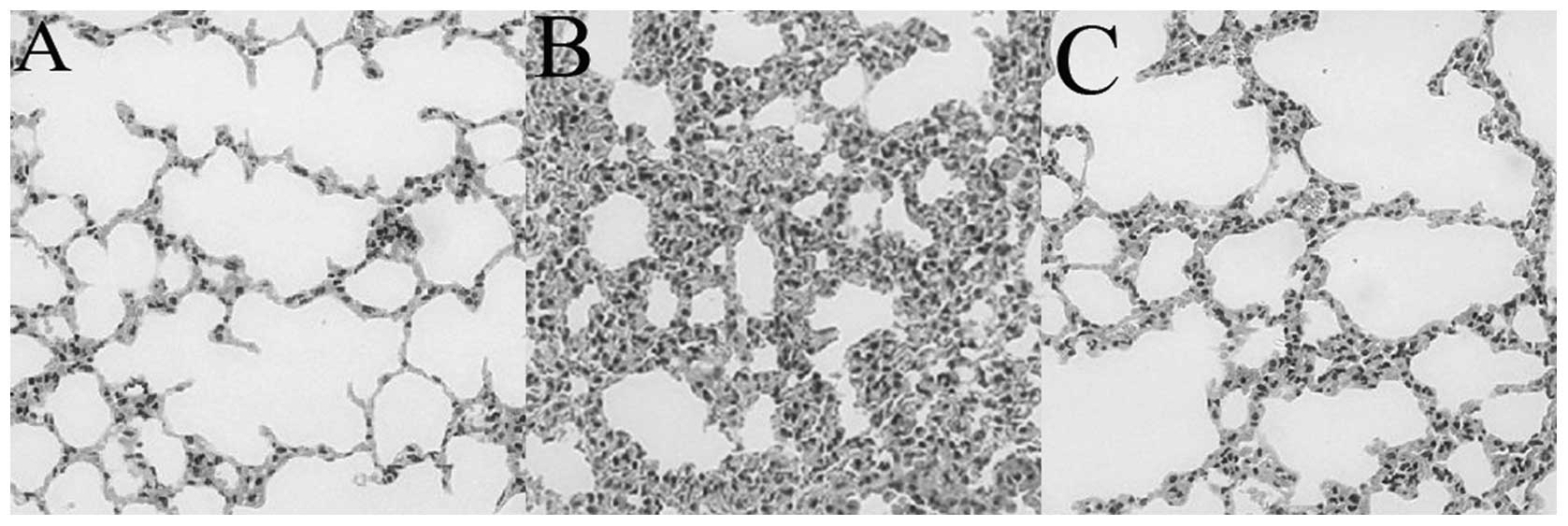
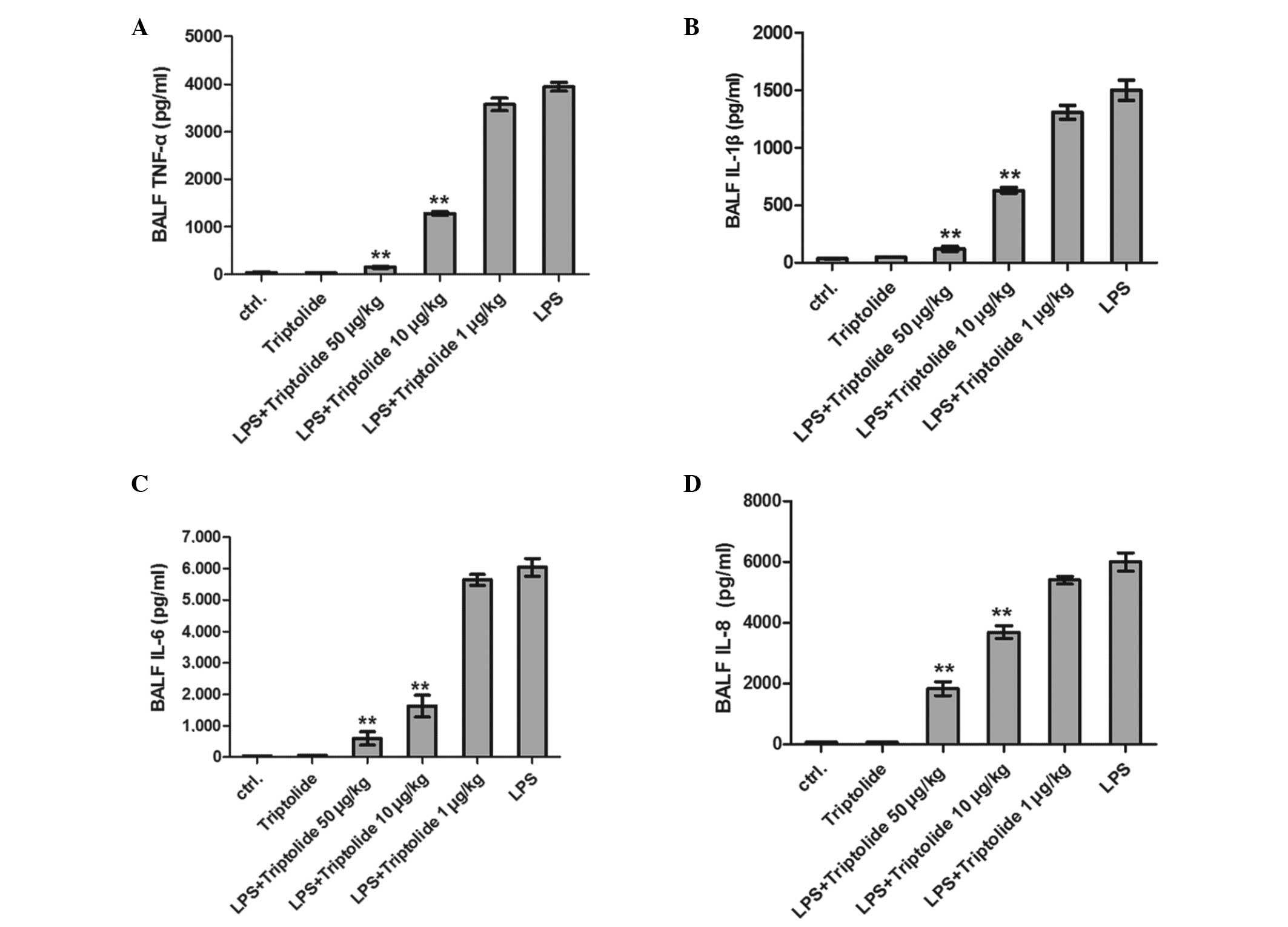
|
1
|
Chang CH, Kao CH, Chio CC, Lin CH, Lin MT
and Chang CP: Attenuating heatstroke-induced acute lung
inflammation, edema, and injury in rats by exercise
preconditioning. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 74:1052–1059. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma S, Smith A, Kumar S, et al:
Mechanisms of nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury: role of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Vascul
Pharmacol. 52:182–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fu PK, Yang CY, Tsai TH and Hsieh CL:
Moutan cortex radicis improves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury in rats through anti-inflammation. Phytomedicine.
19:1206–1215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pati S, Gerber MH, Menge TD, et al: Bone
marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit inflammation and
preserve vascular endothelial integrity in the lungs after
hemorrhagic shock. PLoS One. 6:e251712011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS and Matthay
MA: Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 14:523–535. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wen HL, Liang ZS, Zhang R and Yang K:
Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide improve left ventricular
function in a rat model of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 12:502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seki H, Tasaka S, Fukunaga K, et al:
Effect of Toll-like receptor 4 inhibitor on LPS-induced lung
injury. Inflamm Res. 59:837–845. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jeyaseelan S, Chu HW, Young SK, Freeman MW
and Worthen GS: Distinct roles of pattern recognition receptors
CD14 and Toll-like receptor 4 in acute lung injury. Infect Immun.
73:1754–1763. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kennedy M, Phelps D and Ingenito E:
Mechanisms of surfactant dysfunction in early acute lung injury.
Exp Lung Res. 23:171–189. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ben DF, Yu XY, Ji GY, et al: TLR4 mediates
lung injury and inflammation in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. J
Surg Res. 174:326–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang D, Fang F and Xu F:
Hyperoxia-induced up-regulation of Toll-like receptors expression
in alveolar epithelial cells. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 23:645–649. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Zhong WT, Wu YC, Xie XX, et al: Phillyrin
attenuates LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation via suppression of
MAPK and NF-κB activation in acute lung injury mice. Fitoterapia.
90:132–139. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Matta R, Wang X, Ge H, Ray W, Nelin LD and
Liu Y: Triptolide induces anti-inflammatory cellular responses. Am
J Transl Res. 1:267–282. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qiu D and Kao PN: Immunosuppressive and
anti-inflammatory mechanisms of triptolide, the principal active
diterpenoid from the Chinese medicinal herb Tripterygium
wilfordii Hook. f Drugs R D. 4:1–18. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hoyle GW, Hoyle CI, Chen J, Chang W,
Williams RW and Rando RJ: Identification of triptolide, a natural
diterpenoid compound, as an inhibitor of lung inflammation. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 298:L830–L836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HF, Lee TS and Kou YR:
Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of triptolide on
traumatic brain injury in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 182:1–8.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klawitter M, Quero L, Klasen J, et al:
Triptolide exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-catabolic as well as
anabolic effects and suppresses TLR expression and MAPK activity in
IL-1β treated human intervertebral disc cells. Eur Spine J.
21(Suppl 6): S850–S859. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mei Z, Li X, Wu Q, Hu S and Yang X: The
research on the anti-inflammatory activity and hepatotoxicity of
triptolide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle. Pharmacol Res.
51:345–351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeyaseelan S, Chu HW, Young SK and Worthen
GS: Transcriptional profiling of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury. Infect Immun. 72:7247–7256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo Z, Li Q, Han Y, Liang Y, Xu Z and Ren
T: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by
progranulin. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:5407942012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fujino N, Kubo H, Suzuki T, et al:
Administration of a specific inhibitor of neutrophil elastase
attenuates pulmonary fibrosis after acute lung injury in mice. Exp
Lung Res. 38:28–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lewis CW, Taylor RG, Kubara PM, Marshall
K, Meijer L and Golsteyn RM: A western blot assay to measure cyclin
dependent kinase activity in cells or in vitro without the use of
radioisotopes. FEBS Lett. 587:3089–3095. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vallejo-Illarramendi A, Marciano DK and
Reichardt LF: A novel method that improves sensitivity of protein
detection in PAGE and Western blot. Electrophoresis. 34:1148–1150.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lim YS, Chung MH, Park SH, et al: Acute
and repeated inhalation lung injury by 3-methoxybutyl chloroformate
in rats: CT-pathologic correlation. Eur J Radiol. 62:227–234. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT, et al;
NHLBI Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trials Network.
Lower tidal volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of
inflammation in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med.
33:1–6; discussion 230–232. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Trevejo JM, Marino MW, Philpott N, et al:
TNF-alpha -dependent maturation of local dendritic cells is
critical for activating the adaptive immune response to virus
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:12162–12167. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ning J, Liu QF, Luo XD, Fan ZP and Zhang
Y: Effect and mechanism of acute graft versus host disease on early
diffuse murine lung injury following allogeneic stem cell
transplantation. Sci China C Life Sci. 52:1016–1022. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Y, Wan T, Zhou X, et al: Hsp70-like
protein 1 fusion protein enhances induction of carcinoembryonic
antigen-specific CD8+ CTL response by dendritic cell
vaccine. Cancer Res. 65:4947–4954. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang N, Wang Z, Tang X, et al: Type 1
T-cell responses in chlamydial lung infections are associated with
local MIP-1alpha response. Cell Mol Immunol. 7:355–360. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng XM, Xie JH, Shuai B, et al:
Inhalation of aerosolized perfluorocarbon combined with
tetramethylpyrazine ameliorates hemodynamics and pulmonary
histopathology in a porcine model of acute lung injury. Nan Fang Yi
Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:1382–1386. 2011.(In Chinese).
|