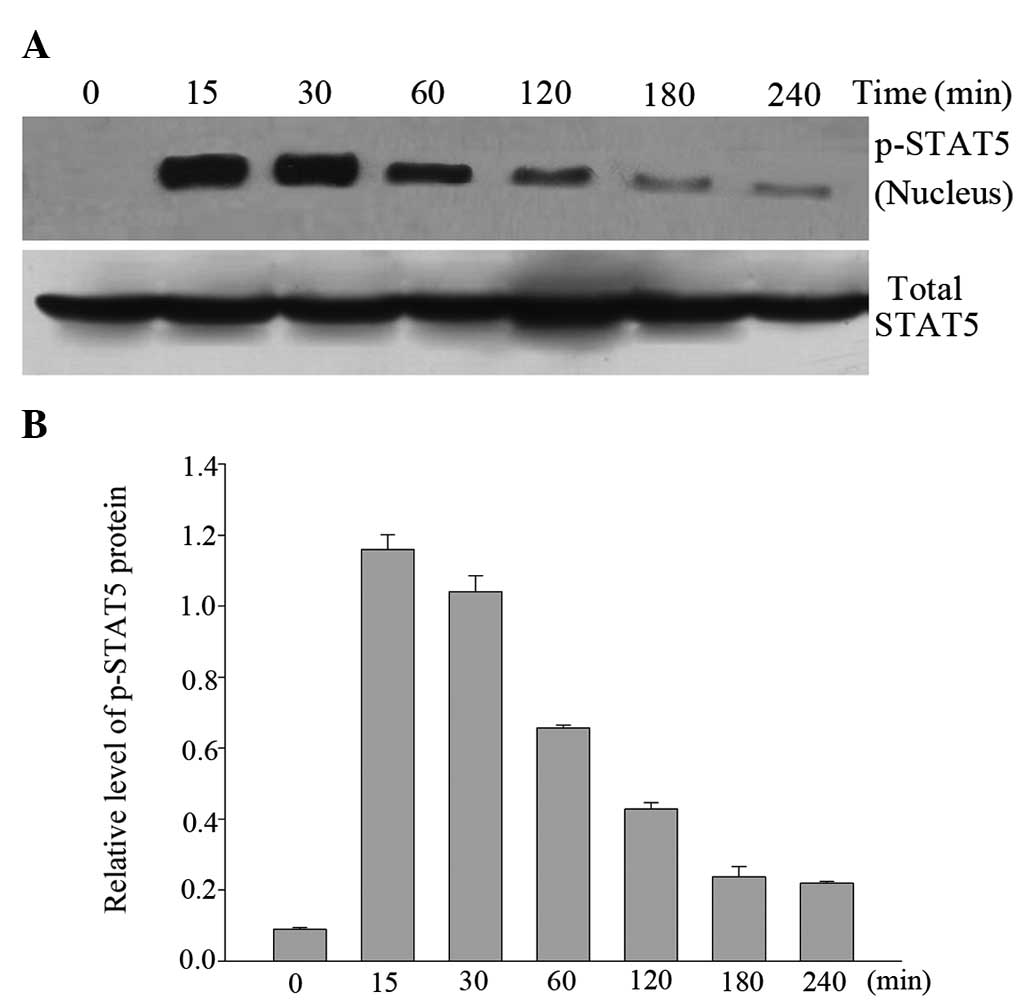
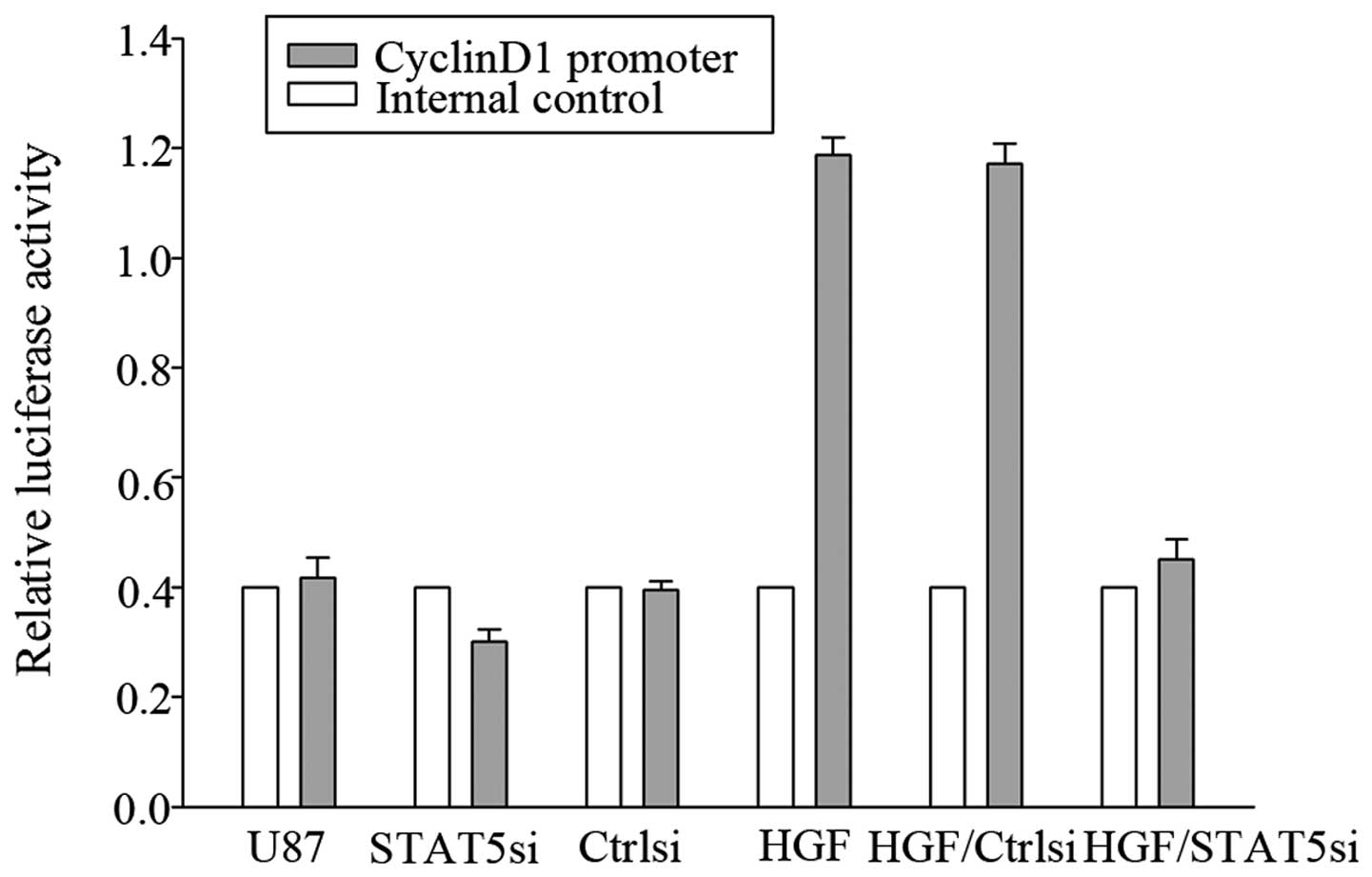
|
1
|
Buitenhuis M, Coffer PJ and Koenderman L:
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5). Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2120–2124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao S, Wang C, Zheng Q, et al: STAT5
regulates glioma cell invasion by pathways dependent and
independent of STAT5 DNA binding. Neurosci Lett. 487:228–233. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang H, Li M, Han Y, et al:
Down-regulation of miR-27a might reverse multidrug resistance of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 55:2545–2551.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang C, Cao S, Yan Y, et al: TLR9
expression in glioma tissues correlated to glioma progression and
the prognosis of GBM patients. BMC Cancer. 10:4152010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heim MH: The Jak-STAT pathway: cytokine
signalling from the receptor to the nucleus. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 19:75–120. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou J, Schindler U, Henzel WJ, Wong SC and
McKnight SL: Identification and purification of human Stat proteins
activated in response to interleukin-2. Immunity. 2:321–329. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mui AL, Wakao H, O’Farrell AM, Harada N
and Miyajima A: Interleukin-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony
stimulating factor and interleukin-5 transduce signals through two
STAT5 homologs. EMBO J. 14:1166–1175. 1995.
|
|
8
|
Foxwell BM, Beadling C, Guschin D, Kerr I
and Cantrell D: Interleukin-7 can induce the activation of Jak 1,
Jak 3 and STAT 5 proteins in murine T cells. Eur J Immunol.
25:3041–3046. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barahmand-pour F, Meinke A, Eilers A,
Gouilleux F, Groner B and Decker T: Colony-stimulating factors and
interferon-gamma activate a protein related to MGF-Stat 5 to cause
formation of the differentiation-induced factor in myeloid cells.
FEBS Lett. 360:29–33. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wartmann M, Cella N, Hofer P, et al:
Lactogenic hormone activation of Stat5 and transcription of the
beta-casein gene in mammary epithelial cells is independent of p42
ERK2 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem.
271:31863–31868. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pallard C, Gouilleux F, Bénit L, et al:
Thrombopoietin activates a STAT5-like factor in hematopoietic
cells. EMBO J. 14:2847–2856. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Joung YH, Lee MY, Lim EJ, et al: Hypoxia
activates the IGF-1 expression through STAT5b in human HepG2 cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 358:733–738. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sultan AS, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Ealley EL,
Nevalainen MT and Rui H: Stat5 promotes homotypic adhesion and
inhibits invasive characteristics of human breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 24:746–760. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Weaver AM and Silva CM: Modulation of
signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b activity in
breast cancer cells by mutation of tyrosines within the
transactivation domain. Mol Endocrinol. 20:2392–2405. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xi S, Zhang Q, Dyer KF, et al: Src kinases
mediate STAT growth pathways in squamous cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. J Biol Chem. 278:31574–31583. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xi S, Zhang Q, Gooding WE, Smithgall TE
and Grandis JR: Constitutive activation of Stat5b contributes to
carcinogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 63:6763–6771. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao S, Yan Y, Zhang X, et al: EGF
stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression through the STAT5 signaling
pathway in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Int J Oncol.
39:383–391. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Spiekermann K, Biethahn S, Wilde S,
Hiddemann W and Alves F: Constitutive activation of STAT
transcription factors in acute myelogenous leukemia. Eur J
Haematol. 67:63–71. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chin H, Nakamura N, Kamiyama R, Miyasaka
N, Ihle JN and Miura O: Physical and functional interactions
between Stat5 and the tyrosine-phosphorylated receptors for
erythropoietin and interleukin-3. Blood. 88:4415–4425.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pircher TJ, Petersen H, Gustafsson JA and
Haldosén LA: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) interacts
with signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 5a.
Mol Endocrinol. 13:555–565. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Koppikar P, Lui VW, Man D, et al:
Constitutive activation of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 5 contributes to tumor growth, epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, and resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor
targeting. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7682–7690. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xiong H, Su WY, Liang QC, et al:
Inhibition of STAT5 induces G1 cell cycle arrest and reduces tumor
cell invasion in human colorectal cancer cells. Lab Invest.
89:717–725. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|