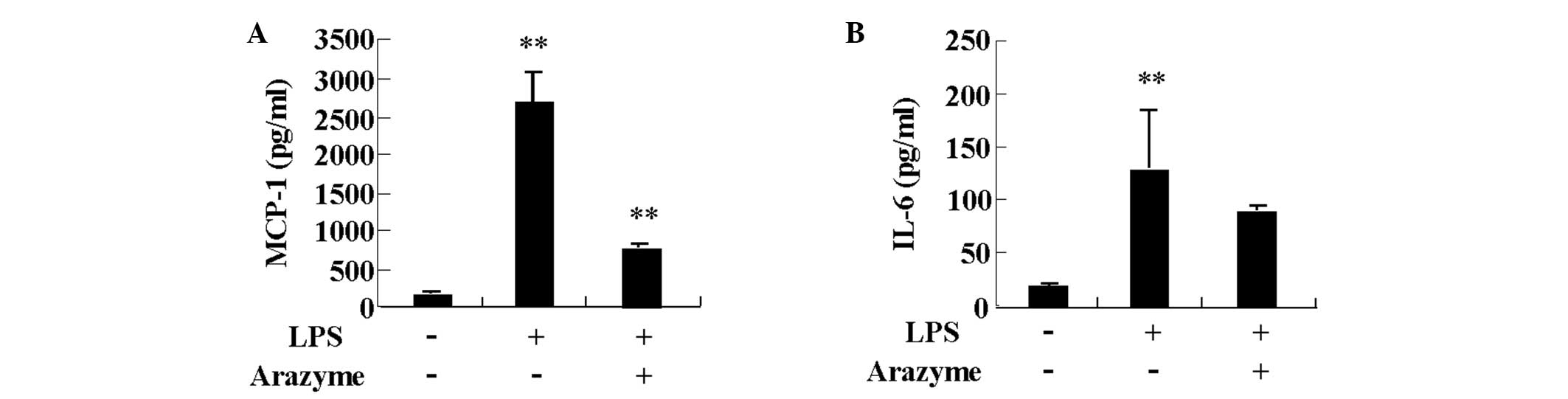
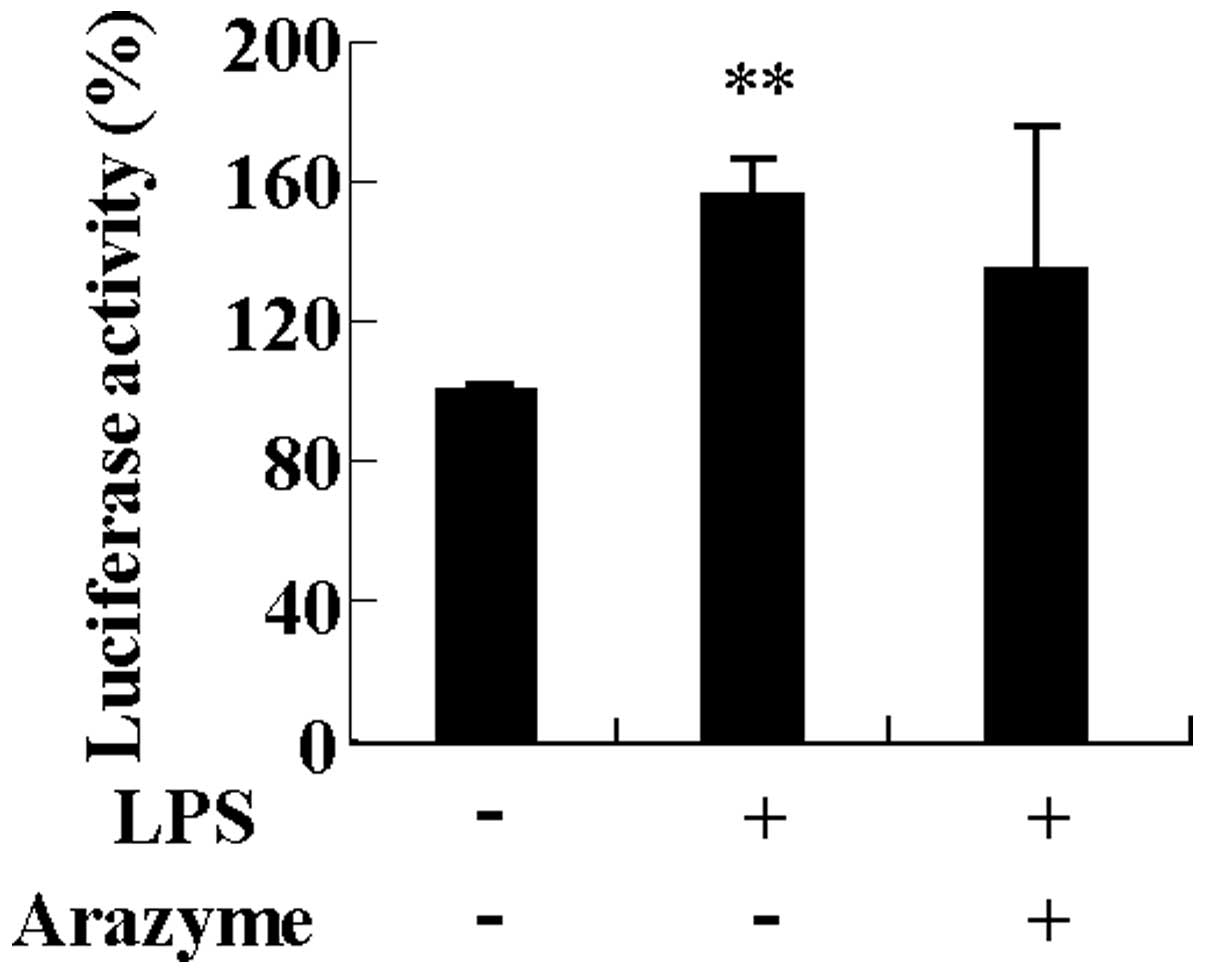
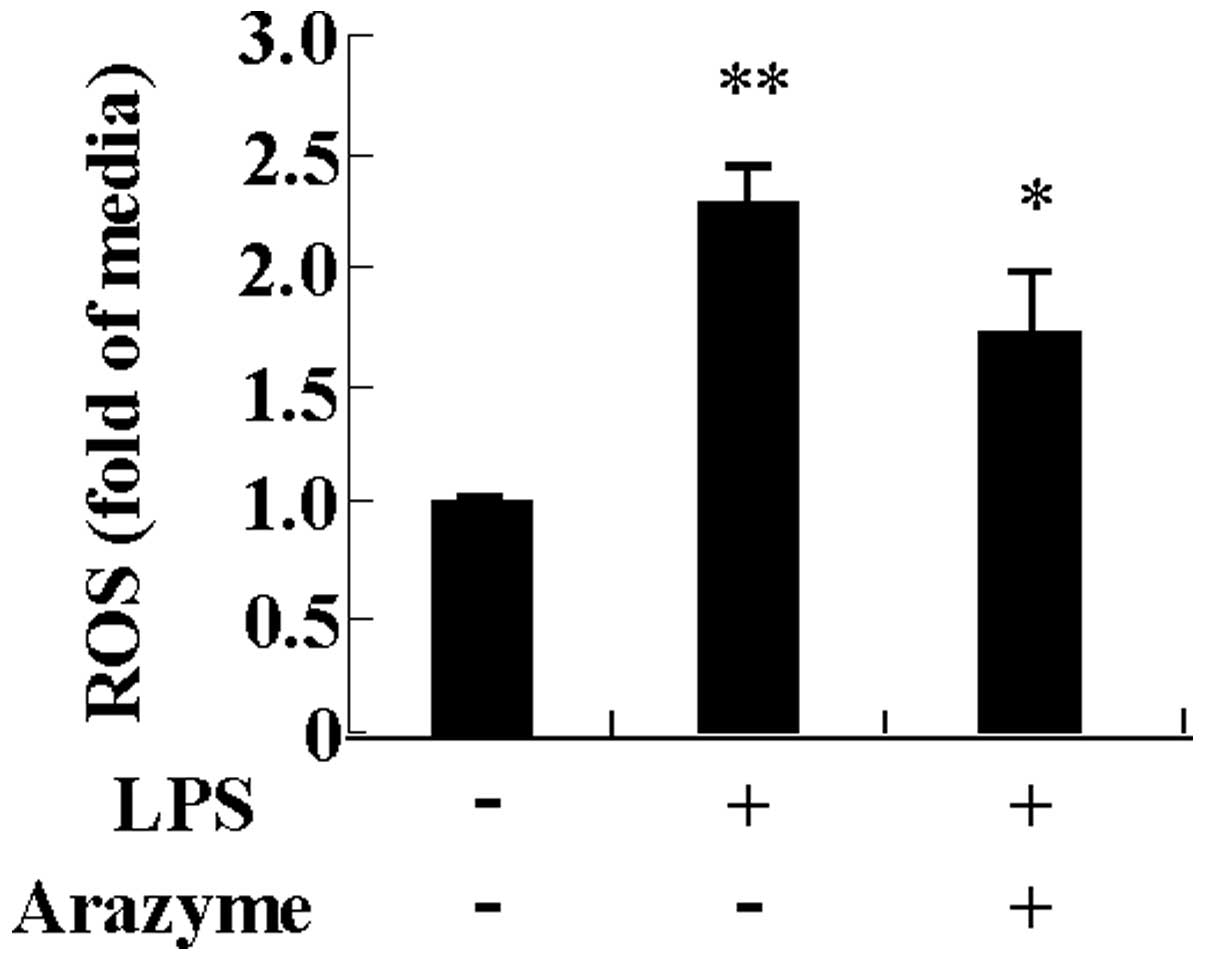
|
1
|
Bersanetti PA, Park HY, Bae KS, Son KH,
Shin DH, Hirata IY, Juliano MA, Carmona AK and Juliano L:
Characterization of arazyme, an exocellular metalloprotease
isolated from Serratia proteamaculans culture medium. Enzyme
Microb Technol. 37:574–581. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kwak J, Lee K, Shin DH, Maeng JS, Park DS,
Oh HW, Son KH, Bae KS and Park HY: Biochemical and genetic
characterization of arazyme, an extracellular metalloprotease
produced from Serratia proteamaculans HY-3. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 17:761–768. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Park JK, Jeong DH, Park HY, Son KH, Shin
DH, Do SH, Yang HJ, Yuan DW, Hong IH, Goo MJ, et al:
Hepatoprotective effect of arazyme on CCl4-induced acute
hepatic injury in SMP30 knock-out mice. Toxicology. 246:132–142.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hadi HA, Carr CS and Al Suwaidi J:
Endothelial dysfunction: cardiovascular risk factors, therapy, and
outcome. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 1:183–198. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu HT, He JL, Li WM, Yang Z, Wang YZ, Yin
J, Du YG and Yu C: Geniposide inhibits interleukin-6 and
interleukin-8 production in lipopolysaccharide-induced human
umbilical vein endothelial cells by blocking p38 and ERK1/2
signaling pathways. Inflamm Res. 59:451–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Szmitko PE, Wang CH, Weisel RD, Jeffries
GA, Anderson TJ and Verma S: Biomarkers of vascular disease linking
inflammation to endothelial activation: Part II. Circulation.
108:2041–2048. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sprague AH and Khalil RA: Inflammatory
cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem
Pharmacol. 78:539–552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Vries IJ, Langeveld-Wildschut EG, van
Reijsen FC, Dubois GR, van den Hoek JA, Bihari IC, van Wichen D, de
Weger RA, Knol EF, Thepen T and Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA: Adhesion
molecule expression on skin endothelia in atopic dermatitis:
effects of TNF-alpha and IL-4. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 102:461–468.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim TH and Bae JS: Ecklonia cava
extracts inhibit lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory responses
in human endothelial cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1682–1687. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Juzyszyn Z, Czerny B, Pawlik A and
Droździk M: The effect of Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.)
extract on ROS generatin in HUVEC cells. Phytother Res.
22:1159–1161. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Lim JH, Woo JS and Shin YW: Cilostazol
protects endothelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced
apoptosis through ERK1/2- and P38 MAPK-dependent pathways. Korean J
Intern Med. 24:113–122. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munshi N, Fernandis AZ, Cherla RP, Park IW
and Ganju RK: Lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of endothelial
cells and its inhibition by vascular endothelial growth factor. J
Immunol. 168:5860–5866. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marui N, Offermann MK, Swerlick R, Kunsch
C, Rosen CA, Ahmad M, Alexander RW and Medford RM: Vascular cell
adhesion molecule-1 (VACM-1) gene transcription and expression are
regulated through an antioxidant-sensitive mechanism in human
vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 92:1866–1874. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sawa Y, Ueki T, Hata M, Iwasawa K, Tsuruga
E, Kojima H, Ishikawa H and Yoshida S: LPS-induced IL-6, IL-8,
VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 expression in human lymphatic endothelium. J
Histochem Cytochem. 56:97–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Joyce DE and Grinnell BW: Recombinant
human activated protein C attenuates the inflammatory response in
endothelium and monocytes by modulating nuclear factor-kappaB. Crit
care med. 20(Suppl 5): S288–S293. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rossi D and Zlotnik A: The biology of
chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 18:217–242. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang EJ, Choi E, Ko J, Kim DH, Lee JS and
Kim IS: Differential effect of CCL2 on constitutive neutrophil
apoptosis between normal and asthmatic subjects. J Cell Physiol.
227:2567–2577. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hirano T: Interleukin 6 and its receptor:
ten years later. Int Rev Immunol. 16:249–284. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gabay C: Interleukin-6 and chronic
inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther. 8(Suppl 2): S32006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bellanti JA: Cytokines and allergic
diseases: clinical aspects. Allergy Asthma Proc. 19:337–341. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V and
Chariot A: Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins:
implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:43–52. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Arora P, Ricks TK and Trejo J:
Protease-activated receptor signalling, endocytic sorting and
dysregulation in cancer. J Cell Sci. 120:921–928. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hauck G: Proceedings: Vitalmicroscopic
investigations of the effects of thrombin, a snake venom enzyme and
histamine effect on the mesenteric microvasculature of rabbit and
cat. Arzneimittelforschung. 26:12331976.
|
|
24
|
Wolz RL and Bond JS:
Phe5(4-nitro)-bradykinin: a chromogenic substrate for assay and
kinetics of the metalloendopeptidase meprin. Anal Biochem.
191:314–320. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|