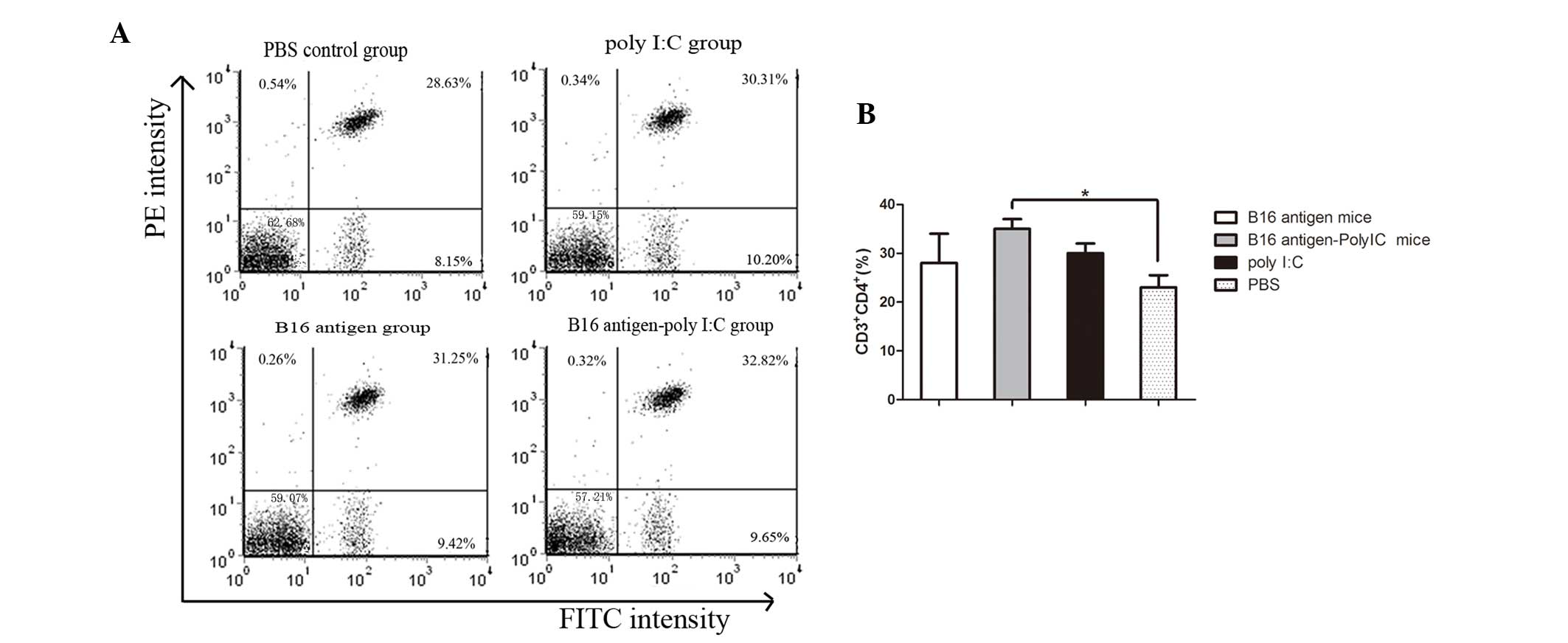
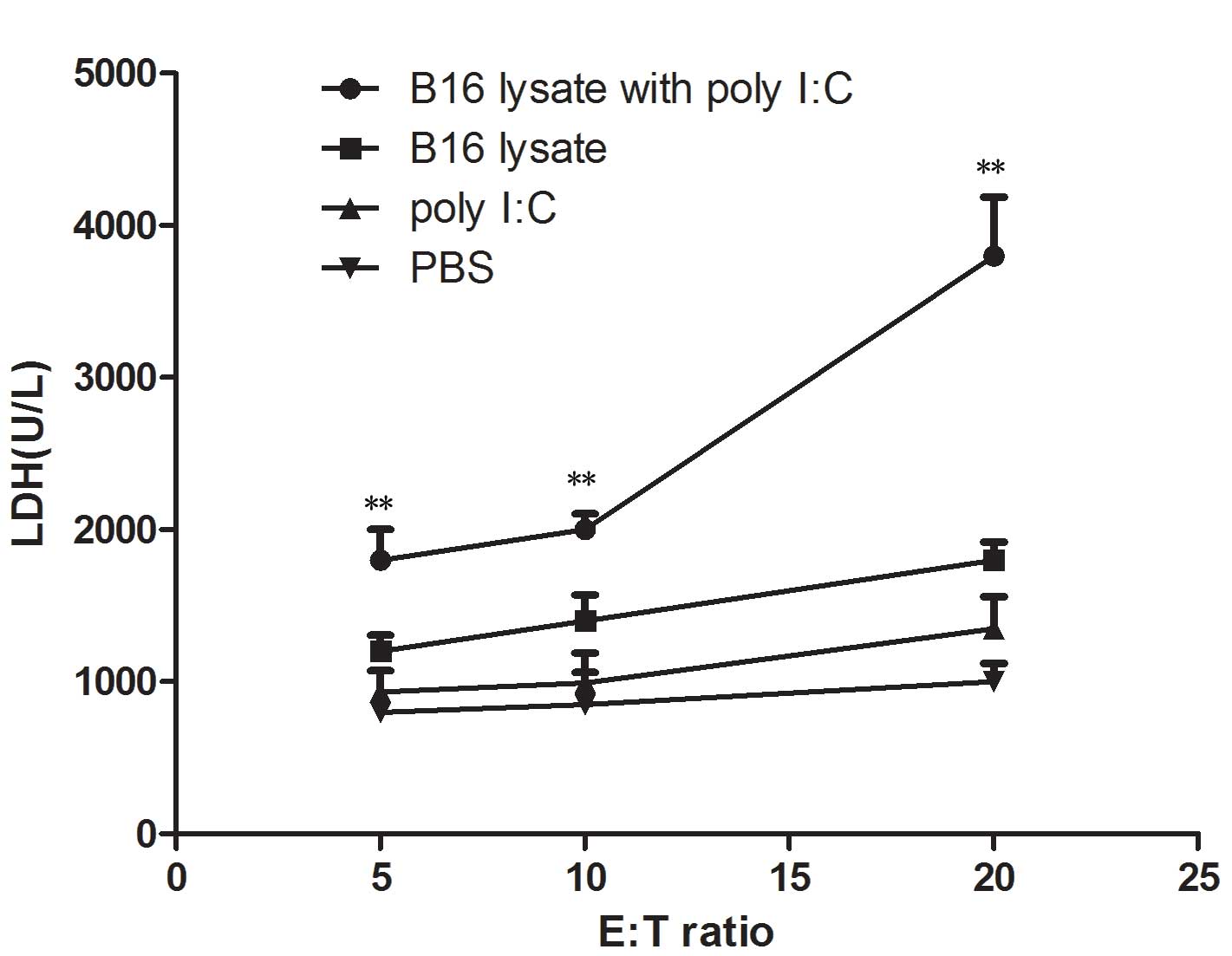
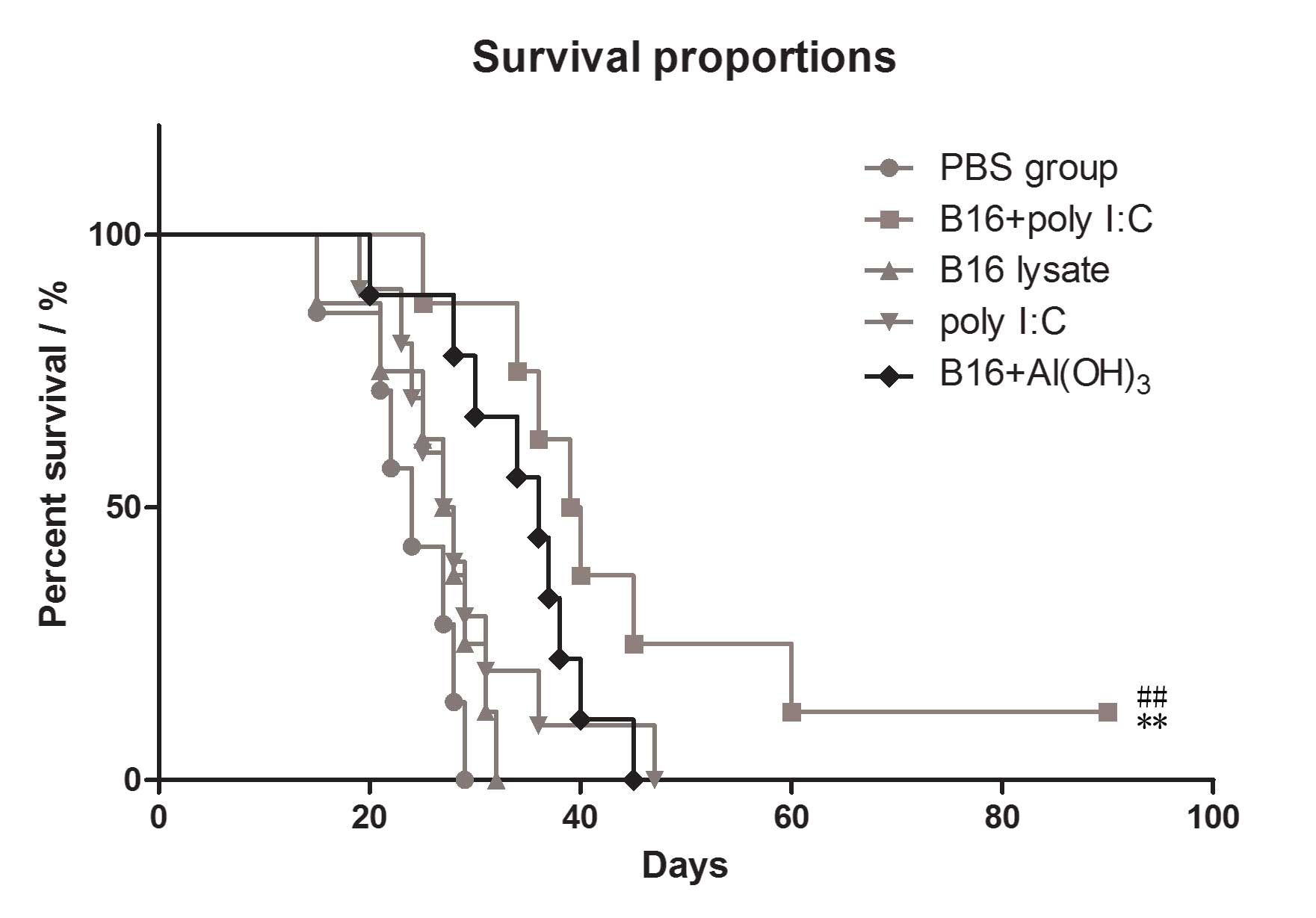
|
1
|
Lee C, Collichio F, Ollila D and Moschos
S: Historical review of melanoma treatment and outcomes. Clin
Dermatol. 31:141–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen LL, Jaimes N, Barker CA, Busam KJ and
Marghoob AA: Desmoplastic melanoma: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol.
68:825–833. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vourc’h-Jourdain M, Martin L and Barbarot
S; aRED. Large congenital melanocytic nevi: therapeutic management
and melanoma risk: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol.
68:493–498. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma C and Armstrong AW: Severe adverse
events from the treatment of advanced melanoma: a systematic review
of severe side effects associated with ipilimumab, vemurafenib,
interferon alfa-2b, dacarbazine and interleukin-2. J Dermatolog
Treat. 25:401–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singh S, Nagpal SJ, Murad MH, et al:
Inflammatory bowel disease is associated with an increased risk of
melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:210–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gogas H, Polyzos A and Kirkwood J:
Immunotherapy for advanced melanoma: fulfilling the promise. Cancer
Treat Rev. 39:879–885. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Engell-Noerregaard L, Hansen TH, Andersen
MH, Thor Straten P and Svane IM: Review of clinical studies on
dendritic cell-based vaccination of patients with malignant
melanoma: assessment of correlation between clinical response and
vaccine parameters. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 58:1–14. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang S, Wang Q and Miao B: Review:
dendritic cell-based vaccine in the treatment of patients with
advanced melanoma. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 22:501–507. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harris RC, Chianese-Bullock KA, Petroni
GR, et al: The vaccine-site microenvironment induced by injection
of incomplete Freund’s adjuvant, with or without melanoma peptides.
J Immunother. 35:78–88. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho DY, Yang WK, Lee HC, et al: Adjuvant
immunotherapy with whole-cell lysate dendritic cells vaccine for
glioblastoma multiforme: a phase II clinical trial. World
Neurosurg. 77:736–744. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang ZY, Xing Y, Liu B, et al: Protective
antitumor immunity induced by tumor cell lysates conjugated with
diphtheria toxin and adjuvant epitope in mouse breast tumor models.
Chin J Cancer. 31:295–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cui Z and Qiu F: Synthetic double-stranded
RNA poly(I:C) as a potent peptide vaccine adjuvant: therapeutic
activity against human cervical cancer in a rodent model. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 55:1267–1279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kato A, Truong-Tran AQ, Scott AL,
Matsumoto K and Schleimer RP: Airway epithelial cells produce B
cell-activating factor of TNF family by an IFN-beta-dependent
mechanism. J Immunol. 177:7164–7172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Inao T, Harashima N, Monma H, et al:
Antitumor effects of cytoplasmic delivery of an innate adjuvant
receptor ligand, poly(I:C), on human breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 134:89–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rajan JV, Warren SE, Miao EA and Aderem A:
Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by intracellular poly I:C.
FEBS Lett. 584:4627–4632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trumpfheller C, Caskey M, Nchinda G, et
al: The microbial mimic poly IC induces durable and protective
CD4+ T cell immunity together with a dendritic cell
targeted vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:2574–2579. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wörnle M, Sauter M, Kastenmüller K, et al:
Novel role of toll-like receptor 3, RIG-I and MDA5 in poly (I:C)
RNA-induced mesothelial inflammation. Mol Cell Biochem.
322:193–206. 2009.
|
|
18
|
Longhi MP, Trumpfheller C, Idoyaga J, et
al: Dendritic cells require a systemic type I interferon response
to mature and induce CD4+ Th1 immunity with poly IC as
adjuvant. J Exp Med. 206:1589–1602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bose A, Lowe DB, Rao A and Storkus WJ:
Combined vaccine+axitinib therapy yields superior antitumor
efficacy in a murine melanoma model. Melanoma Res. 22:236–243.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kayaga J, Souberbielle BE, Sheikh N, et
al: Anti-tumour activity against B16-F10 melanoma with a GM-CSF
secreting allogeneic tumour cell vaccine. Gene Ther. 6:1475–1481.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kirkwood JM, Moschos S and Wang W:
Strategies for the development of more effective adjuvant therapy
of melanoma: current and future explorations of antibodies,
cytokines, vaccines, and combinations. Clin Cancer Res.
12:2331s–2336s. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS,
Smith TJ, Borden EC and Blum RH: Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant
therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 14:7–17.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Terando A, Sabel MS and Sondak VK:
Melanoma: adjuvant therapy and other treatment options. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 4:187–199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Krishnan L, Deschatelets L, Stark FC,
Gurnani K and Sprott GD: Archaeosome adjuvant overcomes tolerance
to tumor-associated melanoma antigens inducing protective CD8 T
cell responses. Clin Dev Immunol. 2010:5784322010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mechl Z and Kopecný J: Current results
with surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy in malignant melanoma. Arch
Geschwulstforsch. 56:367–371. 1986.(In German).
|
|
27
|
Olivier A, Sainz-Perez A, Dong H,
Sparwasser T, Majlessi L and Leclerc C: The adjuvant effect of TLR
agonists on CD4(+) effector T cells is under the indirect control
of regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 41:2303–2313. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang YK, Zheng Z, Cheng CX, Wang LY, Li
YR and Qiu F: The antitumor effect of the toll-like receptor 3
ligand polyinosinic-cytidylic acid as an adjuvant. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 62:237–244. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martínez-Gil L, Goff PH, Hai R,
García-Sastre A, Shaw ML and Palese P: A Sendai virus-derived RNA
agonist of RIG-I as a virus vaccine adjuvant. J Virol.
87:1290–1300. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang S, Du W, Zhang H, et al: Biological
characteristics and antitumor activity of CIK cells activated by
recombinant human fibronectin for human lung cancer cell lines in
vitro. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 13:277–281. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Starska K, Głowacka E, Kulig A,
Lewy-Trenda I, Bryś M and Lewkowicz P: The role of tumor cells in
the modification of T lymphocytes activity - the expression of the
early CD69+, CD71+ and the late
CD25+, CD26+, HLA/DR+ activation
markers on T CD4+ and CD8+ cells in squamous
cell laryngeal carcinoma. Part I Folia Histochem Cytobiol.
49:579–592. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Török L: Adjuvant interferon treatment of
melanoma. Magy Onkol. 47:105–107. 2003.(In Hungarian).
|
|
33
|
Mitchell MS, Kan-Mitchell J, Kempf RA,
Harel W, Shau HY and Lind S: Active specific immunotherapy for
melanoma: phase I trial of allogeneic lysates and a novel adjuvant.
Cancer Res. 48:5883–5893. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jasani B, Navabi H and Adams M: Ampligen:
a potential toll-like 3 receptor adjuvant for immunotherapy of
cancer. Vaccine. 27:3401–3404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
May M, Kendel F, Hoschke B, et al:
Adjuvant autologous tumour cell vaccination in patients with renal
cell carcinoma. Overall survival analysis with a follow-up period
in excess of more than 10 years. Urologe A. 48:1075–1083. 2009.(In
German).
|
|
36
|
May M, Brookman-May S, Hoschke B, et al:
Ten-year survival analysis for renal carcinoma patients treated
with an autologous tumour lysate vaccine in an adjuvant setting.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:687–695. 2010.
|
|
37
|
Markowicz S, Nowecki ZI, Rutkowski P, et
al: Adjuvant vaccination with melanoma antigen-pulsed dendritic
cells in stage III melanoma patients. Med Oncol. 29:2966–2977.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|