|
1
|
Martins T, Narciso-Schiavon JL and
Schiavon LL: Epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection. Rev Assoc
Med Bras. 57:107–112. 2011.(In Portuguese).
|
|
2
|
Alter MJ: Epidemiology of hepatitis C
virus infection. World J Gastroenterol. 13:2436–2441. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lauer GM and Walker BD: Hepatitis C virus
infection. N Engl J Med. 345:41–52. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klenerman P and Gupta PK: Hepatitis C
virus: current concepts and future challenges. QJM. 105:29–32.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liew M, Erali M, Page S, Hillyard D and
Wittwer C: Hepatitis C genotyping by denaturing high-performance
liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 42:158–163. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Simmonds P: Genetic diversity and
evolution of hepatitis C virus-15 years on. J Gen Virol.
85:3173–3188. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pybus OG, Barnes E, Taggart R, et al:
Genetic history of hepatitis C virus in East Asia. J Virol.
83:1071–1082. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thio CL, Thomas DL and Carrington M:
Chronic viral hepatitis and the human genome. Hepatology.
31:819–827. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thio CL: Host genetic factors and
antiviral immune responses to hepatitis C virus. Clin Liver Dis.
12:713–726. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seeff LB: Natural history of chronic
hepatitis C. Hepatology. 36:S35–S46. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Osaki R, Nishimura T, Shioya M, et al:
Interleukin-28B genotypes determine response to
pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin therapy in patients with
hepatitis C virus infection. Mol Med Rep. 5:525–528.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas DL, Astemborski J, Rai RM, et al:
The natural history of hepatitis C virus infection: host, viral,
and environmental factors. JAMA. 284:450–456. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rauch A, Kutalik Z and Descombes P; Swiss
HIV Cohort Study. Genetic variation in IL28B is associated with
chronic hepatitis C and treatment failure: a genome-wide
association study. Gastroenterology. 138:1338–1345. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grebely J, Petoumenos K and Hellard M;
ATAHC Study Group. Potential role for interleukin-28B genotype in
treatment decision-making in recent hepatitis C virus infection.
Hepatology. 52:1216–1224. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thomas DL, Thio CL, Martin MP, et al:
Genetic variation in IL28B and spontaneous clearance of hepatitis C
virus. Nature. 461:798–801. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, et al:
Genetic variation in IL-28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced
viral clearance. Nature. 461:399–401. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, et
al: IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C
interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet. 41:1100–1104.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, et al:
Genome-wide association of IL-28B with response to pegylated
interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat
Genet. 41:1105–1109. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mao XR, Zhang LT, Chen H, et al: Possible
factors affecting thyroid dysfunction in hepatitis C virus-infected
untreated patients. Exp Ther Med. (In Press).
|
|
20
|
Bouwknegt M, Lodder-Verschoor F, van der
Poel WH, Rutjes SA and de Roda Husman AM: Hepatitis E virus RNA in
commercial porcine livers in The Netherlands. J Food Prot.
70:2889–2895. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Viazov S, Zibert A, Ramakrishnan K, et al:
Typing of hepatitis C virus isolates by DNA enzyme immunoassay. J
Virol Methods. 48:81–91. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seeff LB and Hoofnagle JH: Appendix: The
National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference
Management of Hepatitis C 2002. Clin Liver Dis. 7:261–287.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
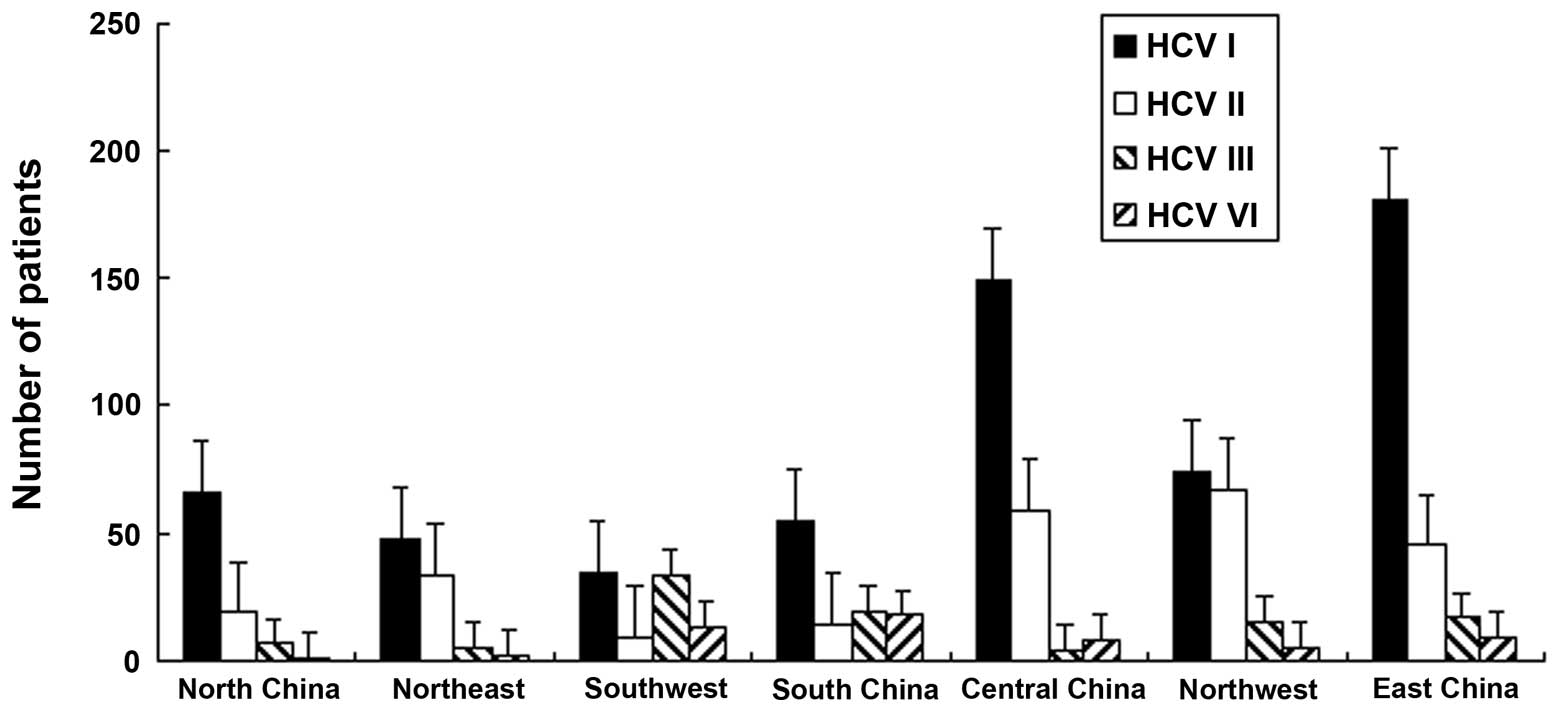
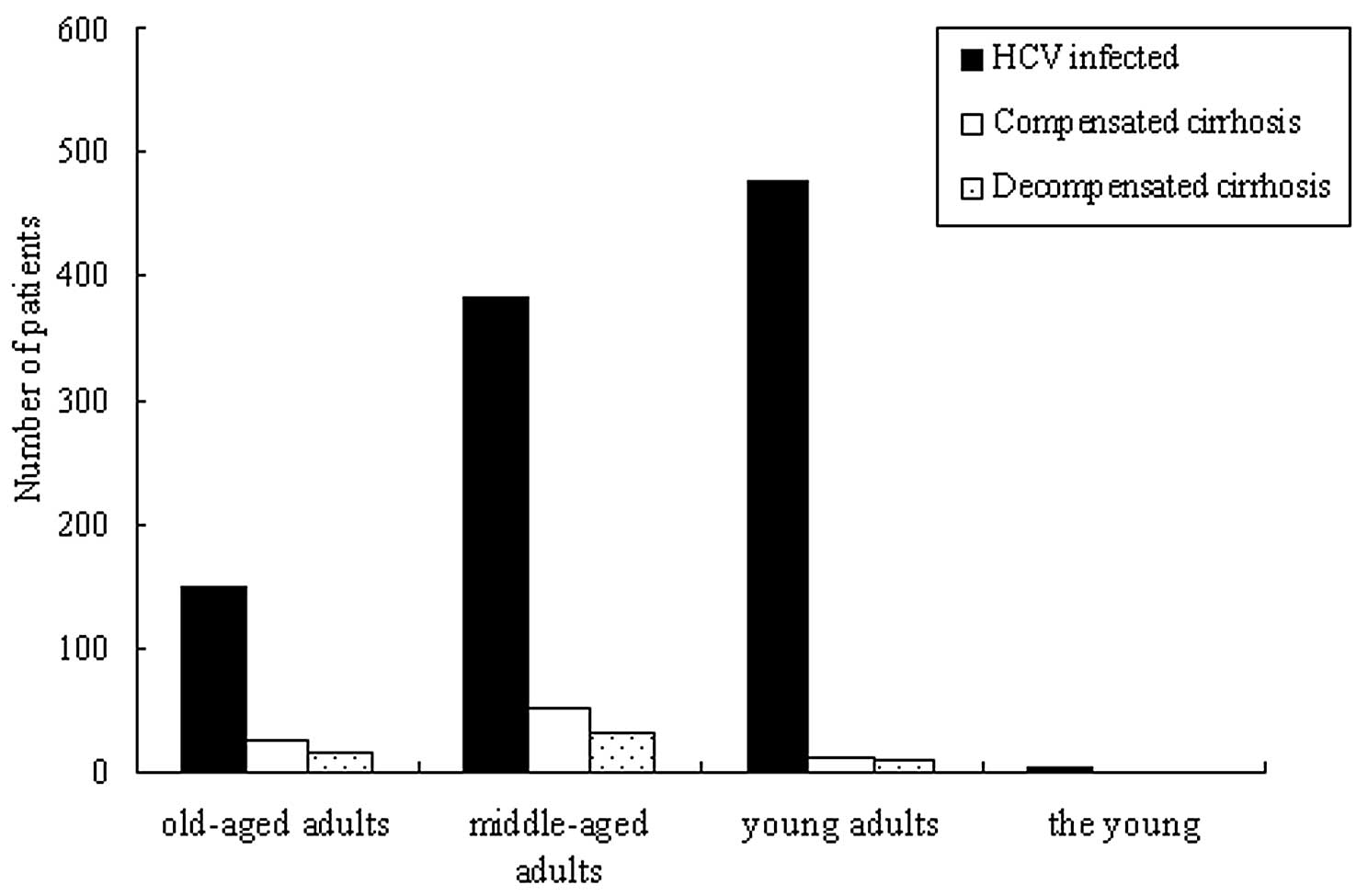
Chen YD, Liu MY, Yu WL, Li JQ, Peng M, Dai
Q, Liu X and Zhou ZQ: Hepatitis C virus infections and genotypes in
China. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 1:194–201. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rao H, Wei L, Lopez-Talavera JC, Shang J,
Chen H, Li J, Xie Q, Gao Z, Wang L, Wei J, et al: Distribution and
clinical correlates of viral and host genotypes in Chinese patients
with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:545–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dong ZX, Zhou HJ, Wang JH, Xiang XG,
Zhuang Y, Guo SM, Gui HL, Zhao GD, Tang WL, Wang H and Xie Q:
Distribution of hepatitis C virus genotypes in Chinese patients
with chronic hepatitis C: correlation with patients’
characteristics and clinical parameters. J Dig Dis. 13:564–570.
2012.
|
|
26
|
Yan Z, Fan K, Wang Y, Fan Y, Tan Z and
Deng G: Changing pattern of clinical epidemiology on hepatitis C
virus infection in Southwest China. Hepat Mon. 12:196–204. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li D, Long Y, Wang T, Xiao D, Zhang J, Guo
Z, Wang B and Yan Y: Epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in
highly endemic HBV areas in China. PLoS One. 8:e548152013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Z, Yao Y, Wu W, Feng R, Wu Z, Cun W
and Dong S: Hepatitis C virus genotype diversity among intravenous
drug users in Yunnan Province, Southwestern China. PLoS One.
8:e825982013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sibbing B and Nattermann J: Hepatitis C
virus infection and genetic susceptibility to therapy. J
Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 20:397–406. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zeuzem S, Berg T, Moeller B, et al: Expert
opinion on the treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C. J
Viral Hepat. 16:75–90. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Asselah T, Bièche I, Paradis V, et al:
Genetics, genomics, and proteomics: implications for the diagnosis
and the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Semin Liver Dis.
27:13–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pearlman BL: The IL-28 genotype: how it
will affect the care of patients with hepatitis C virus infection.
Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 13:78–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Antaki N, Bibert S, Kebbewar K, Asaad F,
Baroudi O, Alideeb S, Hadad M, Abboud D, Sabah H, Bochud PY and
Negro F: IL28B polymorphisms predict response to therapy among
chronic hepatitis C patients with HCV genotype 4. J Viral Hepat.
20:59–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|