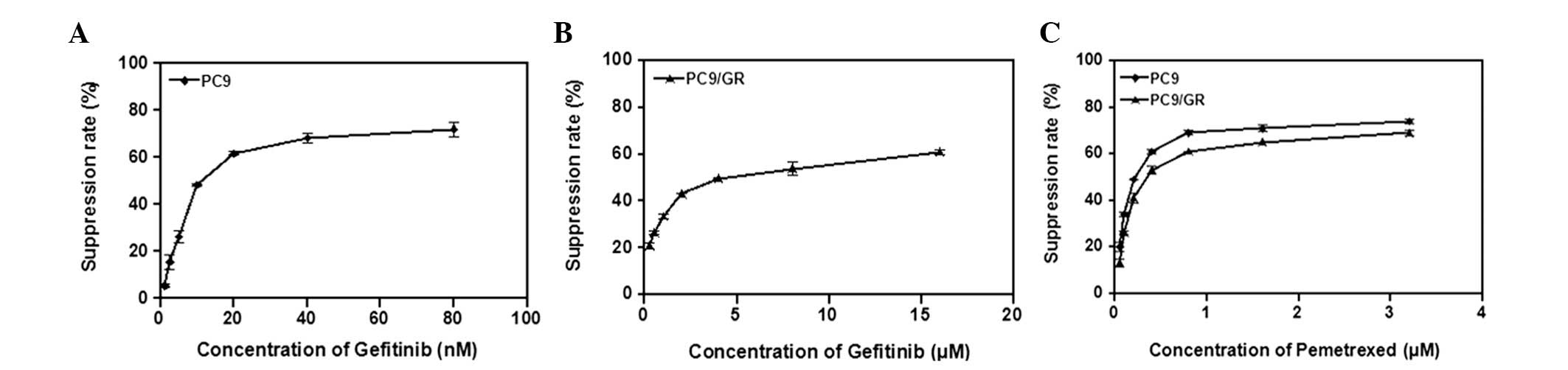
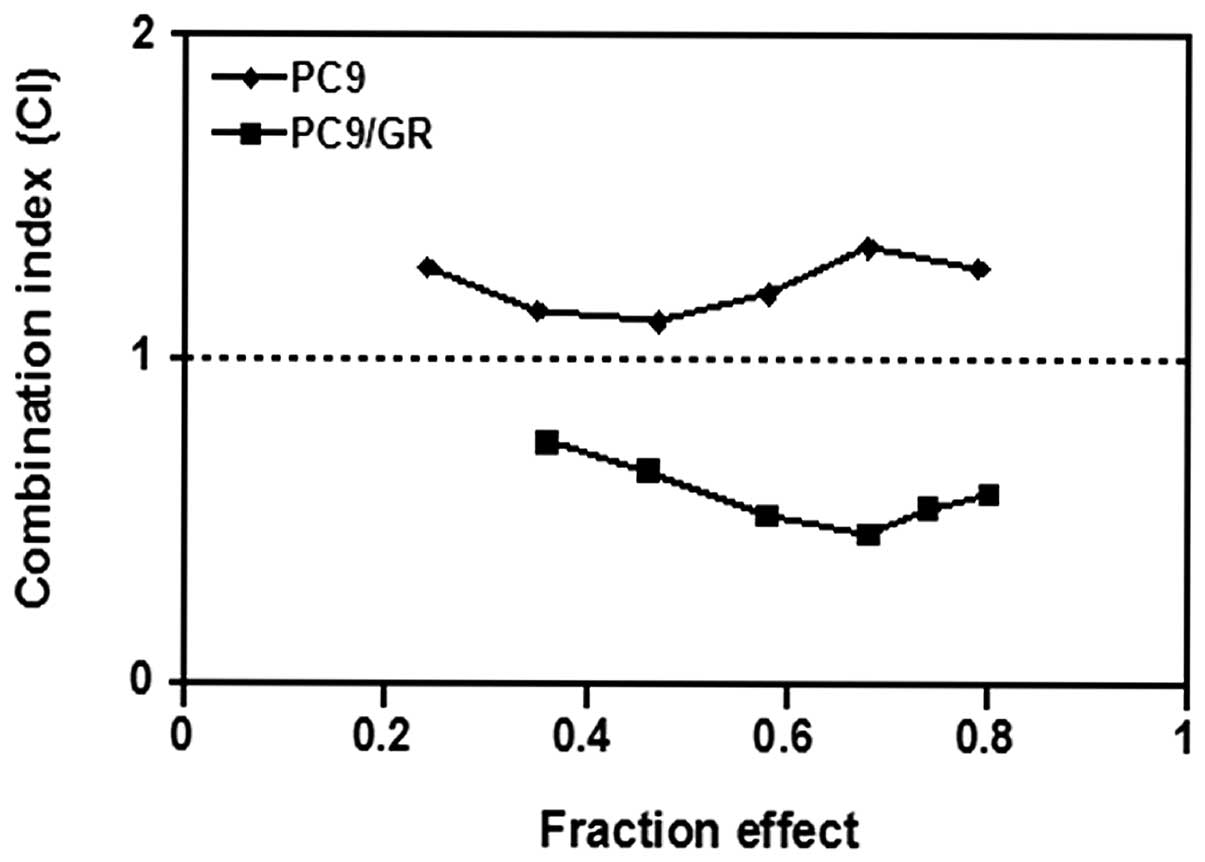
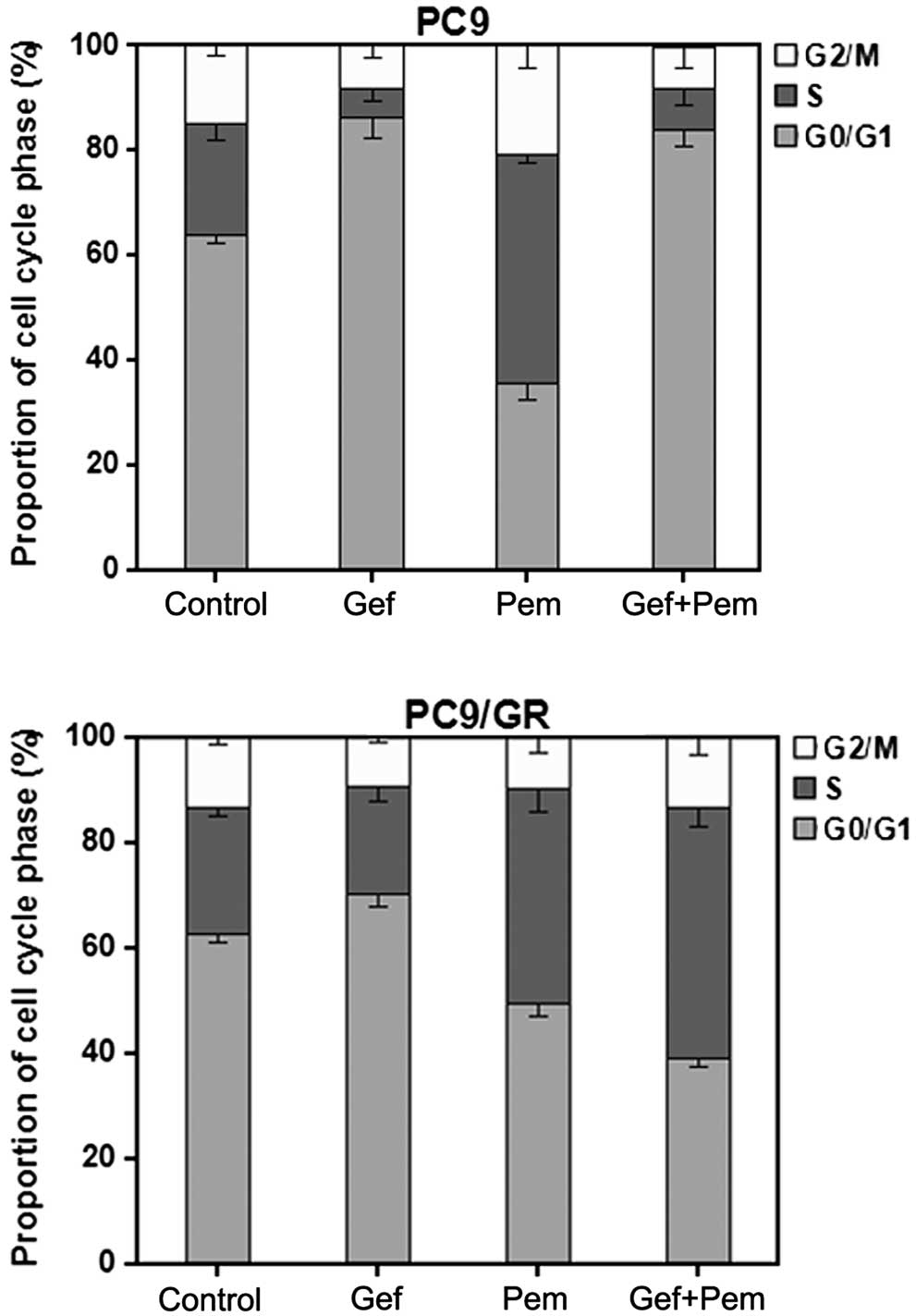
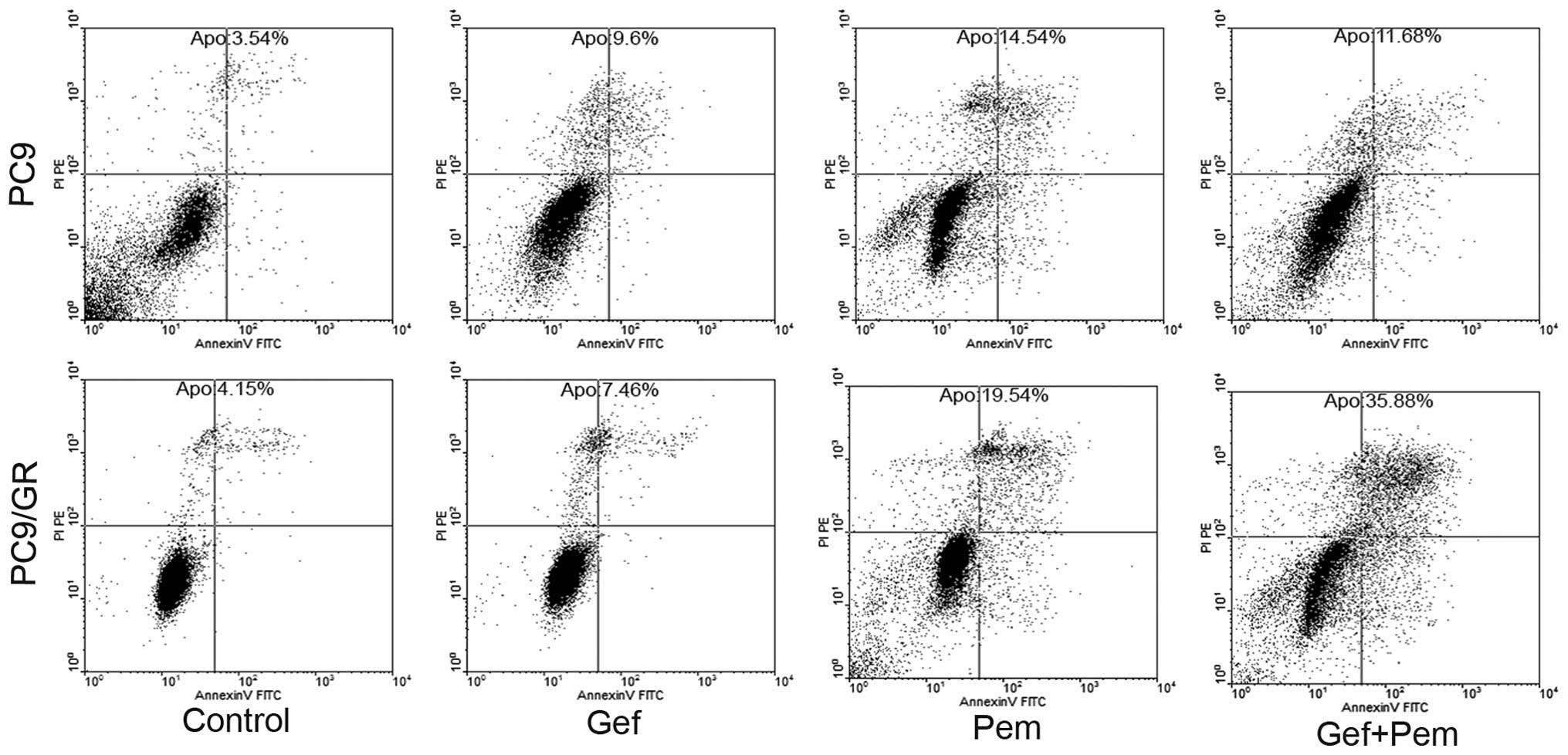
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F and
Normanno N: Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their
receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
19:183–232. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ennis BW, Lippman ME and Dickson RB: The
EGF receptor system as a target for antitumor therapy. Cancer
Invest. 9:553–562. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al:
Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell-lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Masago K, Fujita S, Togashi Y, et al:
Clinicopathologic factors affecting the progression free survival
of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer after
gefitinib therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. 12:56–61. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jackman D, Pao W, Riely GJ, et al:
Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 28:357–360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lovly CM and Horn L: Strategies for
overcoming EGFR resistance in the treatment of advanced-stage
NSCLC. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 13:516–526. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Goldberg SB, Oxnard GR, Digumarthy S, et
al: Chemotherapy with erlotinib or chemotherapy alone in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer with acquired resistance to EGFR
tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncologist. 18:1214–1220. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Haddad R, Allen A, Wirth L, Tishler R and
Posner M: Integrating novel agents into the curative treatment of
head and neck cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 6:157–159. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, et al:
Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with
chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 22:1589–1597. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fukuoka M, Yano S, Giaccone G, et al:
Multi-institutional randomized phase II trial of gefitinib for
previously treated patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer (The IDEAL 1 Trial) [corrected]. J Clin Oncol. 21:2237–2246.
2003.
|
|
13
|
Grunwald V and Hidalgo M: Developing
inhibitors of the epidermal growth factor receptor for cancer
treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:851–867. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim ES, Hirsh V, Mok T, et al: Gefitinib
versus docetaxel in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer
(INTEREST): a randomised phase III trial. Lancet. 372:1809–1818.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Steins MB, Reinmuth N, Bischoff H,
Kindermann M and Thomas M: Targeting the epidermal growth factor
receptor in non-small cell lung cancer. Onkologie. 33:704–709.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baselga J and Arteaga CL: Critical update
and emerging trends in epidermal growth factor receptor targeting
in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2445–2459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Herbst RS and Sandler AB: Overview of the
current status of human epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 6(Suppl 1): S7–S19. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ciardiello F, Caputo R, Borriello G, et
al: ZD1839 (IRESSA), an EGFR-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
enhances taxane activity in bcl-2 overexpressing,
multidrug-resistant MCF-7 ADR human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 98:463–469. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Park JK, Lee SH, Kang JH, Nishio K, Saijo
N and Kuh HJ: Synergistic interaction between gefitinib (Iressa,
ZD1839) and paclitaxel against human gastric carcinoma cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 15:809–818. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sirotnak FM, Zakowski MF, Miller VA, Scher
HI and Kris MG: Efficacy of cytotoxic agents against human tumor
xenografts is markedly enhanced by coadministration of ZD1839
(Iressa), an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4885–4892. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shih C, Chen VJ, Gossett LS, et al:
LY231514, a pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-based antifolate that inhibits
multiple folate-requiring enzymes. Cancer Res. 57:1116–1123.
1997.
|
|
22
|
Chattopadhyay S, Moran RG and Goldman ID:
Pemetrexed: biochemical and cellular pharmacology, mechanisms, and
clinical applications. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:404–417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, et
al: Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with
cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with
advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
26:3543–3551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C, et
al: Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo
plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a
randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet. 374:1432–1440.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rinaldi DA, Kuhn JG, Burris HA, et al: A
phase I evaluation of multitargeted antifolate (MTA, LY231514),
administered every 21 days, utilizing the modified continual
reassessment method for dose escalation. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 44:372–380. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Thödtmann R, Depenbrock H, Dumez H, et al:
Clinical and pharmacokinetic phase I study of multitargeted
antifolate (LY231514) in combination with cisplatin. J Clin Oncol.
17:3009–3016. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
D’Addario G, Pintilie M, Leighl NB, Feld
R, Cerny T and Shepherd FA: Platinum-based versus
non-platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer: a meta-analysis of the published literature. J Clin Oncol.
23:2926–2936. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pfister DG, Johnson DH, Azzoli CG, et al:
American Society of Clinical Oncology treatment of unresectable
non-small-cell lung cancer guideline: update 2003. J Clin Oncol.
22:330–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ardizzoni A and Tiseo M: Second-line
chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). J Chemother. 16(Suppl 4): 104–107. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maemondo M: Timing the change of
chemotherapy for non small cell lung cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
39:1316–1319. 2012.(In Japanese).
|
|
32
|
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Chmielecki J,
Ladanyi M, Miller VA and Pao W: New strategies in overcoming
acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:5530–5537.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Van Schaeybroeck S, Kyula J, Kelly DM, et
al: Chemotherapy-induced epidermal growth factor receptor
activation determines response to combined gefitinib/chemotherapy
treatment in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:1154–1165. 2006.
|
|
34
|
Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID and Perez-Soler
R: Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and
erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer
Res. 13:3413–3422. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Giovannetti E, Lemos C, Tekle C, et al:
Molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic interaction of
erlotinib, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, with the multitargeted antifolate pemetrexed in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 73:1290–1300.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Davies AM, Ho C, Lara PN Jr, Mack P,
Gumerlock PH and Gandara DR: Pharmacodynamic separation of
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and
chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer.
7:385–388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ruvolo PP, Deng X and May WS:
Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and regulation of apoptosis. Leukemia.
15:515–522. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diel P, Smolnikar K and Michna H: The pure
antiestrogen ICI 182780 is more effective in the induction of
apoptosis and down regulation of BCL-2 than tamoxifen in MCF-7
cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 58:87–97. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA and
Settleman J: Gefitinib-sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer
activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 305:1163–1167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Amann J, Kalyankrishna S, Massion PP, et
al: Aberrant epidermal growth factor receptor signaling and
enhanced sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Res.
65:226–235. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Van Schaeybroeck S, Karaiskou-McCaul A,
Kelly D, et al: EGFR activity determines response of colorectal
cancer cells to gefitinib (Iressa) alone and in combination with
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:7480–7489. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|