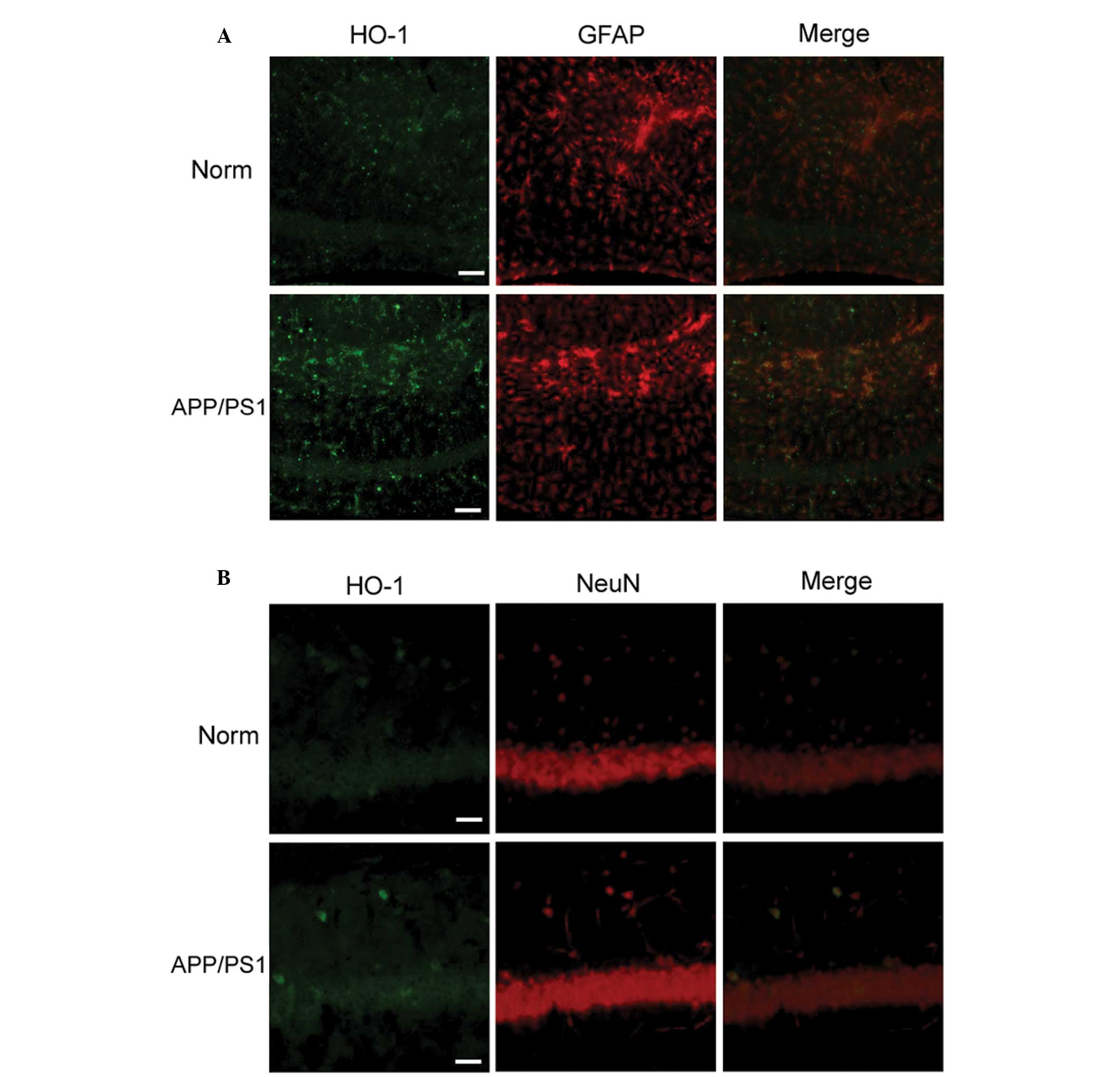
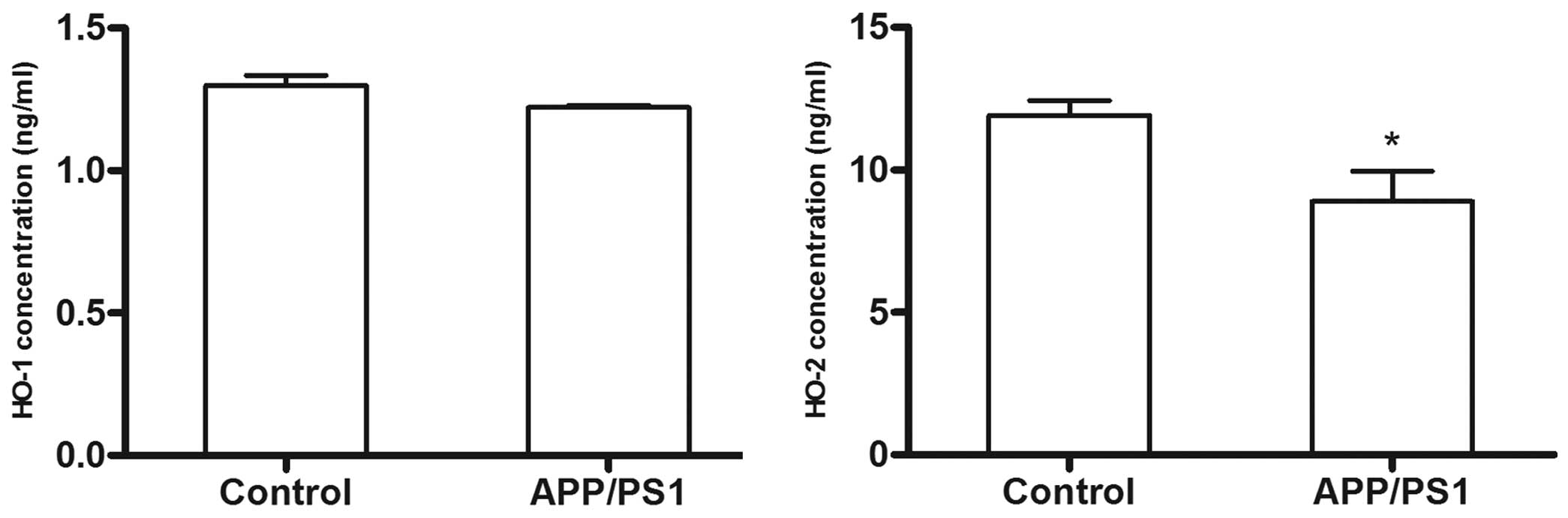
|
1
|
Sayre LM, Perry G and Smith MA: Oxidative
stress and neurotoxicity. Chem Res Toxicol. 21:172–188. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perrig WJ, Perrig P and Stähelin HB: The
relation between antioxidants and memory performance in the old and
very old. J Am Geriatr Soc. 45:718–724. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fujita K, Yamafuji M, Nakabeppu Y and Noda
M: Therapeutic approach to neurodegenerative diseases by medical
gases: focusing on redox signaling and related antioxidant enzymes.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:3242562012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pae HO, Lee YC and Chung HT: Heme
oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide: emerging therapeutic targets in
inflammation and allergy. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov.
2:159–165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barañano DE and Snyder SH: Neural roles
for heme oxygenase: contrasts to nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10996–11002. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schipper HM: Heme oxygenase expression in
human central nervous system disorders. Free Radic Biol Med.
37:1995–2011. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Barone E, Di Domenico F, Sultana R, et al:
Heme oxygenase-1 posttranslational modifications in the brain of
subjects with Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Free
Radic Biol Med. 52:2292–2301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schipper HM, Song W, Zukor H, Hascalovici
JR and Zeligman D: Heme oxygenase-1 and neurodegeneration:
expanding frontiers of engagement. J Neurochem. 110:469–485. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schipper HM, Cissé S and Stopa EG:
Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in the senescent and
Alzheimer-diseased brain. Ann Neurol. 37:758–768. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schipper HM, Bennett DA, Liberman A, et
al: Glial heme oxygenase-1 expression in Alzheimer disease and mild
cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging. 27:252–261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su D, Zhao Y, Xu H, et al: Isoflurane
exposure during mid-adulthood attenuates age-related spatial memory
impairment in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. PLoS One. 7:e501722012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghosh A, Sarkar S, Mandal AK and Das N:
Neuroprotective role of nanoencapsulated quercetin in combating
ischemia-reperfusion induced neuronal damage in young and aged
rats. PLoS One. 8:e577352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ishikawa M, Kajimura M, Adachi T, et al:
Carbon monoxide from heme oxygenase-2 Is a tonic regulator against
NO-dependent vasodilatation in the adult rat cerebral
microcirculation. Circ Res. 97:e104–e114. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vreman HJ, Wong RJ, Kadotani T and
Stevenson DK: Determination of carbon monoxide (CO) in rodent
tissue: effect of heme administration and environmental CO
exposure. Anal Biochem. 341:280–289. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng Y and Wang X: Antioxidant therapies
for Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012:4729322012.
|
|
16
|
Poon HF, Calabrese V, Scapagnini G and
Butterfield DA: Free radicals and brain aging. Clin Geriatr Med.
20:329–359. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mancuso M, Coppede F, Migliore L,
Siciliano G and Murri L: Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative
stress and neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis. 10:59–73.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Migliore L and Coppede F:
Environmental-induced oxidative stress in neurodegenerative
disorders and aging. Mutat Res. 674:73–84. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moulton PV and Yang W: Air pollution,
oxidative stress, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Environ Public Health.
2012:4727512012.
|
|
20
|
Adibhatla RM and Hatcher JF: Role of
lipids in brain injury and diseases. Future Lipidol. 2:403–422.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Markesbery WR and Carney JM: Oxidative
alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 9:133–146.
1999.
|
|
22
|
Butterfield DA, Castegna A, Lauderback CM
and Drake J: Evidence that amyloid beta-peptide-induced lipid
peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer’s disease brain
contribute to neuronal death. Neurobiol Aging. 23:655–664.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cente M, Filipcik P, Pevalova M and Novak
M: Expression of a truncated tau protein induces oxidative stress
in a rodent model of tauopathy. Eur J Neurosci. 24:1085–1090. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Di Domenico F, Barone E, Mancuso C, et al:
HO-1/BVR-a system analysis in plasma from probable Alzheimer’s
disease and mild cognitive impairment subjects: a potential
biochemical marker for the prediction of the disease. J Alzheimers
Dis. 32:277–289. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Butterfield DA, Barone E, Di Domenico F,
et al: Atorvastatin treatment in a dog preclinical model of
Alzheimer’s disease leads to up-regulation of haem oxygenase-1 and
is associated with reduced oxidative stress in brain. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 15:981–987. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang TC, Lu KT, Wo YY, Wu YJ and Yang YL:
Resveratrol protects rats from Aβ-induced neurotoxicity by the
reduction of iNOS expression and lipid peroxidation. PLoS One.
6:e291022011.
|
|
27
|
Hui Y, Wang D, Li W, et al: Long-term
overexpression of heme oxygenase 1 promotes tau aggregation in
mouse brain by inducing tau phosphorylation. J Alzheimers Dis.
26:299–313. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schipper HM: Brain iron deposition and the
free radical-mitochondrial theory of ageing. Ageing Res Rev.
3:265–301. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schipper HM, Chertkow H, Mehindate K,
Frankel D, Melmed C and Bergman H: Evaluation of heme oxygenase-1
as a systemic biological marker of sporadic AD. Neurology.
54:1297–1304. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu HL, Chertkow HM, Bergman H and Schipper
HM: Aberrant profiles of native and oxidized glycoproteins in
Alzheimer plasma. Proteomics. 3:2240–2248. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maes OC, Kravitz S, Mawal Y, et al:
Characterization of alpha1-antitrypsin as a heme oxygenase-1
suppressor in Alzheimer plasma. Neurobiol Dis. 24:89–100. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|