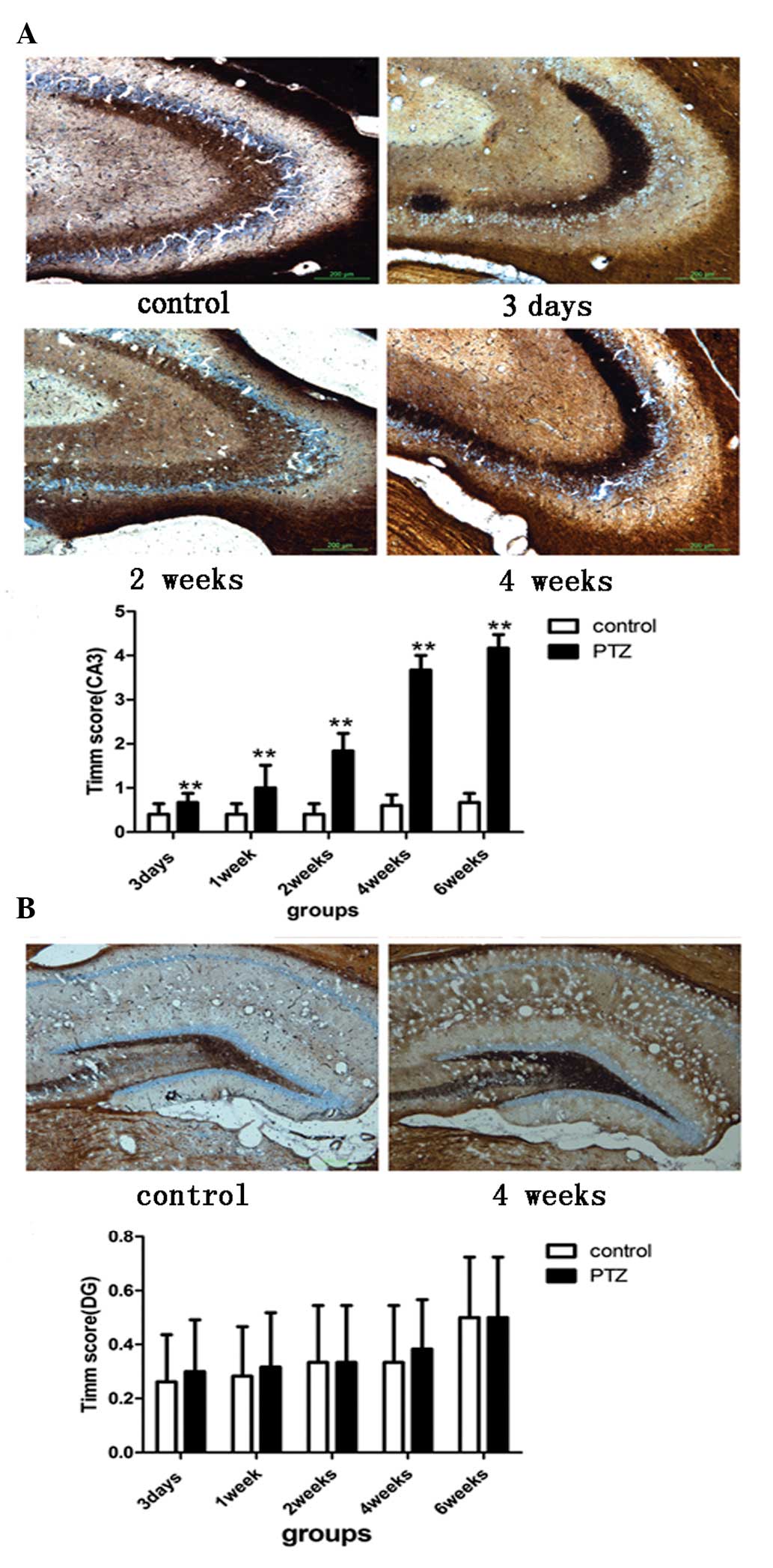
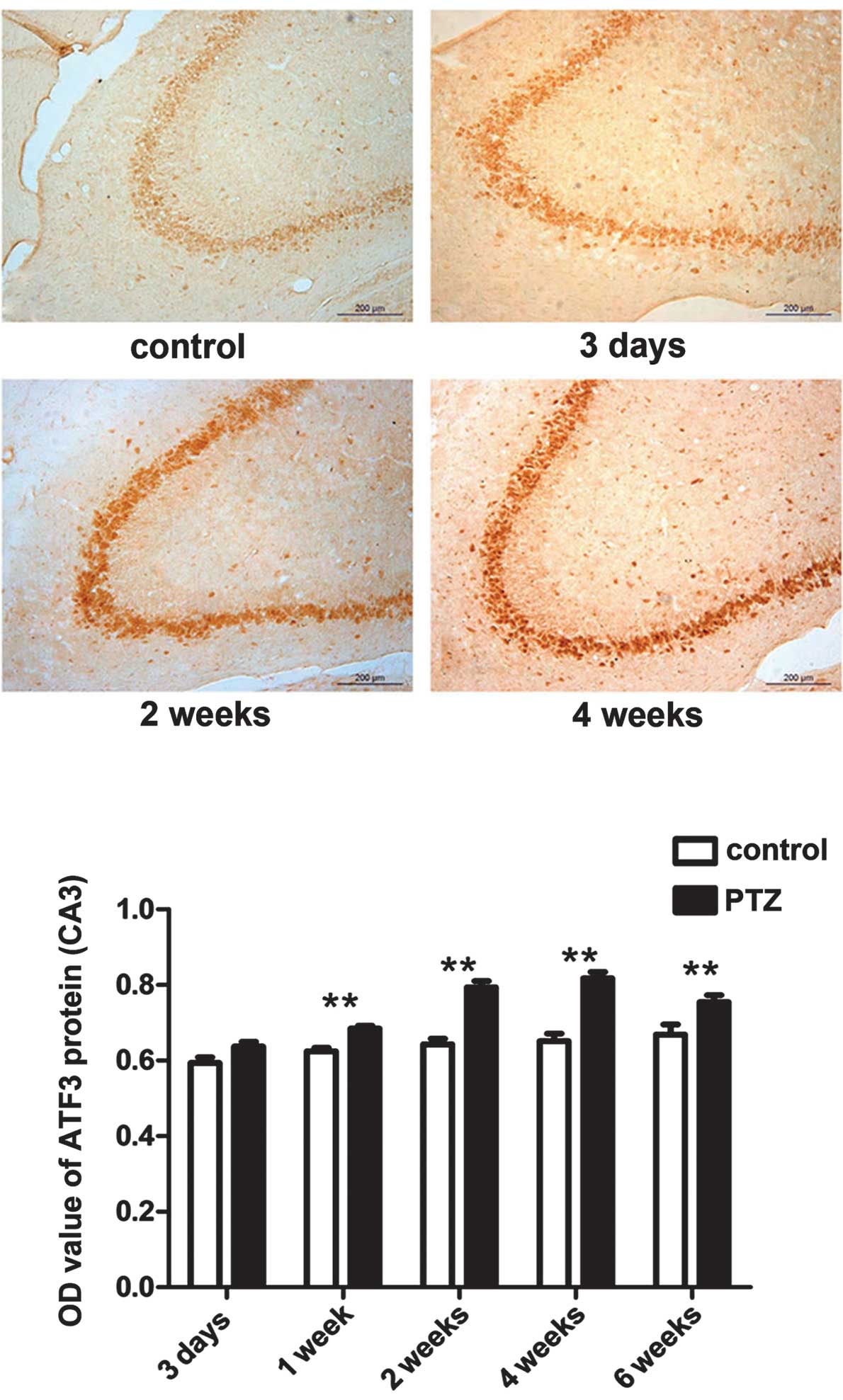
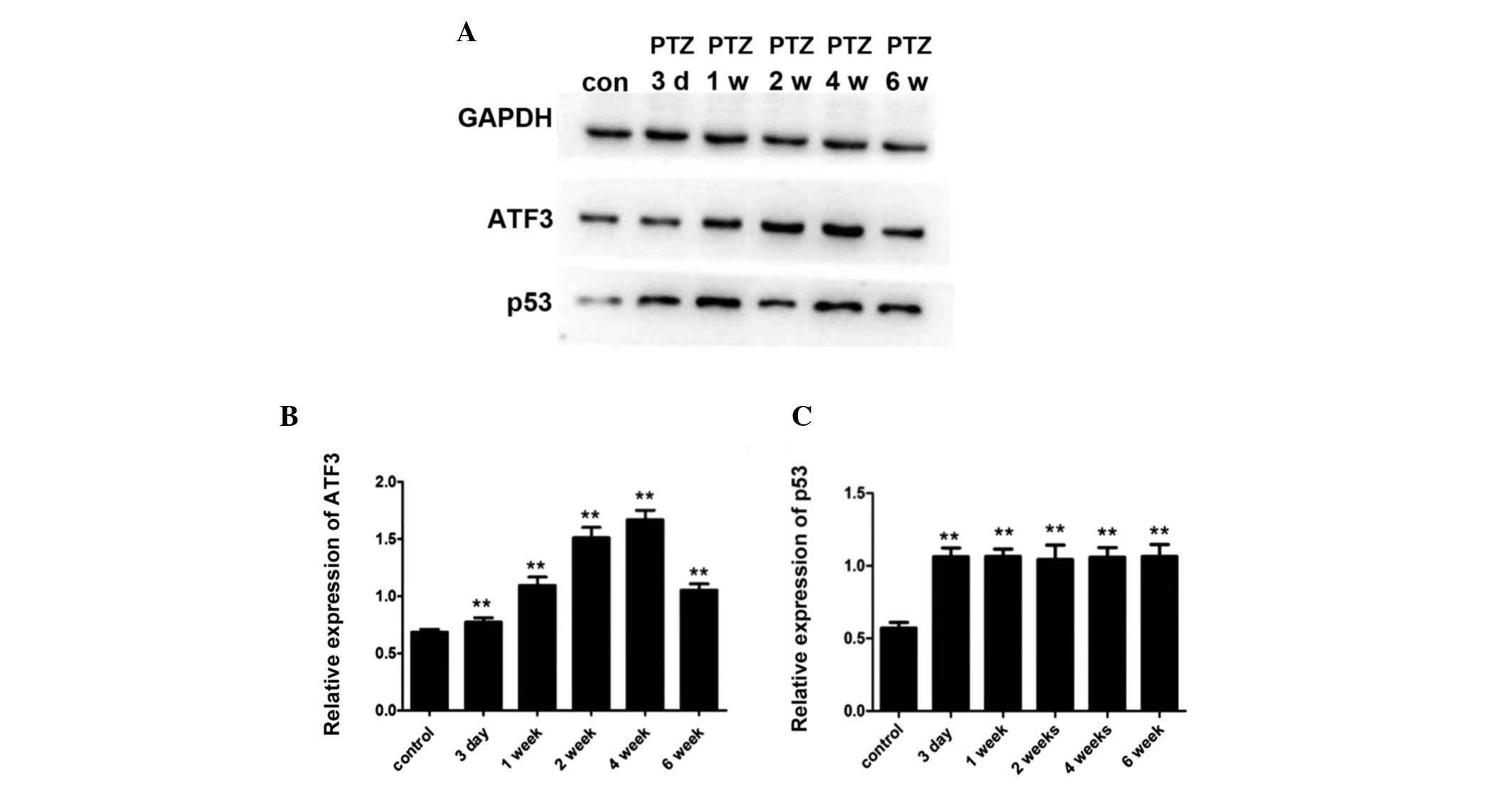
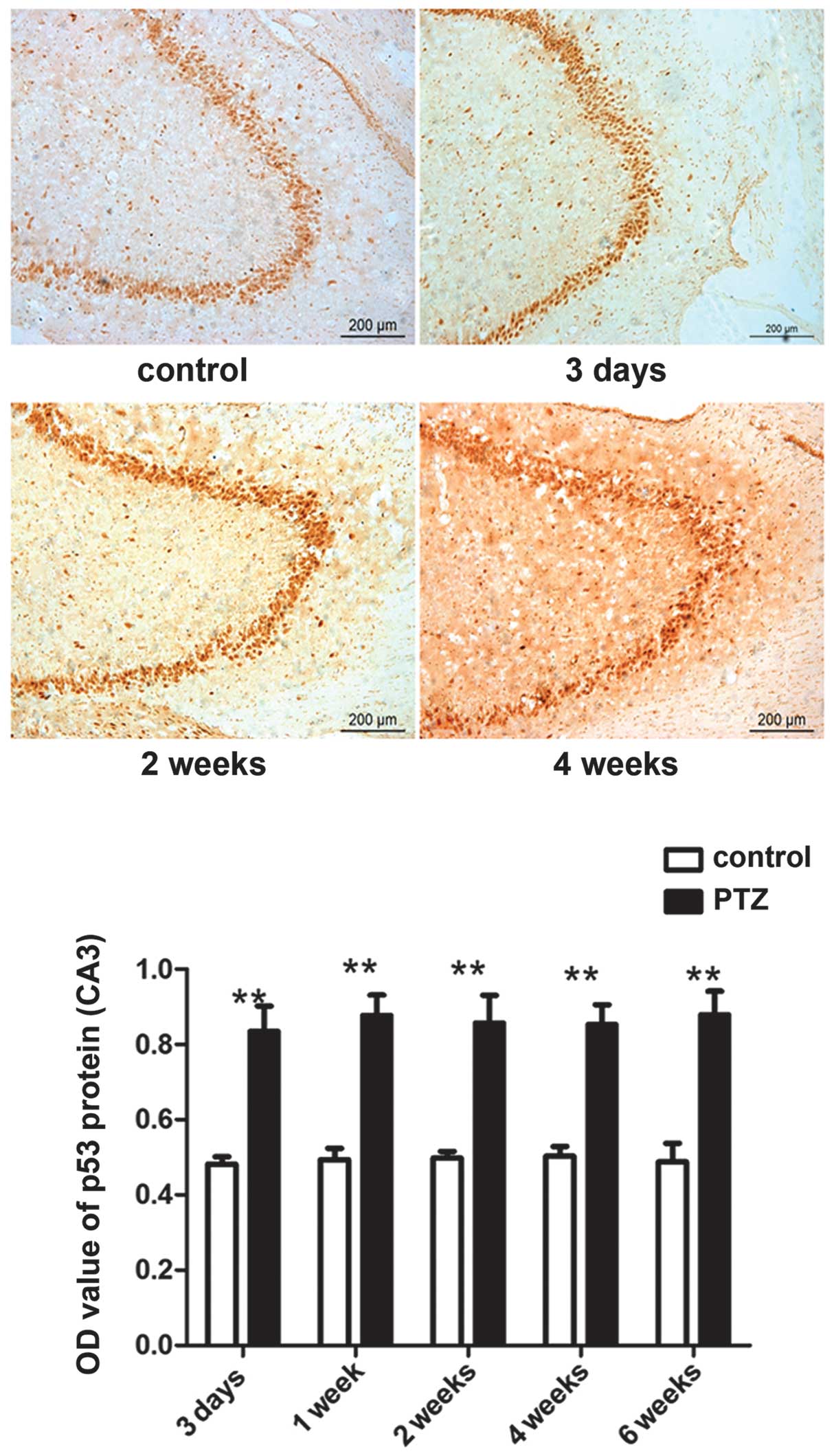
|
1
|
Pitkänen A and Sutula TP: Is epilepsy a
progressive disorder? Prospects for new therapeutic approaches in
temporal-lobe epilepsy. Lancet Neurol. 1:173–181. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
England MJ, Liverman CT, Schultz AM and
Strawbridge LM: Epilepsy across the spectrum: promoting health and
understanding A summary of the Institute of Medicine report.
Epilepsy Behav. 25:266–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pitkänen A: Therapeutic approaches to
epileptogenesis-hope on the horizon. Epilepsia. 51(Suppl 3): 2–17.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perucca E, French J and Bialer M:
Development of new antiepileptic drugs: challenges, incentives, and
recent advances. Lancet Neurol. 6:793–804. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Louboutin JP and Strayer DS: Relationship
between the chemokine receptor CCR5 and microglia in neurological
disorders: consequences of targeting CCR5 on neuroinflammation,
neuronal death and regeneration in a model of epilepsy. CNS Neurol
Disord Drug Targets. 12:815–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Song MY, Tian FF, Liu H, Wang YZ, Dang J,
Huang WJ and Ding DX: Expression of SOCSs and TLRs in the
hippocampus of a pentylenetetrazole kindling model. Clin Lab.
60:233–240. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thompson MR, Xu D and Williams BR:
Activating transcription factor 3 contributes to Toll-like
receptor-mediated macrophage survival via repression of Bax and
Bak. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 33:682–693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Whitmore MM, Iparraguirre A, Kubelka L,
Weninger W, Hai T and Williams BR: Negative regulation of
TLR-signaling pathways by activating transcription factor-3. J
Immunol. 179:3622–3630. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gilchrist M, Thorsson V, Li B, Rust AG,
Korb M, Roach JC, Kennedy K, Hai T, Bolouri H and Aderem A: Systems
biology approaches identify ATF3 as a negative regulator of
Toll-like receptor 4. Nature. 441:173–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fávaro WJ, Nunes OS, Seiva FR, Nunes IS,
Woolhiser LK, Durán N and Lenaerts AJ: Effects of P-MAPA
immunomodulator on Toll-like receptors and p53: potential
therapeutic strategies for infectious diseases and cancer. Infect
Agent Cancer. 7:142012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Menendez D, Shatz M, Azzam K, Garantziotis
S, Fessler MB and Resnick MA: The Toll-like receptor gene family is
integrated into human DNA damage and p53 networks. PLoS Genet.
7:e10013602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yan C, Lu D, Hai T and Boyd DD: Activating
transcription factor 3, a stress sensor, activates p53 by blocking
its ubiquitination. EMBO J. 24:2425–2435. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Epsztein J, Represa A, Jorquera I, Ben-Ari
Y and Crepel V: Recurrent mossy fibers establish aberrant kainate
receptor-operated synapses on granule cells from epileptic rats. J
Neurosci. 25:8229–8239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peddie CJ and Keast JR: Pelvic nerve
injury causes a rapid decrease in expression of choline
acetyltransferase and upregulation of c-Jun and ATF-3 in a distinct
population of sacral preganglionic neurons. Front Neurosci.
5:62011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shokouhi BN, Wong BZ, Siddiqui S,
Lieberman AR, Campbell G, Tohyama K and Anderson PN: Microglial
responses around intrinsic CNS neurons are correlated with axonal
regeneration. BMC Neurosci. 11:132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deshpande LS, Lou JK, Mian A, Blair RE,
Sombati S and DeLorenzo RJ: In vitro status epilepticus but not
spontaneous recurrent seizures cause cell death in cultured
hippocampal neurons. Epilepsy Res. 75:171–179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tedeschi A, Nguyen T, Puttagunta R, Gaub P
and Di Giovanni S: A p53-CBP/p300 transcription module is required
for GAP-43 expression, axon outgrowth, and regeneration. Cell Death
Differ. 16:543–554. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Di Giovanni S, Knights CD, Rao M, Yakovlev
A, Beers J, Catania J, Avantaggiati ML and Faden AI: The tumor
suppressor protein p53 is required for neurite outgrowth and axon
regeneration. EMBO J. 25:4084–4096. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Auvin S, Shin D, Mazarati A, Nakagawa J,
Miyamoto J and Sankar R: Inflammation exacerbates seizure-induced
injury in the immature brain. Epilepsia. 48(Suppl 5): 27–34. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aalbers MW, Rijkers K, Majoie HJ, Dings
JT, Schijns OE, Schipper S, De Baets MH, Kessels A, Vles JS and
Hoogland G: The influence of neuropathology on brain inflammation
in human and experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuroimmunol.
Mar 29–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Diamond ML, Ritter AC, Failla MD, Boles
JA, Conley YP, Kochanek PM and Wagner AK: IL-1beta associations
with posttraumatic epilepsy development: A genetics and biomarker
cohort study. Epilepsia. Apr 22–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Simões PS, Visniauskas B, Perosa SR, et
al: Expression and activity of thimet oligopeptidase (TOP) are
modified in the hippocampus of subjects with temporal lobe epilepsy
(TLE). Epilepsia. Apr 4–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Avanzini G, Depaulis A, Tassinari A and de
Curtis M: Do seizures and epileptic activity worsen epilepsy and
deteriorate cognitive function? Epilepsia. 54(Suppl 8): 14–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamanaka H, Obata K, Fukuoka T, Dai Y,
Kobayashi K, Tokunaga A and Noguchi K: Induction of plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 and -2 in dorsal root ganglion neurons after
peripheral nerve injury. Neuroscience. 132:183–191. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuzuki K, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Yi D,
Tsujino H, Sakagami M and Noguchi K: Differential regulation of
P2X(3) mRNA expression by peripheral nerve injury in intact and
injured neurons in the rat sensory ganglia. Pain. 91:351–360. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang C, Gao C, Kawauchi J, Hashimoto Y,
Tsuchida N and Kitajima S: Transcriptional activation of the human
stress-inducible transcriptional repressor ATF3 gene promoter by
p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 297:1302–1310. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lindå H, Sköld MK and Ochsmann T:
Activating transcription factor 3, a useful marker for regenerative
response after nerve root injury. Front Neurol. 2:302011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yano K, Kawasaki K, Hattori T, Tawara S,
Toshima Y, Ikegaki I, Sasaki Y, Satoh S, Asano T and Seto M:
Demonstration of elevation and localization of Rho-kinase activity
in the brain of a rat model of cerebral infarction. Eur J
Pharmacol. 594:77–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Francis JS, Dragunow M and During MJ: Over
expression of ATF-3 protects rat hippocampal neurons from in vivo
injection of kainic acid. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 124:199–203.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sakhi S, Bruce A, Sun N, Tocco G, Baudry M
and Schreiber SS: p53 induction is associated with neuronal damage
in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:7525–7529. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Buganim Y, Kalo E, Brosh R, Besserglick H,
Nachmany I, Rais Y, Stambolsky P, Tang X, Milyavsky M, Shats I,
Kalis M, Goldfinger N and Rotter V: Mutant p53 protects cells from
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced death by attenuating
activating transcription factor 3 induction. Cancer Res.
66:10750–10759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan C, Wang H and Boyd DD: ATF3 represses
72-kDa type IV collagenase (MMP-2) expression by antagonizing
p53-dependent trans-activation of the collagenase promoter. J Biol
Chem. 277:10804–10812. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|