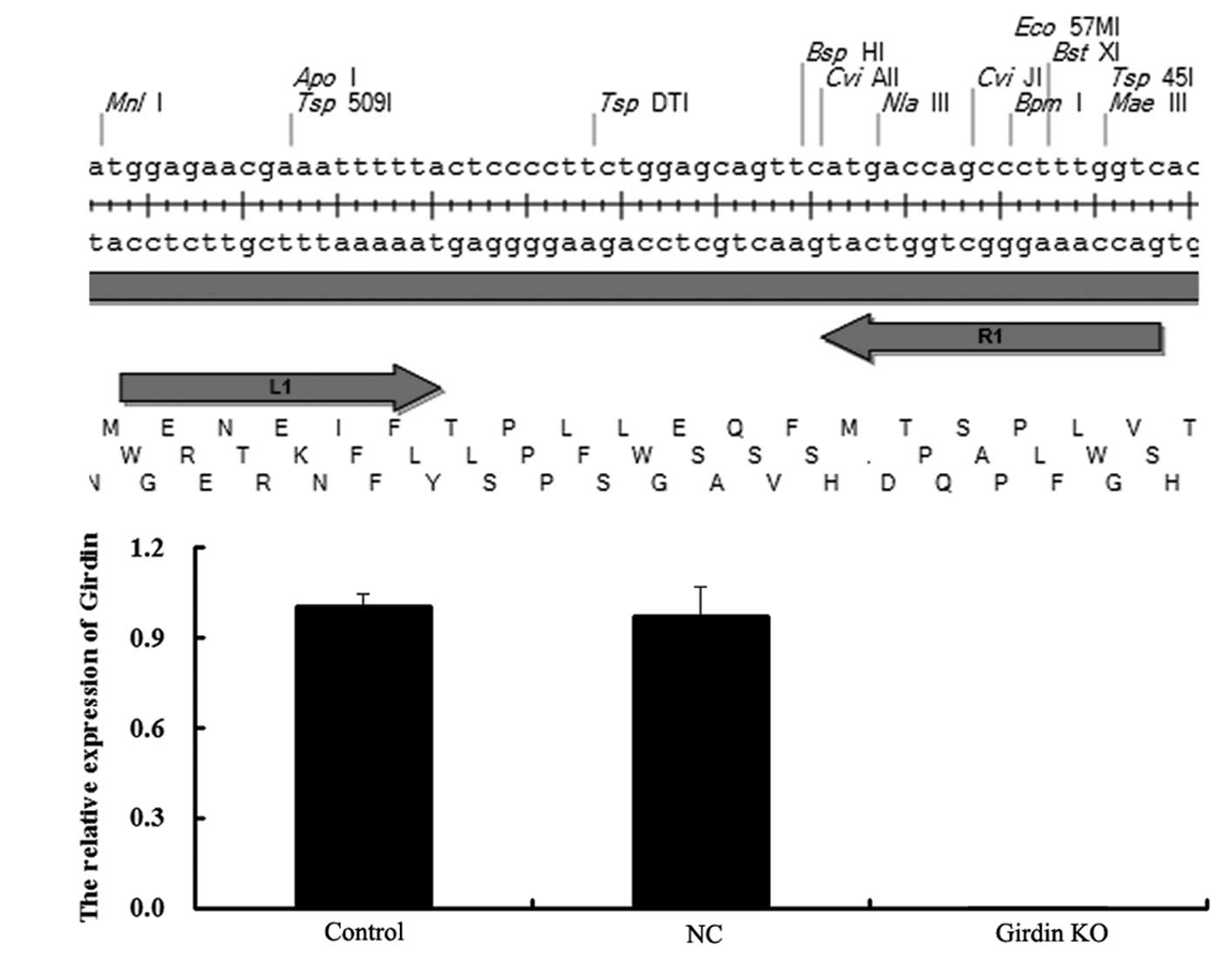
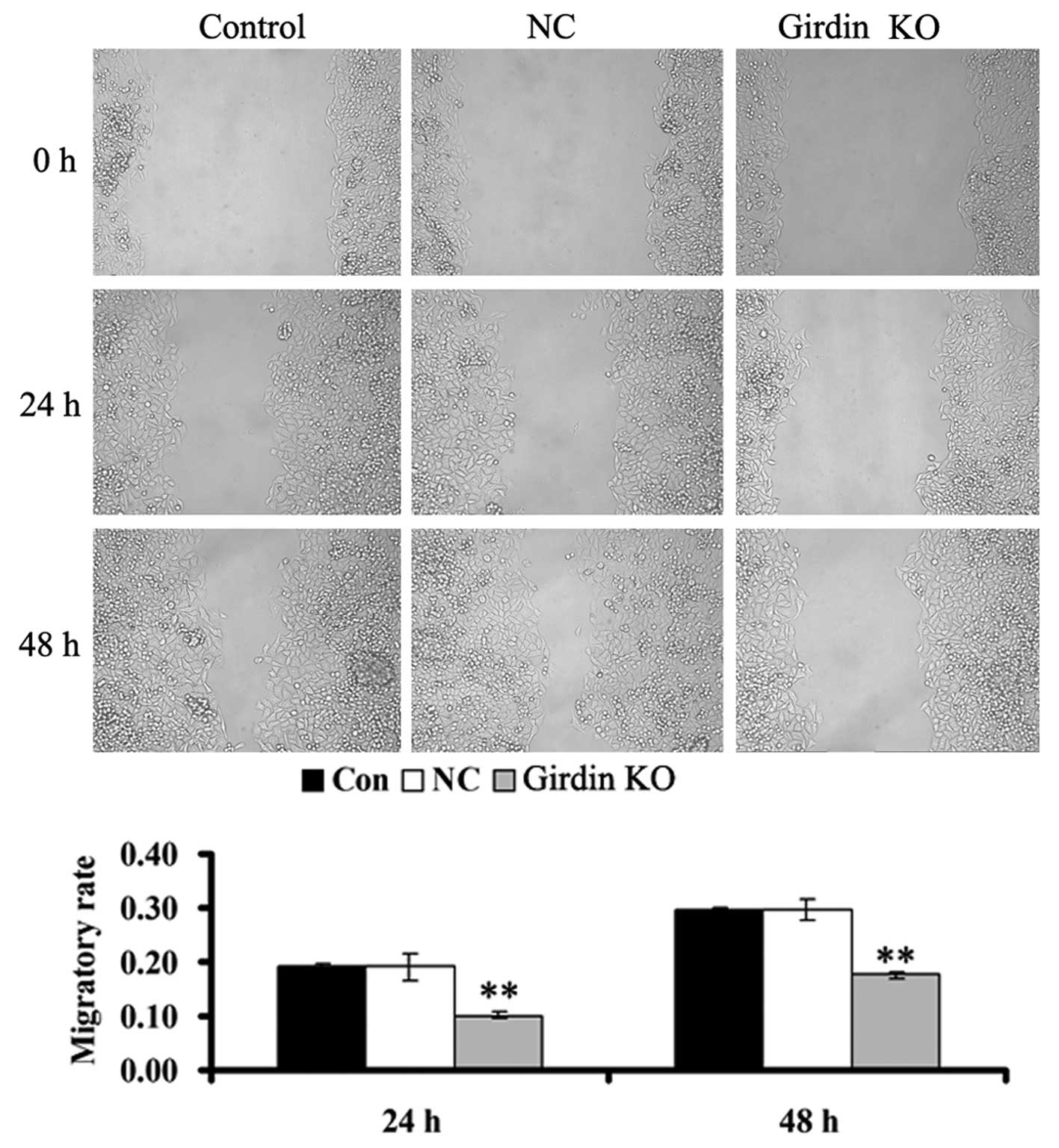
|
1
|
Hofstetter W: Current and future options
for treating esophageal cancer: a paradigm shift toward
organ-sparing therapies. Tex Heart Inst J. 39:846–847.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hong TS, Wo JY and Kwak EL: Targeted
therapies with chemoradiation in esophageal cancer: development and
future directions. Semin Radiat Oncol. 23:31–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kato H, Nakajima M and Sasaki K:
Esophageal cancer. Kyobu Geka. 64(Suppl): 776–781. 2011.(In
Japanese).
|
|
4
|
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B and
Szmitkowski M: The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and
their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sgourakis G, Gockel I, Lyros O, Hansen T,
Mildenberger P and Lang H: Detection of lymph node metastases in
esophageal cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:601–612. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang Y, Fang D and Hu J: MicroRNA and its
roles in esophageal cancer. Med Sci Monit. 18:RA22–RA30. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Enomoto A: Roles of DISC1-interacting
protein Girdin in postnatal development and adult neurogenesis in
the dentate gyrus. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi.
31:23–28. 2011.(In Japanese).
|
|
8
|
Enomoto A, Ping J and Takahashi M: Girdin,
a novel actin-binding protein, and its family of proteins possess
versatile functions in the Akt and Wnt signaling pathways. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1086:169–184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mao JZ, Jiang P, Cui SP, et al: Girdin
locates in centrosome and midbody and plays an important role in
cell division. Cancer Sci. 103:1780–1787. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao W, Guo W, Zhou Q, et al: In vitro
antimetastatic effect of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor
ZSTK474 on prostate cancer PC3 cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:13577–13591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin F, Liu C, Guo Y, Chen H and Wu Y:
Clinical implications of Girdin and PI3K protein expression in
breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:1549–1553. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shibata T, Matsuo Y, Shamoto T, et al:
Girdin, a regulator of cell motility, is a potential prognostic
marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
29:2127–2132. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu C, Xue H, Lu Y and Chi B: Stem cell
gene Girdin: a potential early liver metastasis predictor of
colorectal cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 39:8717–8722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Natsume A, Kato T, Kinjo S, et al: Girdin
maintains the stemness of glioblastoma stem cells. Oncogene.
31:2715–2724. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tangoku A, Yamamoto Y, Furukita Y, Goto M
and Morimoto M: The new era of staging as a key for an appropriate
treatment for esophageal cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
18:190–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thosani N, Singh H, Kapadia A, et al:
Diagnostic accuracy of EUS in differentiating mucosal versus
submucosal invasion of superficial esophageal cancers: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 75:242–253. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ohara K, Enomoto A, Kato T, et al:
Involvement of Girdin in the determination of cell polarity during
cell migration. PLoS One. 7:e366812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin C, Ear J, Pavlova Y, et al: Tyrosine
phosphorylation of the Galpha-interacting protein GIV promotes
activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase during cell migration. Sci
Signal. 4:ra642011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, Xu H, et al: Girdin
protein: a new potential distant metastasis predictor of breast
cancer. Med Oncol. 29:1554–1560. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mittal Y, Pavlova Y, Garcia-Marcos M and
Ghosh P: Src homology domain 2-containing protein-tyrosine
phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) binds and dephosphorylates
G(alpha)-interacting, vesicle-associated protein (GIV)/Girdin and
attenuates the GIV-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt
signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 286:32404–32415. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ghosh P, Garcia-Marcos M and Farquhar MG:
GIV/Girdin is a rheostat that fine-tunes growth factor signals
during tumor progression. Cell Adh Migr. 5:237–248. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyake H, Maeda K, Asai N, et al: The
actin-binding protein Girdin and its Akt-mediated phosphorylation
regulate neointima formation after vascular injury. Circ Res.
108:1170–1179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Garcia-Marcos M, Ear J, Farquhar MG and
Ghosh P: A GDI (AGS3) and a GEF (GIV) regulate autophagy by
balancing G protein activity and growth factor signals. Mol Biol
Cell. 22:673–686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kneussel M and Wagner W: Myosin motors at
neuronal synapses: drivers of membrane transport and actin
dynamics. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:233–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mullins RD and Hansen SD: In vitro studies
of actin filament and network dynamics. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
25:6–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang P, Enomoto A, Jijiwa M, et al: An
actin-binding protein Girdin regulates the motility of breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 68:1310–1318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burris HA 3rd: Overcoming acquired
resistance to anticancer therapy: focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:829–842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|